-
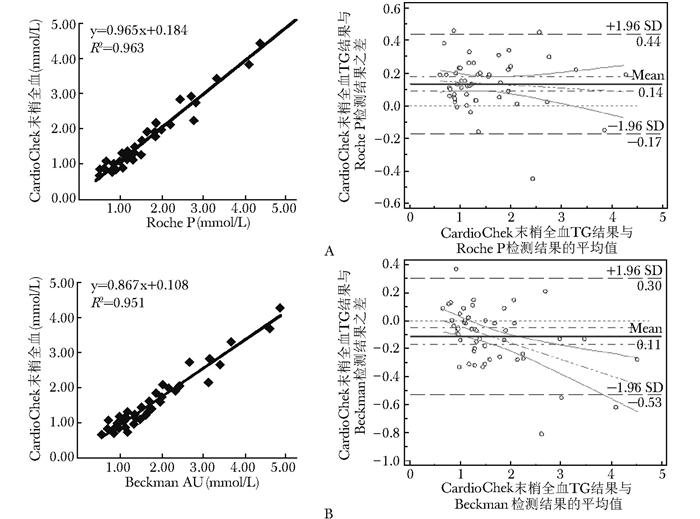
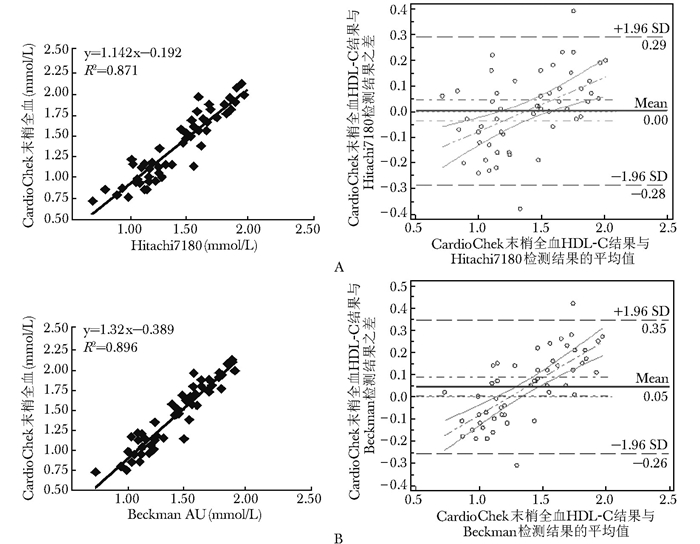
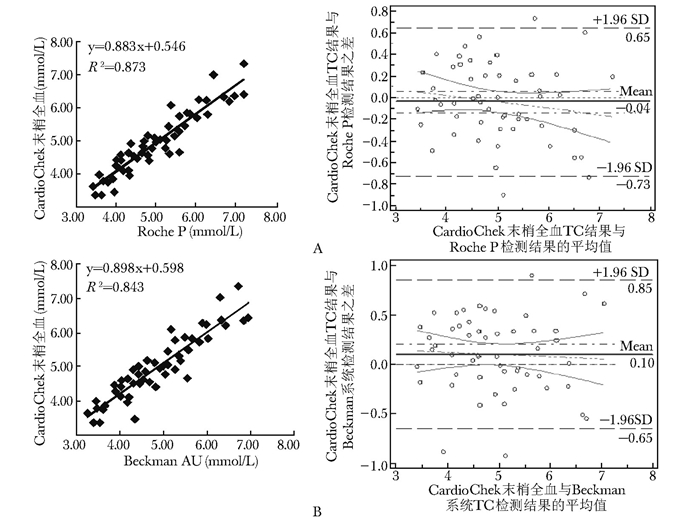
摘要:目的 验证CardioChek PA床旁血脂检测仪测定全血总胆固醇(total cholesterol, TC)、甘油三酯(triglyceride, TG)和高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C)的准确度及其与全自动生化分析仪结果的可比性。方法 使用同一批号试纸条分别在3台CardioChek PA血脂检测仪上连续检测低、中、高三个浓度水平全血20次, 评价TC、TG和HDL-C各项目的批内不精密度和仪器间总不精密度; 在同一台仪器上使用三个批号的试纸条检测全血各10次, 计算批内不精密度和总不精密度。筛选血脂浓度覆盖高、中、低三个水平的54名志愿者, 清晨空腹采集末梢全血, 在3台床旁血脂仪上测定血脂; 同时采集静脉血, 在4种不同的全自动生化分析仪检测血清TC、TG及HDL-C。绘制Bland-Altman图, 比较CardioChek PA与各生化分析仪测定结果的离散趋势; 将CardioChek PA检测结果与不同生化分析系统及参考方法检测结果进行线性回归; 计算CardioChek PA与不同生化分析系统的偏差及百分偏差, 同时判定在医学决定水平处偏差是否符合相关要求。结果 3台CardioChek PA仪器低、中、高水平的总不精密度TC分别为:2.69%、4.88%、3.51%, TG分别为5.51%、5.27%、4.96%, HDL-C分别为7.27%、6.84%、6.79%;相同仪器、不同批号试纸间总不精密度TC为4.70%, TG为7.66%, HDL-C为8.61%。CardioChek PA检测系统与4种全自动生化仪分析比对结果显示:TC与各系统的偏差最小, 在-2.21%~2.56%之间, HDL-C在-1.12%~5.57%之间, TG除与BeckmanDxC 800偏差较大外(25.85%), 与其他3个系统的平均百分偏差在-4.55%~13.34%之间。医学决定水平偏差分析显示:TC在不同医学决定水平处的偏差在-3.27%~1.96%之间, TG在-11.05%~13.06%之间, HDL-C在-5.86%~11.56%之间, 均满足美国国家胆固醇教育计划总允许误差标准(15%)。进一步的正确度验证结果显示:与参考方法比对, TC在医学决定水平处偏倚分别为1.96%和0.77%;HDL-C分别为2.34%和4.87%。结论 CardioChek PA床旁血脂检测仪准确度满足临床需求, 适用于临床血脂异常筛查及治疗检测。Abstract:Objective To validate the accuracy of CardioChek PA lipid point-of-care devices in determining total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in whole blood and the comparability with results determined by full-automatic biochemical analyzer.Methods We determined the low, medium, and high levels of TG, TC, and HDL-C in whole blood with single reagent lot number 20 times using 3 different CardioChek PA devices to evaluate inter-run and devices' coefficient of variations(CVs), and used single CardioChek PA device with 3 reagent lot number to determine the whole blood 10 times for evaluating inter-run and total CVs. Fifty-four volunteers whose lipid profiles covered up high, medium, and low levels were recruited. Lipids in fasting periphery whole blood and venous serum were collected and determined using 3 different CardioChek PA devices and 4 kinds of full-automatic biochemical analyzers, respectively. Bland-Altman plot was made to analyze the comparability of results from CardioChek PA and the full-automatic biochemical analyzers. Linear regression was analyzed using results of CardioChek PA and full-automatic biochemical analyzers. Bias and percentage bias were determined between CardioChek PA and different automatic biochemical analyzers; meanwhile, whether they satisfied the requirements of medical decision levels was determined.Results The total CVs of TC in low, medium, and high levels in 3 different devices were 2.69%, 4.88%, and 3.51%, respectively; for TG, they were 5.51%, 5.27% and 4.96%; and for HDL-C, they were 7.27%, 6.84% and 6.79%. The total CVs of TC, TG, and HDL-C determined with the same device but different reagent lot number were 4.70%, 7.66%, and 8.61%, respectively. Comparison of the results from CardioChek PA devices and the 4 kinds of full-automatic biochemical analyzers showed lowest deviation for TC with -2.21%-2.56%, and for HDL-C with -1.12%-5.57%; the deviation of TG results of BeckmanDxC800 was relatively high with 25.85%, but in other 3 systems were -4.55%-13.34%. Deviation of TC, TG, and HDL-C in different medical decision levels were -3.27%-1.96%, -11.05%-13.06%, and -5.86%-11.56%, respectively, all of which could satisfy the requirements of the National Cholesterol Education Program(NCEP). Compared with reference methods, the biases of TC in medical decision levels were 1.96% and 0.77%; for HDL-C, they were 2.34% and 4.87%.Conclusion The accuracy of CardioChek PA lipid point-of-care device can satisfy the clinical requirements, and the device can be used in the screening and monitoring of dyslipidemia.
-
Keywords:
- point-of-care testing /
- imprecision /
- accuracy /
- comparison test
-
改革开放40年来,中国社会经济高速发展,人民对健康生活的需求日益增长。对于中国的卫生工作者来说,以下问题显得愈发重要:如何提高卫生政策制定和医疗资源分配的科学性?怎样帮助医生正确、高效、合理地作出临床决策?怎样生成、传播和应用研究证据以提高医疗质量?如何回应大数据、人工智能等思潮给医学带来的冲击?回答这些重大问题,是我国临床流行病学和循证医学工作者肩负的历史使命。本文将简要论述新时期临床流行病学和循证医学的学科建设,包括发展历史、人才队伍、基地建设、面临的机遇和挑战等,以就教于同道。
1. 学科定义
追本溯源,“流行病学(epidemiology)”一词来自希腊语,包括三个词根:epi、demos和logos。“epi”的意思是上面,“demos”指人群,“logos”代指研究或学问。顾名思义,流行病学是研究健康状态或事件在人群中分布及其决定因素的一门学科。传统意义上的流行病学主要关注疾病(尤其是传染病)对人群的影响。流行病学造福人类的例子不胜枚举。例如,北京协和医学院和哈佛大学毕业生陈志潜(MD,MPH)于1932年深入河北定县地区,将流行病学理论转化为行动,旨在改变人民“愚、弱、病、私”,“辗转死于沟壑”的旧中国。在此后的5年里,陈志潜利用极为有限的卫生资源,和同事们一起忘我工作,成功建立起一个“便宜、安全、有效、必要”的三级乡村医疗网络。这样一个依靠当地百姓,甚至有点“土气”的网络成功抵御了20世纪30年代肆虐华北的天花和霍乱疫情,不仅保障了定县父老乡亲的健康,而且在46年后得到联合国《阿拉木图宣言》的推崇,成为全世界初级医疗保健的标杆[1-2]。陈志潜及其同事建立的“定县模式”,是临床医学和预防医学的结合,是科学精神的胜利,更是现代流行病学事业深入中国乡村的伟大创举。
1938年,美国耶鲁大学内科学教授John Paul最早提出“临床流行病学(clinical epidemiology)”的概念,强调将患病个体而非群体作为研究对象,但仍视其为预防医学的一部分[3]。20世纪70年代末至80年代初,经Alvan Feinstein、David Sackett及Robert Fletcher等学者的不懈努力,临床流行病学的学科范畴逐渐为学术界所接受[4-5]。目前公认,临床流行病学是指在临床医学领域内引入现代流行病学和统计学方法,从患病个体诊治扩大到患病群体研究,以探讨疾病的病因、预防、诊断、治疗、预后等规律的临床基础学科[6]。临床流行病学的核心元素是设计、测量和评价,不仅为临床研究提供方法指导,同时也为医疗实践提供科学依据。
依靠临床流行病学的方法学支撑,循证医学得以产生并壮大。1991年David Sackett的学生Gordon Guyatt在ACP J Club上撰文,正式提出“循证医学”这一概念[7]。1992年Gordon Guyatt成立循证医学工作组,并在JAMA上发表“Evidence-based medicine: a new approach to teaching the practice of medicine”一文,标志着循证医学的正式诞生[8]。循证医学包涵3大原则:(1)临床决策应基于现有最佳证据;(2)必须确定证据的有效性和真实性;(3)临床决策单靠证据是不够的,还必须结合医生的临床知识和经验,权衡不同诊疗策略的获益、风险和成本,并尊重患者的价值观(value)和偏好(preference)[9-10]。循证医学通过对传统经验医学的反思,主张医疗应基于科学证据,用科学方法寻求临床问题的最佳解决方案。循证医学的这一思想并非凭空出现,而是有着深厚的思想土壤。其哲学基础是绵延千年的西方理性主义传统:应用精确的数学工具、严密的科学试验和正确的逻辑推导,人类就有希望揭示自然界的奥秘。医生是临床实践的主体,患者是医疗服务的对象。向医患双方提供可靠、可及、便捷的证据资源,是临床流行病学和循证医学的努力方向。
2. 人才培养
医学知识正在快速增长,终身学习是对医生的必然要求。循证医学的初衷是传授循证临床实践技能,希望每一位医生在面对新的临床问题时,都能够独立检索、解读和评价证据,并结合自身经验与患者商议后作出决策[10]。完整的循证临床实践应包括5个步骤:(1)提出问题(ask);(2)寻找证据(acquire);(3)评估和解释证据(appraise and interpret);(4)应用证据(apply);(5)效果评价(evaluate)[11]。培养循证实践的能力应当在医学本科阶段开始,毕业后教育虽有助益,但很可能已错过最佳时机[12]。令人欣喜的是,2008年教育部和原卫生部(现为国家卫生健康委员会)联合颁发文件,将临床流行病学和循证医学列为医学本科教育的核心课程。由衷地希望,未来中国的广大医务工作者能够像使用听诊器、手术刀一样熟练应用临床流行病学方法,通过正确使用证据造福于广大患者。
授人以鱼不如授人以渔,临床流行病学传授的是方法学,不仅适用于临床医学,还适用于公共卫生、统计学、社会科学、经济学、信息学、公共管理等领域,其影响力远不止学校和医院范畴。无论是什么专业,人才培养和梯队建设均是第一要务。我们需要创新临床流行病学和循证医学的教学方法和评估体系。循证医学的宗旨是解决临床问题,建议采用床旁教学、问题式学习(problem-based learning, PBL)、小组讨论等方法,生动活泼地传授循证医学技能。应努力建设以高年资临床医生为主体的教学队伍。这些医生不仅是各自领域的临床专家,而且熟谙临床流行病学方法学,同时还对教学怀有极大的热情,可谓之“医生方法学家(physician methodologist)”。医生方法学家是研究、传播和实践临床流行病学和循证医学的主力,在本科教育、住院医师规范化培训、专科医师培养以及各类短期培训班中,都是不可替代的骨干力量。
3. 基地建设
1982年,美国洛克菲勒基金会发起并支持成立了国际临床流行病学工作网络(International Clinical Epidemiology Network, INCLEN)。1988年,时任the Journal of Chronic Disease主编的Alvan Feinstein将杂志更名为the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology(J Clin Epidemiol),从此成为INCLEN的官方刊物[4]。30多年来,INCLEN相继在22个国家和地区建立了临床流行病学单位(clinical epidemiology unit, CEU),其中包括我国的上海医科大学和华西医科大学[13]。20世纪90年代,这两家中心均通过了INCLEN的评审,升级为临床流行病学资源和培训中心。1984年在原卫生部(现为国家卫生健康委员会)的领导下,召开了全国首次“设计、测量和评价医学讨论会”,前来参会的国外专家就包括David Sackett本人。会后经过积极筹办,于1989年建立了中国临床流行病学网(CHINACLEN)。1993年,中华医学会临床流行病学分会正式成立。1996年循证医学被正式介绍到中国。王吉耀教授为此专门撰文,并将“evidence-based medicine”翻译为“循证医学”[14]。1997年,中国循证医学中心落户华西医科大学。此后复旦大学、北京大学、兰州大学、武汉大学、香港中文大学、北京中医药大学等院校相继成立了循证医学研究中心。
从20世纪30年代华北的乡间地头到如今遍布全国的学术中心,在过去近一个世纪里,流行病学的理论和实践在我国生根、发芽,并茁壮成长。如今,临床流行病学和循证医学在医疗实践、医学教育和卫生政策制定等方面,学科影响力正在不断扩大。2018年,在北京市卫生主管部门的支持下,北京协和医院依托CEU成立了“北京市临床研究质量促进中心”。该中心以CEU的师资力量为主体,负责核查和督导北京市政府资助的各项临床研究,同时以多种形式积极开展方法学培训,帮助全市各医疗单位提升研究质量。未来,学科还将努力建设循证医学“生态系统”,提高卫生政策制定者对循证决策的重视程度,将相对稀缺的医疗资源用在最需要的地方。
4. 机遇、挑战和方向
循证医学自诞生以来,一直面临各种质疑和挑战。有学者担心,倘若证据“一家独大”,医疗行为可能会落入唯证据是从的陷阱,而忽视临床实践的多样性和丰富性[15]。更激烈的观点则认为,各类临床指南已被医药企业等利益集团所绑架,助推了不合理的过度医疗[16]。为此,1996年David Sackett提出:“慎重、准确和明智地应用当前所能获得的最佳证据,结合医生技能和经验,并综合患者的价值和愿望,将三者结合起来作出医疗决策[9]。”这一定义综合考虑了外部证据(研究文献)和内部证据(医生经验),强调了医疗决策必须尊重患者意愿,但并未说明什么才是“最佳证据”。2015年Gordon Guyatt进一步完善了循证医学的定义:“临床实践应结合医生经验、患者意愿和来自系统评价和合成的研究证据”,从而明确了最佳证据来源[10]。
当然,即使经过系统评价形成的最佳证据,往往也只是在高度选择的患者群体中测试某种单一干预是否有效,这与真实的临床情境往往相去甚远。因此,证据能否外推仍有赖于医生审慎的临床判断。同时,系统综述和荟萃分析的方法学本身也存在一定局限性,例如“异质性”问题始终存在一定的争议[17]。但究其实质,临床指南、系统综述、随机对照试验等作为现代医学的重要标志,本身仅仅是一种工具。掌握工具的是人,而人人皆会犯错(to err is human)。将人的错误归咎于工具是不公平的,如果因为人的错误而抛弃工具甚至否定工具的价值,则不啻是一种倒退。因此,与其质疑循证医学的科学性,不如设法加强对医疗服务人员、政策制定者及公众的循证医学教育,使决策能够真正基于高质量的证据。
随着互联网对知识的快速传播,患者参与自身医疗决策的意愿和能力不断增强。循证医学应当与医患共同决策(shared decision-making)相结合,努力实现患者利益最大化[18]。同时,大数据、真实世界研究、转化医学、精准医学、人工智能等方兴未艾,向临床流行病学和循证医学提出了新的挑战。这些学术思潮的出现,或是提出了获取和分析数据的新方法,或是为了促进科研成果的转化,或是拓展了新的研究领域,是对临床流行病学和循证医学的补充和延伸,不仅不会取代这门学科,反而为学科注入了新的思想和生命力[19-21]。以大数据研究为例,一个明显的事实是,大样本量带来的统计学精确性并不等同于科学理论的真实性。大数据研究要想得到可信的结果,还有数据质量、研究设计、临床相关性等诸多问题需要解决。另一方面也应看到,大数据具有大规模、多样性和时效性等特征,有别于继往临床流行病学研究方法。目前还缺少针对大数据证据质量的评价体系和分级标准,需要在此方向上不断努力,以期早日填补空白。精准医学试图建立从微观分子机制到宏观临床表型的桥梁,人工智能旨在用计算机算法来辅助(甚至替代)医疗工作中人脑的作用,这些都是重要的发展方向。但是,无论学术思潮如何变化,临床流行病学和循证医学所代表的实践理性哲学思想不会过时,那就是:以正确构建临床问题为起点,以患者-重要结局为导向,以证据的真实性、全面性和可及性为普遍追求,以医生的技术能力为落脚点,充分尊重每一位患者的特殊性,以此作出临床最佳决策。
2017年,BMJ和牛津大学主办的“Evidence Live”会议上提出了循证医学的未来宣言[22]。中国学者将和全世界同道携起手来共同奋斗,争取早日实现宣言提出的目标:(1)扩大患者、医疗专业人员和政策制定者在研究中的作用和参与;(2)促进现有证据的系统性应用;(3)为最终用户提供相关、可重复和可及的研究证据;(4)避免不必要的和不可信的研究,努力减少研究偏倚和利益冲突;(5)对药品和医疗器械实施健全、透明和独立的监管政策;(6)制定质量更高、使用更方便的临床指南;(7)更好地利用真实世界数据以支持医学创新,改善医疗质量并保障患者安全;(8)加强对专业人士、政策制定者和公众的循证医学教育,真正实现基于证据的决策;(9)鼓励和培养新一代循证医学领军人才。
“见自己,见天地,见众生”,中国的临床流行病学和循证医学学科建设将以完善人才梯队为抓手,以促进医疗质量提高和资源合理分配为已任,以造福苍生百姓为终极使命,为建设“健康中国”作出应有的贡献。
-
表 1 受试者血脂分布情况
血脂项目 分布 TC 浓度(mmol/L) 2.60 ~4.15 4.16 ~5.19 5.20 ~6.23 6.24 ~7.27 >7.27 例数 9 20 19 5 1 TG 浓度(mmol/L) 0.55~1.10 1.11~1.65 1.66~2.20 2.21~3.30 >3.30 例数 25 12 7 5 5 HDL-C 浓度(mmol/L) 0.39~0.91 0.92~1.17 1.18~1.42 1.43~1.82 >1.82 例数 3 16 11 20 4 TC:总胆固醇;TG:甘油三酯;HDL-C:高密度脂蛋白胆固醇 表 2 3台CardioChek PA的批内不精密度及不同仪器间总不精密度
血脂
项目仪器序列号 L M H MEAN
(mmol/L)CV
(%)CV
(%)MEAN
(mmol/L)MEAN
(mmol/L)CV
(%)TC SN 3017711 3.79 3.60 4.07 3.99 4.91 3.39 SN 3015966 3.73 2.78 4.06 4.69 5.04 3.36 SN 3017755 3.72 2.71 4.06 5.10 4.97 3.57 总计 3.72 2.69 4.06 4.88 5.00 3.51 TG SN 3017711 0.74 4.18 1.87 2.95 3.35 4.03 SN 3015966 0.76 6.99 1.88 4.39 3.45 5.52 SN 3017755 0.75 4.64 1.86 5.75 3.39 4.66 总计 0.75 5.51 1.87 5.27 3.41 4.96 HDL-C SN 3017711 1.05 6.14 1.12 6.38 1.46 5.72 SN 3015966 1.10 7.24 1.16 7.89 1.49 7.69 SN 3017755 1.09 7.43 1.14 6.34 1.48 6.44 总计 1.09 7.27 1.15 6.84 1.49 6.79 TC、TG、HDL-C:同表 1;L:血脂低水平;M:血脂中间水平;H:血脂高水平;MEAN:平均值;CV:不精密度 表 3 不同批号试纸条批内不精密度和批间总不精密度
血脂
项目试纸条
批号MEAN
(mmol/L)CV
(%)diffmean
(mmol/L)diff%mean
(%)TC 221 4.21 1.51 0.223 5.78 219 3.94 3.31 -0.036 -0.91 215 3.97 5.49 - - 总计 4.04 4.70 - - TG 221 0.67 8.18 0.015 2.30 219 0.72 6.61 -0.068 10.43 215 0.65 3.95 - - 总计 0.68 7.66 - - HDL-C 221 1.53 5.62 -0.236 -13.36 219 1.59 7.02 -0.180 -4.53 215 1.77 5.58 - - 总计 1.63 8.61 - - TC、TG、HDL-C:同表 1;MEAN、CV:同表 2;diffmean:平均偏差;diff%mean:平均百分偏差 表 4 CardioChek PA检测系统与4种常规生化检测系统医学决定水平偏差判定
常规生化检测系统 TC TG HDL-C 水平 医学决定水平
(mmol/L)偏差
(mmol/L)百分偏差
(%)医学决定水平
(mmol/L)偏差
(mmol/L)百分偏差
(%)医学决定水平
(mmol/L)偏差
(mmol/L)百分偏差
(%)Beckman AU5400 高 5.17 0.03 0.61 1.69 -0.11 -6.49 1.03 -0.06 -5.86 中 6.24 -0.09 -1.38 2.26 -0.18 -8.13 1.56 0.11 7.00 低 5.65 -0.62 -11.05 Roche P Modular 高 5.17 -0.07 -1.36 1.69 0.13 7.65 1.03 -0.04 -3.62 中 6.24 -0.20 -3.19 2.26 0.11 4.96 1.56 0.01 0.67 低 5.65 0.01 0.19 Hitach 7180 高 5.17 0.08 1.51 1.69 0.04 2.57 1.03 -0.05 -4.45 中 6.24 0.00 0.05 2.26 -0.04 -1.61 1.56 0.03 1.82 低 5.65 -0.51 -9.04 BeckmanDxC 800 高 5.17 -0.06 -1.07 1.69 0.22 13.16 1.03 0.00 0.02 中 6.24 -0.15 -2.43 2.26 0.20 8.83 1.56 0.18 11.56 低 5.65 0.06 1.13 参考方法 高 5.17 0.10 1.96 1.69 1.03 0.02 2.23 中 6.24 0.05 0.77 2.26 1.56 0.08 4.87 低 5.65 TC、TG、HDL-C:同表 1 -
[1] 陆再英, 钟南山.内科学[M].7版.北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010: 267-272. [2] 陈文祥, 王抒.血脂测定标准化及有关问题[J].浙江实验医学, 2006, 4:31-33. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JYYY200601011.htm [3] 中国成人血脂异常防治指南制订联合委员会.中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2007版)[J].中华心血管病杂志, 2007, 5:4. [4] 李智.POCT技术在临床应用的现状与问题[J].中华检验医学杂志, 2012, 35:1062-1065. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zhyxjy201212002 [5] Stein JH, Carlsson CM, Papacke-Benson K, et al. Inaccuracy of lipid measurements with the portable Cholestech LDX analyzer in patients with hypercholesterolemia[J]. Clin Chem, 2002, 48:284-290. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/48.2.284
[6] Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Method comparison and bias estimation using patient samples. EP9-A2[S].Wayne, PA: CLSI, 2002.
[7] 夏寿扬.改良Bland-Altman图评价血糖仪结果准确性[J].检验医学与临床, 2009, 6:1738-1739. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jyyxylc200920025 [8] 丛玉隆. POCT的临床应用与存在的问题[J].中华检验医学杂志, 2007, 30:1325-1328. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zhyxjy200712001 [9] 陶志华.加强医院内部管理保证POCT检验质量[J].中华检验医学杂志, 2012, 35:1077-1080. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zhyxjy201212005 [10] 华美媛.浅谈血糖POCT的质量管理[J].医学信息学, 2013, 26:6. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yxxxzz201315461 -
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 杨叶,杨晨,李迎君. 健康中国战略背景下临床流行病学教学改革思路. 科技风. 2024(10): 125-127 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈海燕,杨丽,李红俊,李晓霞,杨尹,王静,张国美,刘蜻蜻. 以精准诊断为导向的超声医学住培教学实践. 中国继续医学教育. 2023(08): 178-182 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李长玲,李方,姚小美,褚传莲,张涌,王滨. 案例教学结合翻转课堂应用于临床流行病学本科生教学的效果研究. 中国社区医师. 2023(12): 164-166 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 贾福运,高晟玮,张茜,徐强. 中医药临床疗效评价方法研究进展. 时珍国医国药. 2023(07): 1720-1723 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 胡付兰,胡东生,张明. 混合教学模式在临床流行病学教学中的实践应用——以微课、超星学习通、TBL与LBL相结合为例. 教育教学论坛. 2023(34): 121-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 朱金明. 新时代背景下胃肠外科青年医师培养的几点思考. 中华消化病与影像杂志(电子版). 2022(01): 52-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵天易,雒琳,何丽云,吕晓颖,宫嫚,李筠,李少红,李洪皎,刘佳,刘保延,艾艳珂. 多源异构数据整合在中医药真实世界临床研究中的应用及展望. 世界中医药. 2022(05): 614-619 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 车贺宾,徐洪丽. 临床数据处理流程规范构建. 医学信息学杂志. 2022(03): 52-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李健爽,郭艳萍,张涛,刘加勇,李欣,马翠. 翻转课堂联合案例分析教学法在流行病学教学中的应用. 继续医学教育. 2022(08): 24-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李雪航,武文君,马玉,宋扬,王盛书,王建华,贾王平,韩珂,刘少华,陈仕敏,何耀,刘淼. 对医学研究生《临床流行病学》课程教学的满意度及影响因素分析. 转化医学杂志. 2022(06): 337-340+359 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 陆玉林,骆文,陆丽明. 开展真实世界中医药临床研究的机遇与挑战. 中华中医药杂志. 2021(08): 4443-4446 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 王倩,陶宁,阿提开木·吾布力,培尔顿·米吉提,戴江红. 基于雨课堂的临床流行病学教学改革与实践. 中国医学教育技术. 2020(02): 206-208+213 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 金倩莹,李星明. 流行病学方法在医学研究中的应用概述. 北京医学. 2020(05): 444-451 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 符宇,邵明义,赵瑞霞,吴明慧,远佳瑶,余海滨,崔伟峰. 基于中医证据的中医临床疗效评价方法探讨. 中医杂志. 2020(13): 1124-1129 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 吴东,刘晓清. David Sackett:循证医学之父. 协和医学杂志. 2020(04): 449-452 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 熊益权,谭婧. 在高等医学院校临床科研培训课程中开设真实世界数据与研究模块的探讨. 成都中医药大学学报(教育科学版). 2020(02): 36-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: