Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification Technology for Detection of Mitochondriopathy
-
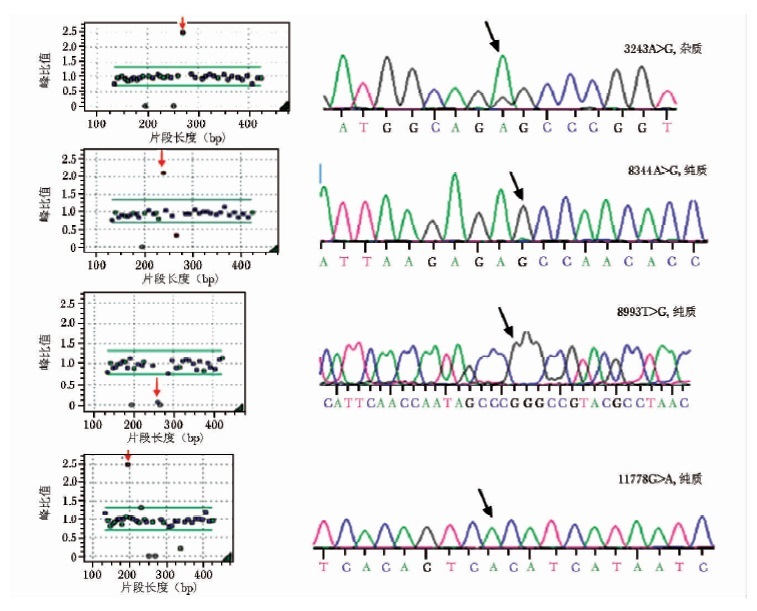
摘要:目的 探讨多重连接探针扩增技术(multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification, MLPA)用于常见线粒体疾病基因检测的可行性。方法 收集2010年5月至2012年8月北京协和医院281例可疑线粒体异常病例, 包括神经科存在神经系统损伤的患者233例及眼科疑诊Leber遗传性视神经病变的患者48例, 运用MLPA法对常见线粒体疾病突变位点进行检测, 并使用线粒体基因序列测定方法进行验证。结果 281例标本中共38例检测到线粒体基因突变, 总检出率为13.5%。眼科48例标本中, 3460G > A、11778G > A和14484T > C 3种突变共检测到19例, 检出率为39.6%;神经科233例标本中, 3243A > G、8344A > G、8993T > G和大片段缺失共检测到19例, 检出率为8.2%。除1例大片段缺失暂无PCR测序验证外, 其余MLPA结果均经序列测定验证为相符。结论 MLPA法是一种可行的快速、准确、简便的基因诊断方法, 可作为筛查常见线粒体疾病的检测工具, 为临床诊断和治疗提供依据。
-
关键词:
- 线粒体疾病 /
- 多重连接探针扩增技术 /
- 基因突变 /
- Leber遗传性视神经病变 /
- 线粒体脑肌病伴乳酸血症和卒中样发作
Abstract:Objective To investigate the feasibility of multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) for the molecular diagnosis of mitochondriopathy.Methods Totally 281 patients with suspected mitochondriopathy in Peking Union Medical College Hospital from May 2010 to August 2012 were enrolled in this study. Among them 233 with nervous system damage were from the department of neurology and 48 with suspected Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) were from the department of ophthalmology. The common mutation sites for mitochondrial disease were detected with MLPA, and the results were verified by mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) sequencing.Results We found 38 cases carried mtDNA mutations from all 281 cases, and the total detection rate was 13.5%. Among 48 cases suspected of LHON, 19 cases (39.6%) were found containing 3460G > A, 11778G > A or 14484T > C. Among 233 cases suspected of mitochondria related neuropathies, 19 cases (8.2%) were found containing 3243A > G, 8344A > G, 8993T > G or a large deletion. Except that the large deletion could not be sequenced, the other mutations detected by MLPA were all verified as consistent with gene sequencing results.Conclusions MLPA is a rapid, accurate, and simple method for detecting mtDNA mutation for common mitochondriopathy. It is feasible to be used in clinical diagnostic laboratory. -
术后快速康复,或加速康复外科(enhanced recovery after surgery,ERAS)近年来日益受到外科医生和护理人员的关注。ERAS的理念强调,通过术前咨询、避免术前灌肠、术中使用局部麻醉、术后早期进食、避免过多静脉补液、减少不必要引流管放置等措施可减轻手术应激,加速术后恢复,降低手术并发症和医疗费用[1-2]。ERAS在妇科手术中对住院天数、术后疼痛等临床结局的改善作用已经得到多中心研究的证实[3],包括产科[4]、盆底手术[5]、妇科肿瘤手术[6]、微创手术[7]。ERAS不仅具有明显的卫生经济学效益[8],患者也有较好的满意度[9]。在ERAS的理念下,产生了大量日间手术,不仅用于妇科良性疾病,还用于妇科肿瘤和盆底手术[10]。本文着重讨论妇科肿瘤手术创伤对ERAS的影响及可能的改进措施。
1. 妇科肿瘤加速康复外科指南和争论
目前已有多个妇科肿瘤ERAS指南和清单[2, 11-15],包括肿瘤手术方案[16-19],均根据不同证据级别提供相应推荐。2019年指南还新加入了患者报告结果、盆腔廓清术、盆腔热灌注、出院路径以及评估和报告等诸多新条目[11],系统性地执行和评估ERAS已成为妇科肿瘤治疗的共识[20]。妇科肿瘤ERAS项目甚至还延伸至术前患者的锻炼和康健指导[21]以及卫生经济学领域[22]。中国医师协会妇产科医师分会于2019年亦成立了专门的ERAS学组,可见对该问题的重视。
尽管如此,ERAS在妇产科手术中的应用仍有很多未知之处[23],在复杂手术治疗如妇科肿瘤手术中仍存在不同看法[24-28],特别是对卵巢癌的治疗[29-30]。研究发现,在卵巢癌治疗中,ERAS对于初始手术和中间型手术的恢复并无明显区别[25]。但系统性回顾并未得到更多有关卵巢癌手术实施ERAS的效应信息[30]。值得关注的是,在讨论ERAS的众多研究中,手术创伤对于术后康复的影响一直未得到应有的重视,这可能是目前ERAS研究中最大的悖论和矛盾,然而这方面的研究较少。在临床实践中,笔者认为减少手术创伤始终是快速康复的决定因素,如不能避免和减少预期或计划外手术创伤,ERAS的大部分举措则不仅无益,还可能产生负面效应。
2. 妇科肿瘤手术执行加速康复外科的要点
2.1 尊重学习曲线,减少研究偏倚
手术学的学习曲线是每个外科医生必须经历的过程。尽管个人天赋或能力具有差异,学习曲线或长或短,但为了达到可接受的熟练程度和安全阈值,手术医生无不需要经历一系列严格的培训。已有研究发现,不同妇科肿瘤团队施行ERAS的实践和效果具有很大的异质性[24]。因此,在施行ERAS之前,应把医生的学习曲线作为重要的变量予以考虑和平衡;在评估ERAS效果之时,应将医生的学习曲线作为重要的因素予以分层和校正[31]。而ERAS本身也有其学习曲线的问题[32],多学科合作下的ERAS对于重大肿瘤手术才能发挥有益价值[16],医生的拥护亦是ERAS实践成功的关键[33]。
良性手术以及开腹手术是目前妇产科领域ERAS研究的主要对象。在妇科恶性肿瘤手术,尤其是微创妇科肿瘤手术中对ERAS的效果仍然存在争议,究其原因还是手术的复杂性和高风险影响了ERAS的实施与效果评定[34]。微创手术有巨大的异质性,从简单的探查术、诊断术、活检术,到复杂的根治术、分期术、廓清术,手术创伤存在巨大的层级差异,复杂程度和并发症风险亦有天壤之别,这种异质性对ERAS的实施和评估必然产生重大影响[35]。因此,对于复杂手术实施ERAS的情境下,适宜在相同手术类型中进行风险比较,并充分考虑医生的学习曲线,从而减少临床研究偏倚,充分阐释ERAS的效果。如果忽略这些问题,则有可能得出过于激进或过于保守的结论,无法指导复杂多变的临床问题。
2.2 全面规划手术,规避手术风险
手术永远存在风险,实施手术永远是在利大于弊的前提下进行的决策判断。为了保证ERAS的实施,规避手术风险,消除医患矛盾,应对手术进行全面规划设计,充分考虑到所有的意外和最大的风险,这一点对任何级别的医师来说都是必备素质。尽管实施ERAS的患者满意度较高,亦需根据患者具体情况区别对待。研究发现,日间手术患者中独居或年龄较大者对术后当天出院的感受会差很多[10]。对于不同年龄和功能评分的妇科肿瘤患者,实施ERAS的安全性亦需进一步证实[36]。美国妇产科医师协会指南认为,实施ERAS前应仔细审查手术和护理框架及流程,并将ERAS植入卫生系统以获得持续效果[2]。
支持ERAS的证据很多,严密实施ERAS的好处亦很多,但ERAS的地位永远是辅助手术、以手术为中心的。不能因为ERAS而去破坏和干扰已经成熟实施、卓有成效的临床路径和方案,而应采用ERAS的理念修订、改善和弥补现有的临床路径及方案,并在修订、改善和弥补的过程中,尊重传统手术学经验,因为经验也是一种证据[37]。现有的循证医学材料和证据则应在全面规划的前提下审慎地改造、植入和运用,以避免新证据在老传统中“水土不服”,避免新事物在老环境下“夭折短命”。这种系统性工作并非一朝一夕、一人一事就能够实现的。经历6年的多中心研究已经证实,如果能够在术中和围手术期严格遵循妇科手术的ERAS指南,可改善患者的临床结局[3]。而一项德国妇科医生的调查发现,仅有1/3的被调查者会遵循ERAS相关指南[38]。很难想象,在一个管理混乱、缺乏规范准入制度的手术中心能够很好地推广和延续ERAS;即便能够强行推广,也不过是手术风险增加的导火索。
2.3 总结失利经验,开展前瞻研究
ERAS可以降低手术并发症,但不能完全消除手术并发症。除了手术学本身的机会性风险之外,手术创伤与ERAS的相关性问题目前尚未得到充分研究。这是一个非常有趣且存在巨大挑战的课题。从这样的相关性研究中,不仅可深入了解ERAS促进术后康复的机制,还可阐释手术学创伤对ERAS的效应与后果,诸如镇痛与住院时间的关系等[6, 27]。手术的失利包括未达到预期目的、严重的并发症、超出一般水平的恢复时间和花费。分析这些失利的可能因素,无论是从个体层面,还是从研究层面,都将有助于手术学和ERAS的完善与革新,有益于患者的身心健康和快速康复。
ERAS成功和失利的教训都会为临床实践提供宝贵的经验,尤其是失利的经验,对于复杂性、高风险手术而言具有更加宝贵的警示和帮助作用,为高质量的前瞻性研究提供切入点。这些内容包括:患者心理因素与生活质量的变化及其对手术预后和生存结局的影响[39];围手术期饮食与禁食应激对肠道微环境的影响[40];麻醉方式对机体免疫环境以及预后的影响[41];不同方式引流及放置时长对于术后康复的影响,等等。这些研究涉及临床、护理、病/生理和分子机制等多个方面,无论阴性结果还是阳性结果,均可为ERAS的广泛开展和个体化操作提供更多细节和更可靠的证据。
3. 结语
手术创伤永远是决定手术结局的关键因素,而减少手术创伤始终是ERAS的决定性因素,这一点在目前的ERAS研究中尚未得到充分重视,在诸如妇科肿瘤等复杂手术中尤甚。作为外科医生,我们应该尊重手术学的学习曲线,在复杂手术应用ERAS的评估中减少术者因素的偏倚。而每一个重视自己手术技巧、珍爱患者预后的术者都会因地制宜、扬长避短地全面规划手术及围手术期护理,从而规避手术风险,保证ERAS实施的有效性和可持续性。无论是手术还是ERAS的失利,都需要总结经验、及时完善和修订,并在前瞻性研究中探讨成功和失利的潜在因素,从而保证诊疗技术的全面进步,并为患者健康提供可靠保障。
-
表 1 线粒体常见突变位点引物序列及扩增条件

表 2 MLPA检测各位点比例及序列测定验证结果

-
[1] Schouten JP, McElgunn CJ, Waaijer R, et al. Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligationdependent probe amplification[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2002, 30:e57. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gnf056
[2] 陈竺.医学遗传学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2002:158-159. [3] A human mitochondrial genome database[DB/OL].[2012-12-7]. http://www.mitomap.org/MITOMAP.
[4] DiMauro S, Schon EA. Mitochondrial respiratory-chain diseases[J]. N Engl J Med, 2003, 348:2656-2668. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra022567
[5] 陈刚, 杜卫东, 曹慧敏.线粒体DNA突变与相关人类疾病[J].遗传, 2007, 29:1299-1308. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yc200711003 [6] Chinnery PF, Howell N, Lightowlers RN, et al. MELAS and MERRF. The relationship between maternal mutation load and the frequency of clinically affected off spring[J]. Brain, 1998, 121:1889-1894. DOI: 10.1093/brain/121.10.1889
[7] Howell N, Chinnery PF, Ghosh SS, et al. Transmission of the human mitochondrial genome[J]. Hum Reprod, 2000, 15:235-245. DOI: 10.1093/humrep/15.suppl_2.235
[8] Cao L, Shitara H, Horii T, et al. The mitochondrial bottleneck occurs without reduction of mtDNA content in female mouse germ cells[J]. Nat Genet, 2007, 39:386-390. DOI: 10.1038/ng1970
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 祝健婵,熊小琴,刘海燕. 加速康复外科理念及电生理技术对妇科腹腔镜术后患者肠道功能恢复的研究. 实用妇科内分泌电子杂志. 2024(19): 80-82+119 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李金科,欧阳玲. 加速康复外科理念在卵巢癌围手术期应用的研究进展. 现代肿瘤医学. 2023(18): 3507-3511 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李哲. 中西医结合护理在宫颈癌患者围手术期中临床应用价值评价. 辽宁中医药大学学报. 2020(08): 197-199 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载:











