-
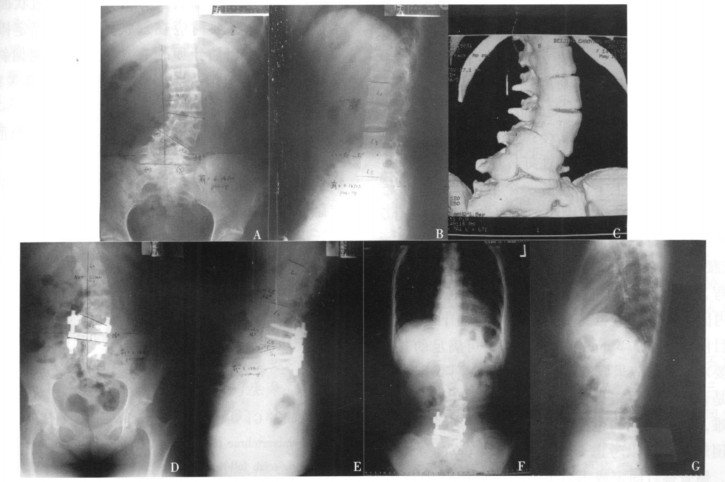
摘要:目的 探讨腰骶段半椎体手术治疗策略。方法 本科2001年1月至2010年1月共收治了877例先天性脊柱侧凸患者, 其中腰骶段半椎体所致先天性脊柱侧凸8例。通过术前、术后及随访时X线片, 对这8例患者的半椎体特点、手术方式、侧凸冠状面Cobb角、矢状面Cobb角、躯干偏移进行回顾性分析。结果 完全分节型半椎体5例, 部分分节型半椎体3例。一期前后路半椎体切除1例, 一期后路半椎体切除7例。手术出血量200~2300 ml, 平均692 ml; 手术时间平均6.5 h。短节段固定6例, 长节段固定2例。手术前后及末次随访时腰骶弯冠状面Cobb角分别平均为33.1°、9.8°和14.0°, 术后即刻矫正率为70.4%, 最终矫形率为57.7%;手术前后和末次随访时近端腰弯冠状面Cobb角分别平均为32.5°、12.6°和14.2°, 术后即刻矫正率为61.2%, 最终矫形率为56.3%。术前4例患者有冠状面躯干失平衡。全部病例随访12~82个月, 平均30.9个月。并发症包括伤口裂开1例, 椎弓根螺钉位置不良2例, 一过性神经根损伤1例, 其中1例行翻修手术。最终随访时7例患者冠状面躯干偏移改善, 1例患者发生冠状面躯干失平衡加重, 无矢状面失平衡发生。结论 腰骶段半椎体畸形可引起明显的冠状面躯干失平衡, 应及早手术治疗。早期病例往往畸形较轻, 可采用半椎体切除+短节段固定融合术。如果畸形较重或代偿弯较明显则需要延长融合范围。Abstract:Objective To summarize the surgical treatment results and discuss the surgical strategy of congenital scoliosis due to lumbosacral hemivertebrae.Methods Totally 877 patients with congenital scoliosis were treated in our hospital between January 2001 and January 2010. Among them, there were 8 cases of lumbosacral hemivertebrae(3 males and 5 females, with the average age at surgery of 11 years old). The clinical data including the anatomic data of hemivertebrae, coronal and saggital Cobb angle, coronal and sagittal trunk shift, surgical approach, and fusion area were retrospectively analyzed for these 8 patients.Results There were 5 full-segmented hemivertebrae and 3 semi-segmented hemivertebrae. Seven patients underwent hemivertebrae resection with posterior approach only, 1 patients underwent hemivertebrae resection with one-stage anterior and posterior approach. The intra-operative blood loss ranged 200-2300 ml(mean:692 ml). The average operation time was 6.5 h. Six patients had short segment fixation and 2 patients had long segment fixation. The mean coronal Cobb angle of lumbosacral curve was 33.1° before surgery, 9.8° after surgery, and 14.0° at latest follow-up. The mean coronal Cobb angle of proximal lumbar curve was 32.5° before surgery, 12.6° after surgery, and 14.2° at latest follow-up. Four patients had coronal trunk imbalance before surgery. The complications included wound dehiscence(n=1) and nerve root injury(n=1). Two patients had malpostion of pedicle screw. One revision surgery was performed. All patients were followed up from 12 to 82 months, with an average follow-up duration of 30.9 months. Coronal trunk shift was improved in 7 patients after surgery, 1 patient had coronal trunk decompensation at final follow-up, and no saggital trunk decompensation was noted.Conclusions Lumbosacral hemivertebrae may cause scoliosis with obvious coronal trunk imbalance, which needs early intervention. The early surgery with hemivertebrae resection and short segment fixation is able to avert severe local deformity and prevent secondary deformity. If the compensatory lumbar curve is severe, extensive fusion is preferred.
-
Keywords:
- scoliosis, congenital /
- hemivertebrae /
- lumbar /
- surgical treatment
-
1. 病例与问题
X女士78岁,来自中国,是一名退休教师,丧偶,独居,患有多种慢性疾病,包括糖尿病、高血压、缺血性心肌病、慢性肾脏病3期、骨质疏松症和轻度老年痴呆。她的儿子生活在其他城市,很少能来探望她。去年,她注意到自己大便带血,经检查发现患有结肠腺癌,并已转移至肝脏和肺部。儿子知道后坚持让母亲接受化疗,并与妻子共同照顾其起居。
接受化疗后的一段时间,X女士病情确有缓解,但体质量持续下降,胸片检查结果显示,肺部转移灶仍在扩大。她一天中的大部分时间都在床上度过,不再愿意与邻居及以前的同事聊天,现在连上厕所也需要助行器和他人帮助。1个月前,儿媳购物回来时发现,X女士躺在地板上,已经神志不清。紧急送往医院后,被诊断为肺炎、脓毒性休克、肺水肿和急性肾衰竭,进入ICU后不久,因心脏骤停接受了心肺复苏。心肺复苏后的评估结果显示,X女士多处肋骨骨折、气胸、肾衰竭并出现了缺血性卒中。在儿子的坚持下,X女士接受了气管插管、机械通气、血管活性药物和血液透析治疗,并依靠呼吸机和血液透析维持了两周。在医生提议可以进行胃造瘘手术后,儿子立即要求进行手术,术后继续住在ICU。然而1周后,X女士再次出现心脏骤停,尽管医生全力抢救,30 min后仍因抢救无效而宣布死亡。事后,大多数亲戚都对X女士的儿子表达了称赞,认为他是个孝顺的儿子。
问题:中国传统死亡文化中将“善终”作为人的最终追求。X女士的经历能否算作善终?如果答案是肯定的,善终究竟是什么意思?对于个体,善终的含义如何确定?什么样的医疗才能使善终成为可能?X女士在生命末期是否得到了最好的关怀?如果没有,什么才是最好的关怀?
2. 关于回应他人痛苦:历史溯源
照顾病痛中的亲人以及濒临死亡的人,并不是什么新鲜事,在有文字记载的历史长河中,我们可以看到许多关怀他人痛苦的相关证据。例如,儒家经典《孝经》中提到,孝顺的孩子应该在父母生病时给予他们特别的照顾,并加倍奉养[1]。这种责任源于“孝顺”,它体现了家庭关系的最高价值。大约在同一时期,巴利文典籍《摩诃婆伽》描述了佛陀如何关爱病患:“谁照顾病患,谁就是在照顾我。”[2]这里,照顾他人似乎是一种责任,因为每个人都具有神性或者是神的代表。
为需要的人提供照护场所同样有着悠久的历史。根据伊斯兰历史学家穆罕默德·伊本·贾里尔·塔巴里的记载,早在公元9世纪,伊斯兰就在贸易和军事路线沿线设立了照顾病患的“临终关怀院”。从公元11世纪开始,基督教十字军也在地中海和朝圣路线沿线建立了临终关怀医院。
1633年,一个名为“圣文森特·德·保罗慈善之女”的天主教修女协会在法国成立,承担起了在临终关怀医院和家中照顾穷人和病患的工作。然而,当时西方哲学正在经历一场革命,这场革命从根本上改变了照顾病患和临终者的方式及目的。
3. 笛卡尔医学模式
17世纪初,法国哲学家勒奈尔·笛卡尔提出,“存在”意味着成为“思考的自我”(ego cogitans)的客体。思考的自我,即思考的主体,对于这个主体而言,世界完全由客体组成,所有客体均可被思考主体测量、研究、操纵和处置。换言之,一切事物都可被认知和掌握。通过阐明自然的力量,即产生、改变和毁灭所有客体并决定其每一次互动的力量,思考主体就能够了解客体。原则上,任何事物都无法抗拒思考主体的阐释和认知。笛卡尔在其1632年出版的《方法论》一书中明确指出了这一点:“……我们可以清楚地认识火、水、空气、星辰、宇宙以及周围一切其他物体的力量和作用,就像熟知什么匠人做什么活一样;我们可以像匠人一样,因势利导将这些知识用于所有适当目的,从而成为大自然的主人和拥有者。”[3-4]
关于主体认知最适合用于什么目的,笛卡尔认为:“……最重要的是保护健康。健康无疑是人生中最重要的一种幸福,也是其他一切幸福的基础。”即在主体掌握的科学客观领域中,医学是最重要的。虽然所有技术都能够通过保障人类的利益,推动其对幸福的追求,但最大的利益是健康。医学能够通过了解人体及疾病来确保并维护健康这一至高无上的幸福。
在笛卡尔看来,医学与其他科学一样,只能认知客体。这并不是说医学忽略了主观数据。相反,主观数据通常是关于客体的数据,因此只是客观思考的另一个方面。医学寻求了解正常生理和病理生理知识,进而掌控正常生理和病理生理,通过阐明人体的功能、功能障碍或疾病的原因来认知人体。医学还寻求了解疾病如何发生以及如何恢复和保持健康。笛卡尔认为:“……如果充分认识了各种疾病的原因以及自然界向我们提供的一切药物,我们可以摆脱很多种躯体疾病和精神疾病,甚至可能抵抗衰老、延年益寿。”笛卡尔断言,医学可以驾驭身体,在一定程度上也可以驾驭心灵,从而无限期地保持健康。
在《方法论》和《第一哲学沉思录》中,笛卡尔都将人体描述为一台机器,称之为“人体机器”[5],其由神经、肌肉、静脉、血液、皮肤和其他器官等多个部分组成,这些部件可能像“制作拙劣的时钟”一样失灵,结果就是产生疾病。主体客观化的医学思考模式认为,原则上可以通过明确故障原因和发明治疗方法来排除这些故障。对于某些故障,可以利用药物作为治疗手段。但由于人体机器的复杂性,故障可能产生于一个或多个部件,原则上,医学可以修复或替换任何一个部件。换言之,人体就是由一次性部件和可能被替换的部件组成。
在科技时代之初,笛卡尔就认为可将器官替换和维持生命的技术作为维持健康的手段,并提出生命可以无限持续,健康也可以无限维持。按照笛卡尔的观点,当医学掌握了足够的人体知识,就能够将人类从“年老体弱”中解放出来,通过治疗疾病、修复或更换故障部件,不断向后延缓死亡时间。掌握了足够的知识和技能后,医学就能战胜死亡本身,与其他任何自然现象一样,死亡也是一个可以阐释和认知的客体。笛卡尔关于掌控死亡的梦想在很大程度上影响了现代西方医学的教育、研究和实践。它将死亡医学化,死亡因而变成了一个主要需要医学干预的技术问题。因此在20世纪50年代之后,西方文化中死亡的地点从家庭转移到了医院[6]。
笛卡尔“战胜死亡”的计划催生了维持生命/延缓死亡的技术,比如心肺复苏、机械通气、血液透析、人工营养等。在美国的短暂历史中,这些维持生命的技术有两个重要共同点:首先,这些技术均在20世纪60年代开始普及,且一旦普及开来,就很难不去使用;其次,早在20世纪70年代中期,人们就开始认识到维持生命的技术不仅能为患者带来明显好处,其也可能是有害的。这些技术既是给我们的伟大恩赐,也会带来不可预见的危险,甚至可能加剧痛苦。从那时起,美国的患者、家属和医生一致认为,有时候最好的选择反而是暂停或撤除维持生命的治疗,法院也找到了允许在某些情况下暂停或撤除维持生命技术的法律依据。例如,医院成立了临床伦理委员会,以帮助患者权衡接受特定维持生命治疗的利弊,开展病例会诊已成为北美地区的标准做法。
4. 维持生命技术与善终
维持生命技术的不利影响通常包括延长或加剧患者的痛苦和衰弱,甚至导致患者出现焦虑、谵妄、抑郁等症状。当患者家属被问及是否使用这些技术时,无论他们作何选择,都可能感到焦虑或内疚,而这些情绪可能会伴随他们一生。对于有机会康复或出院并拥有可接受的生活质量的患者来说,维持生命的技术利大于弊,但许多患者(如X女士)却因病情危重而并无康复的机会。
回到文章开头的问题:在中国,“善终”意味着什么?现代医学如何实现或推进“善终”?维持生命的技术对于实现“善终”有何作用?是否可能阻碍“善终”的实现?照顾病弱长者的传统责任是否仍有意义?“孝顺”在当今社会的含义与孔子时代的含义是否相同?甚至可以探讨与几十年前的含义是否相同?有创生命维持技术的出现是否应改变“孝顺”的表达方式?或者说改变是否已经发生?掌控生命的技术目标是否在不知不觉中侵蚀或改变了传统文化价值观和意义?维持生命的技术看似是表达孝顺、实现健康和长寿的手段,但技术本身是否已成为目的[7]?
当技术手段成为目的,心肺复苏、机械通气、血液透析等技术本身可能变得至关重要。延缓死亡可能变得比待在家里、感到舒适、和亲人在一起、与亲人告别、与疏远的亲人和解、给予和请求宽恕更为重要,甚至比患者是否有能力做这些事情更为重要。在北美地区,20世纪60年代和70年代的技术思维已经不知道如何不使用维持生命的技术手段,结果对患者造成了很大伤害[4]。如果孝顺不能适应或不符合当前的社会和医疗技术环境,在中国是否也会面临类似的风险?更具体地说,在当代中国,维持生命的有创性治疗如何才能得到最优化利用,实现利益最大化和伤害最小化?对“善终的意义”这一问题的回答可能部分取决于如何回答上述问题。
5. 对中国缓和医疗的再思考
与其他医学领域或医疗模式不同,缓和医疗并不是一种固定不变的技能或活动。如果面临严重的疾病、不同的社会经济背景或文化价值观与西方高收入国家存在差异,缓和医疗的需求和实践方式也应有所不同[8-10]。
在我看来,现代缓和医疗的兴起源于对笛卡尔医学模式忽视、制造和再造痛苦的反思。缓和医疗的主要目的是缓解重病患者的痛苦,同时关注维持生命的技术本身可能带来的不必要伤害。缓和医疗并不完全排斥医疗技术的使用,因为缓和医疗关注的是解除痛苦,因此其更强调负责任地使用技术。然而,这并不意味着其主要目的是对适当使用维持生命的治疗或其他医疗技术进行伦理考量,相反,缓和医疗注重倾听患者的痛苦声音并积极响应他们的需求,并以此来决定技术的使用方式。
缓和医疗会利用医疗技术来缓解患者的痛苦,包括维持生命的必要技术[11],然而缓和医疗并不拘泥于这些技术,甚至可能在必要时放弃使用维持生命的技术,其关注的焦点是缓解患者的痛苦,维持生命的技术并不总是必需的。缓和医疗并非完全由技术所驱动,而是强调技术的使用应当自然、顺应病情。更为重要的是,缓和医疗尊重并接纳死亡的自然过程。这并不意味着忽视临终患者或放弃治疗可能恢复的患者,其目标不仅仅是战胜死亡,而是无目的性地关怀每一位患者,没有预设的目标使缓和医疗能够真正倾听患者的声音。
在利用最先进的医疗技术快速缓解患者痛苦和其他不适的同时,缓和医疗也关注疾病管理医疗模式所忽视的痛苦。这些痛苦可能来自于身体上的不适,但更多时候来自于患者内心的失落感,比如失去健康、工作、收入、独立生活能力、社交联系以及生活意义,甚至在面对死亡时感到自我价值的丧失。并无任何一种方法可以准确地衡量痛苦,或者完美地应对痛苦,因此不可能制定一个基本的方案来缓解痛苦。真正重要的,是如何关注和应对患者个体化的痛苦,然后制定最适合他们的缓和医疗措施。
缓和医疗承认自身的局限性和所有技术的局限性,承认死亡是不可避免的,并积极与患者共同寻找最合适的方式,以最自然的方式离世。最重要的是,缓和医疗更关注患者作为“他者”的感受,不仅将患者视为医疗对象,而是让他们在有意义的环境中、在亲密关系网中、在符合其传统文化背景中得到关怀,这种关怀允许“他者”保持他们的独特性。
近年来,笔者有幸应邀参加了中国关于缓和医疗的讨论,同时倾听了两个紧密相关话题的探讨,即如何翻译“palliative care”这一词汇?如何将西方的缓和医疗实践引入中国?在这两个问题的讨论中,与会者达成了共识,将治疗和缓解严重疾病痛苦的这一学科翻译为“缓和医疗”。医疗保健应以舒适与“和”(harmony)为导向。但是,“和”指的是什么呢?自身的和谐?与他人的和谐?与社会和自然环境的和谐?还是包括以上所有这些含义?无论是何种情况,中文对缓和医疗的重新诠释至少为“善终”的定义提供了部分答案。中国医疗服务提供者和中国医疗体系如何才能让重病患者获得舒适与“和”?孝顺是否意味着年轻人有责任帮助长辈获得舒适与“和”?
回到文章最初的问题:X女士的经历是否可以被视为“善终”?她的儿子是否尽到了孝顺的责任?他是否可以做得更好,为母亲提供更为人道的临终关怀,让母亲在生命最后的日子里不再受更多的痛苦折磨?比如将母亲接回家,给予她温馨的照料?这样的照护模式能否在全中国得到普及?我们能否认同,尽孝的最佳方式是让母亲在家中获得舒适与和谐,而不是坚持在ICU依赖各种医疗器械尽可能延长和维持她的生命?即使X女士的儿子在感情上能够接受这种观念的转变,他的家人是否会指责甚至排斥他,认为他是不孝之子?开展全国性的讨论和教育能否改变这种态度?
我认为,找到这些问题的答案对于增进中国人和海外华人的福祉都非常重要。同时,在中国找到的答案也可能为西方文化提供新的视角,帮助其寻找疾病、死亡和医学的真正意义,因为笛卡尔式掌控自然和战胜死亡的模式已经让西方文化在面对死亡时感到迷茫。
-
表 1 8例腰骶段半椎体患者术前影像学特点

-
[1] Bollini G, Docquier PL, Viehweger E, et al.Lumbosacral hemivertebrae resection by combined approach:medium- and long-term follow-up[J].Spine, 2006, 31:1232-1239. DOI: 10.1097/01.brs.0000217616.17692.a0
[2] MacMaster MJ, Ohtsuka K.The natural history of congenital scoliosis:a study of two hundred and fifty-one patients[J].J Bone and Joint Surg Am, 1982, 64:1128-1147. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-198264080-00003
[3] 仉建国, 邱贵兴, 于斌, 等.后路半椎体切除治疗先天性脊柱侧后凸的初步结果[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006, 26:156-160. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zhgkzz98200603003 [4] Jalanko T, Rintala R, Puisto V, et al.Hemivertebra resection for congenital scoliosis in young children:comparison of clinical, radiographic, and health-related quality of life out-comes between the anteroposterior and posterolateral approaches[J].Spine, 2011, 36:41-49. DOI: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181ccafd4
[5] Leong JC, Day GA, Luk KD, et al.Nine-year mean follow-up of one-stage anteroposterior excision of hemivertebrae in the lumbosacral spine[J].Spine, 1993, 18:2069-2074. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-199310001-00025
[6] Slabaugh PB, Winter RB, Lonstein JE, et al.Lumbosacral hemivertebrae.Areviewof twenty-fourpatients, with excision in eight[J].Spine, 1980, 5:234-244. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-198005000-00006
[7] Nakamura H, Matsuda H, Konishi S, et al.Single-stage excision of hemivertebrae via the posterior approach alone for congenital spine deformity:follow-up period longer than ten years[J].Spine, 2002, 27:110-115. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-200201010-00026
[8] Ruf M, Harms J.Hemivertebra resection by a posterior approach:innovative operative technique and first results[J].Spine, 2002, 27:1116-1123. DOI: 10.1097/00007632-200205150-00020
[9] Hosalkar HS, Luedtke LM, Drummond DS.New technique in congenital scoliosis involving fixation to the pelvis after hemivertebra excision[J].Spine, 2004, 29:2581-2587. DOI: 10.1097/01.brs.0000145414.43650.62

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载:
