Effect of Transplantation of Bone Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on the Apoptosis of Neurons in Ischemic Rats
-
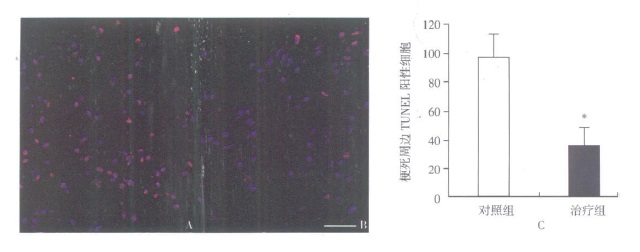
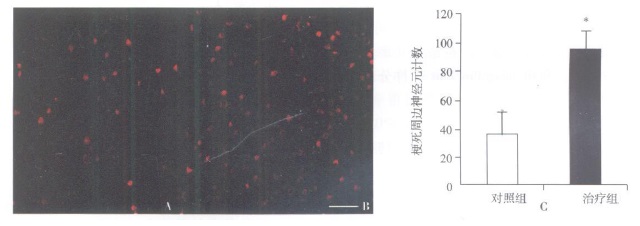
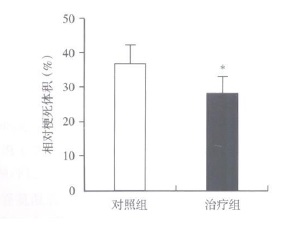
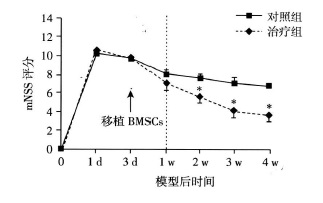
摘要:目的 探讨移植骨髓间充质干细胞(bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stemcells, BMSCs)治疗大鼠脑梗死及其减轻半暗带神经元的凋亡作用。方法 采集成人志愿者骨髓, 分离培养BMSCs; 线栓法建立大鼠大脑中动脉栓塞(middle cerebral artery occlusion, MCAO)2h再灌注脑梗死模型; 建模后第3天分别立体定向脑内移植5×105BMSCs和等量生理盐水, 改良神经功能损害评分(modified neurological severity scores, mNSS)观察神经功能恢复; 建模后第14天TUNEL法检测梗死周边神经细胞凋亡; 建模后第28天免疫荧光染色检测梗死周边神经元的存活; 采用依红-苏木素染色评估梗死体积。结果 治疗组和对照组比较, 梗死周边TUNEL阳性细胞显著减少(P=0.017), 而神经元核抗原(neuronal nuclei antigen, NeuN)阳性细胞显著增多(P=0.015);同时, BMSCs可显著降低MCAO大鼠的相对梗死体积(P=0.041);mNSS评分显示, 从MCAO后第14天开始, 治疗组评分均显著低于对照组(P < 0.05)。结论 脑梗死急性期移植BMSCs可显著减少半暗带神经元凋亡, 缩小梗死范围, 有效促进神经功能的恢复。Abstract:Objective To investigate the apoptosis of neurons in the penumbra of cerebral ischemic rats transplanted with bone marrow derived-mesenchymal stem cells(BMSCs).Methods Bone marrow of a healthy adult volunteer was collected, and BMSCs were cultivated and harvested.Adult rats subjected to 2 h middle cerebral artery occlusion(MCAO)were randomly assigned to the BMSCs-treated group(n=12)and the control group(n=12), in which rats were transplanted with 5×105 BMSCs or saline, respectively, into the ipsilateral brain parenchyma on the 3rd post-MCAO day.The modified neurological severity scores(mNSS)was used to measure functional recovery.On the 14th post-MCAO day, apoptotic cells in the penumbra were detected by TUNEL analysis.On the 28th post-MCAO day, neurons were stained by immunoflu-orescence, and hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to evaluate the relative ischemic volume.Results TUNEL-positive cells were significantly reduced(P=0.017), and in contrast, neuronal nuclei antigen(NeuN)-positive cells were significantly increased(P=0.015)in the penumbra in BMSCs-treated group compared with control group.The relative ischemic volume was decreased in the BMSCs-treated group(28.3±4.5)% compared with the control group(36.8±5.6)%(P=0.041).The mNSS was significantly decreased in BMSCs-treated group at each time point starting on the 14th post-MCAO day compared with control group(P < 0.05).Conclusion BMSCs treatment can decrease ischemic volume and improve functional recovery after cerebral ischemia, which may, at least partially, attribute to the reduced apoptosis of neurons in the penumbra.
-
Keywords:
- cerebral ischemia /
- mesenchymal stem cells /
- neuron /
- apoptosis
-
2019新型冠状病毒(2019 novel coronavirus, 2019-nCoV)属于β属冠状病毒,2019年12月以来我国陆续出现该病毒感染引起的以肺部病变为主的新型传染病。临床特征为发热、干咳、气促、外周血白细胞一般不高/降低、胸部X线检查显示炎症性改变等。我国已将2019-nCoV感染的肺炎定为法定传染病。为规范诊疗,北京协和医院特成立专家组并制订2019-nCoV感染的肺炎诊疗方案(V2.0)。
1. 医务人员的防护
1.1 接诊医护准入
一线医护人员应进行上岗前筛查和2019-nCoV知识培训,并需排除以下情况:孕妇、年龄超过55岁、慢性疾病史(慢性肝炎、慢性肾炎、糖尿病、自身免疫性疾病及肿瘤)、合并急性发热者。
上岗前筛查血常规、尿常规、生化、肌酸激酶,并进行胸部X线检查。
1.2 隔离和防护要求
参见国家卫生健康委员会发布的“新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎诊疗方案(试行第三版)”[1]。
1.3 2019-nCoV密切接触后医护人员的隔离观察
(1) 与2019-nCoV感染的肺炎患者密切接触的医护人员应相对隔离,避免到处走动,避免广泛接触。
(2) 出现发热、咳嗽、气短等症状时应立即隔离,并进行相关检查。
(3) 结束2019-nCoV感染的肺炎病区工作时,应进行咽拭子及血常规检查,有异常者应接受严格隔离观察;无异常者普通隔离观察1周后恢复工作。
2. 2019-nCoV感染患者的诊疗
2.1 筛查标准[1-2]
(1) 流行病学史:发病前2周内有湖北旅行或居住史,或发病前14 d内曾接触过来自湖北、发热且伴有呼吸道症状的患者,或有聚集性发病。
(2) 72 h以内的急性发热,不伴流感样症状,且未证实其他病因者。
2.2 诊断标准
(1) 流行病学史。
(2) 临床表现:发热;发病早期白细胞总数正常/降低,或淋巴细胞计数减少;胸部影像学早期呈现多发小斑片影及间质改变,以肺外带明显, 进而发展为双肺多发磨玻璃影、浸润影,严重者可出现肺实变。
(3) 确诊:痰液、咽拭子、下呼吸道分泌物等标本行实时荧光RT-PCR检测2019-nCoV核酸阳性。
(4) 对于急性发热(72 h内,体温>37.5 ℃)且肺部影像学正常者,若外周血淋巴细胞绝对值<0.8×109/L,或出现CD4+及CD8+T细胞计数明显下降者,即使核酸检测未呈现阳性,均应居家隔离密切观察;必要时可考虑24 h后复查核酸检测,并依据临床表现复查胸部CT。
2.3 2019-nCoV感染患者检查常规
2.3.1 筛查病例就诊当天
应进行痰/咽拭子的核酸检查、血常规、尿常规、血气、肝肾功能、C-反应蛋白、降钙素原、肌酸激酶+肌红蛋白、凝血及胸部CT。可酌情查炎症因子[如白细胞介素(interleukin, IL)-6、IL-10、肿瘤坏死因子-α]、TB淋巴细胞亚群11项、补体[3-5]。
2.3.2 确诊患者序贯检查
(1) 留观后第3、5、7天及出院时依据病情,可检查血细胞、肝肾功能、肌酸激酶+肌红蛋白、凝血、C-反应蛋白;第5~7天若有条件可复查降钙素原及TB淋巴细胞亚群11项[3-5]。
(2) 留观后1~2 d均需复查胸部X线,之后视病情决定,但复查时间不超过5 d。
(3) 非转院患者出院前应复查血常规、胸部X线、肝肾功能及入院时所有异常检查。
2.4 根据病情严重程度确定治疗场所
所有具有筛查指征的病例均需就地医学隔离(单间隔离),一旦确诊均需前往指定医院救治。
2.4.1 重症病例
按照国家卫生健康委员会定义[1], 符合如下标准之一,需留院治疗并尽快转运至北京市定点诊治医疗机构: (1)呼吸频率增快(≥30次/min),呼吸困难;(2)吸空气时指氧饱和度≤95%,或动脉血氧分压/吸氧浓度≤300 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa);(3)肺部影像学显示多叶病变或48 h内病灶进展>50%;(4)快速序贯性器官功能衰竭评分(quick sequential organ failure assessment,qSOFA)≥2分;(5)社区获得性肺炎CURB-65评分≥1分;(6)合并气胸;(7)需住院治疗的其他临床情况。
2.4.2 危重症病例
按照国家卫生健康委员会定义[1], 符合呼吸衰竭、感染性休克、合并其他器官功能衰竭标准之一,立即进入ICU并在条件允许时尽快转运至定点医疗机构诊治。
2.5 治疗
2.5.1 一般治疗
卧床休息,监测生命体征、指氧饱和度,支持对症治疗,保证热量,维持水、电解质及酸碱平衡等内环境稳定。
2.5.2 氧疗
存在低氧血症者立即进行氧疗,血氧饱和度维持目标:非妊娠患者≥90%,妊娠患者92%~ 95%。
2.5.2.1 氧疗方式
轻症患者初始给予普通鼻导管吸氧,以5 L/min开始;重症患者如呼吸窘迫加重或标准氧疗无效时,可给予高流量鼻导管吸氧,以20 L/min起始,逐步上调至50~60 L/min,同时依据氧合目标调整吸氧浓度。
2.5.2.2 呼吸支持方式
无创呼吸机仅在患者可很好耐受无创通气时使用,不建议先于高流量鼻导管吸氧使用;有创呼吸机气管插管应由经验丰富人员完成,操作时按全面防护要求进行,呼吸机设置遵循急性呼吸窘迫综合征保护性通气策略进行;当有创呼吸机无法维持氧合时,可给予俯卧位体外膜肺氧合相应治疗,由于该操作复杂,需同时注意全面防护以及预防院内感染。
2.5.3 抗病毒治疗
目前尚无循证医学证据支持现有抗病毒药物对2019-nCoV有效,可酌情用洛匹那韦/利托那韦每次2粒×2次/d,疗程14 d。
2.5.4 糖皮质激素
重症患者酌情早期使用糖皮质激素,静脉滴注甲泼尼龙40~80 mg×1次/d,疗程5 d;可根据患者临床病情及影像学表现酌情延长疗程。
2.5.5 人免疫球蛋白
重症患者依据病情可酌情早期静脉输注人免疫球蛋白0.25~0.50 g/ (kg·d),疗程3~5 d[6-7]。
2.5.6 经验性抗菌治疗
根据患者临床和影像学表现,如不能除外合并细菌感染,轻症患者可口服针对社区获得性肺炎的抗菌药物,如二代头孢或氟喹诺酮类;重症患者需覆盖所有可能的病原体。
3. 防护和转运
(1) 重症患者一旦确诊,且有气管插管风险,应立即转运至有负压条件的ICU病房进行治疗;操作时按全面防护要求进行。
(2) 转运途中使用储氧面罩15 L/min以上给氧,保证储氧气囊充气满意。
(3) 气管插管应使用标准快速顺序诱导插管,尽可能使用肌松药物,最大程度避免患者呛咳引起飞沫传播。
(4) 插管后的眼罩等重复使用物品应使用健之素消毒后方可拿出负压病房。
(5) 插管患者应使用密闭吸痰器吸痰,避免呼吸机气流引起空气传播。
(6) 特殊情况下必须断开呼吸机进行气道操作时,应使用呼吸机的待机功能,避免呼吸机气流引起空气传播。如呼吸机无待机功能,应阻断呼吸机Y型管口,避免空气播散。
4. 解除隔离和出院标准[1]
体温恢复正常3 d以上,呼吸道症状明显好转,肺部影像学炎症明显吸收,且连续两次呼吸道病原核酸检测阴性(采样时间间隔至少1 d),可解除隔离出院或根据病情转至相应科室治疗其他疾病。
执笔人
李太生 (北京协和医院感染内科)
曹玮 (北京协和医院感染内科)
翁利 (北京协和医院内科ICU)
范洪伟 (北京协和医院感染内科)
施举红 (北京协和医院呼吸与危重症医学科)
参与讨论专家 (按姓氏汉语拼音排序)
柴文昭 杜斌 郭娜 韩丁 韩扬 胡小芸
焦洋 金征宇 刘正印 隆云 马小军 潘慧
王惠珍 王孟昭 吴文铭 吴欣娟 徐英春 许文兵
张波 张奉春 张圣洁 朱华栋
-
-
[1] Paolo B, Pamela GR, Paul JS.Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Revisiting History, Concepts, and Assays[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2008, 2:313-319. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.03.002
[2] Liu L, Sun Z, Chen B, et al.Ex vivo expansion and in vivo infusion of bonemarrow-derived Flk-1 + CD31-CD34-mesenchymal stem cells:feasibility and safety from monkey to human[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2006, 15:349-357. DOI: 10.1089/scd.2006.15.349
[3] Zhang Z, Wang R, Wang R, et al.Transplantation of neural stem cells modified by human neurotrophin-3 promotes functional recovery after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2008, 444:227-230. DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.08.049
[4] Kim SS, Yoo SW, Park TS, et al.Neural induction with neurogenin1 increases the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in the ischemic brain[J]. Stem Cells, 2008, 26:2217-2228. DOI: 10.1634/stemcells.2008-0108
[5] Andrews EM, Tsai SY, Johnson SC, et al.Human adult bonemarrow-derived somatic cell therapy results in functional recovery and axonal plasticity following stroke in the rat [J]. Exp Neurol, 2008, 211:588-592. DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.02.027
[6] Shen LH, Li Y, Chen J, et al.Therapeutic benefit of bone marrow stromal cells administered1 month after stroke[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2007, 27:6-13. DOI: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600311
[7] Li J, Zhu H, Liu Y, et al.Human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation protects against cerebral ischemic injury and up regulates interleukin-10 expression in Macaca fascicularis [J]. Brain Res, 2010, 1334:65-72. DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.080
[8] 魏俊吉, 曾立芬, 樊晓彤, 等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠缺血性脑卒中的实验研究[J].中华医学杂志, 2007, 87:184-189. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zhyx200703009 [9] Bang OY, Lee JS, Lee PH, et al.Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients[J]. Ann Neurol, 2005, 57:874-882. DOI: 10.1002/ana.20501
[10] Prockop DJ." Stemness" does not explain the repair of many tissues by mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells (MSCs) [J]. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2007, 82:241-243. DOI: 10.1038/sj.clpt.6100313
[11] Li Y, Chen J, Chen XG, et al.Human marrow stromal cell therapy for stroke in rat:neurotro phins and functional recovery[J]. Neurology, 2002, 59:514-523. DOI: 10.1212/WNL.59.4.514
[12] Li J, Zhu H, Lu S, et al.Migration and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in the normal rat brain [J/OL]. Neurol Res, 2010 http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/maney/nres.
[13] Raichle ME.The pathophysiology of brain ischemia[J]. Ann Neurol, 1983, 13:2-10. DOI: 10.1002/ana.410130103
[14] The STEPS Participants.Stem cell therapies as an emerging paradigm in stroke(STEPS) :bridging basic and clinical science for cellular and neurogenic factor therapy in treating stroke[J]. Stroke, 2009, 40:510-515. DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.526863
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 尚亚细亚,杜菊梅. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗帕金森病5例. 内蒙古医学杂志. 2016(09): 1048-1049 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵明珠,孙伟,刘向阳,朱景伟,黑岩敏彦,宫武伸一,刘卫东. 转染肝细胞生长因子基因的骨髓间质细胞治疗大鼠缺血性脑卒中的效果观察. 中国临床神经外科杂志. 2014(07): 414-417 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 窦玲,杨朝鲜. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗缺血性脑卒中的研究进展. 四川解剖学杂志. 2012(03): 26-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: