Epidemiology of Clinical Mold Infections in China: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
-
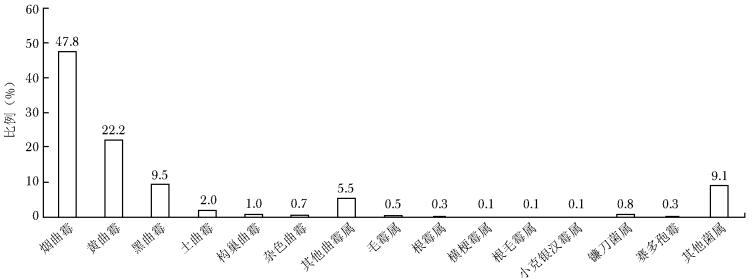
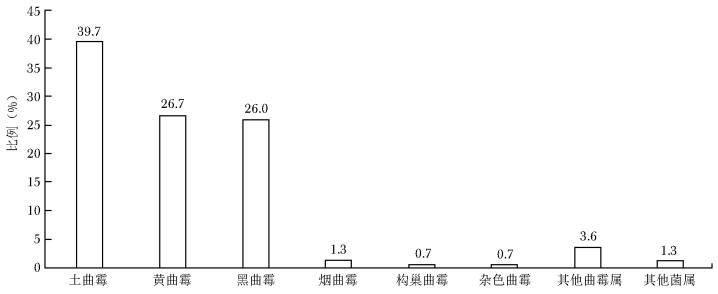
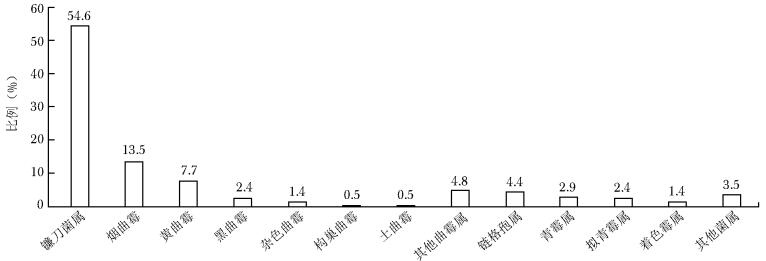
摘要:目的 分析我国霉菌感染的流行病学现状。方法 选取2019年1月—2022年6月中国医院侵袭性真菌病监测网中19家参与单位的霉菌感染患者临床资料,采用WHONET软件分析霉菌菌种构成及临床感染情况等流行病学特征。结果 共纳入16 285例霉菌感染患者,其中男性患者占比(62.1%)高于女性患者(37.9%);以老年患者为主,年龄中位数为60岁,年龄≥61岁患者占比49.3%(8023/16 285);主要分布科室为内科、ICU及外科;标本类型以下呼吸道标本为主(81.7%),其次为脓液及分泌物标本(7.8%);霉菌菌种构成以曲霉属为主(84.8%),青霉属、镰刀菌属、毛霉目和赛多孢霉占比分别为5.1%、3.0%、1.3%和0.4%;霉菌引起的常见感染性疾病中,下呼吸道感染霉菌以曲霉属为主(88.7%),其中烟曲霉最为常见(47.8%);耳部感染霉菌中曲霉属占比高达98.7%,其中土曲霉占比最高(39.7%);眼部感染霉菌中镰刀菌属占比最高(54.6%)。结论 霉菌引起的下呼吸道、耳部和眼部感染的主要菌种分别为烟曲霉、土曲霉和镰刀菌属,在临床治疗时需注意不同部位霉菌感染的菌种分布差异。Abstract:Objective To study the epidemiology of mold infections in China.Methods Based on the surveillance data of 19 hospitals participating in the China Hospital Invasive Fungal Surveillance Net from Jan 2019 to Jun 2022, the general information of patients and the epidemiological characteristics such as the proportion of different strains and clinical infection were analyzed by WHONET software.Results A total of 16 285 mold infection cases were included in the analysis, of which 49.3% were patients aged 61 and over, with the median age of 60 years old. The proportion of males was significantly higher than that of females (62.1% vs. 37.9%). The patients were mainly from the internal medicine, ICU and surgical wards. Most strains were isolated from lower respiratory tract, accounting for 81.7%, followed by pus and secretions (7.8%). In terms of species distribution, Aspergillus spp. accounted for the highest proportion (84.8%), with Penicillium spp., Fusarium spp., order Mucorales and Sedosporium spp. accounting for 5.1%, 3.0%, 1.3% and 0.4%, respectively. For species distribution among different mold infection, 88.7% of lower respiratory tract mold infections were caused by Aspergillus spp., and Aspergillus fumigatus(47.8%) was the most common species. Otomycosis was mainly caused by Aspergillus spp.(98.7%), of which Aspergillus terreus accounted for 39.7%, and ophthalmomycosis was mainly caused by Fusarium spp.(54.6%).Conclusions By the retrospective analysis of mold isolation from multicenter in China, we found that Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus terreus, and Fusarium spp. were the most common species causing pneumonomycosis, otomycosis, and ophthalmomycosis, respectively. Therefore, it is necessary to pay attention to the differences in species distribution among different mold infections in clinical empirical treatment of fungal infections.
-
Keywords:
- fungi /
- mold /
- infection /
- epidemiology
-
在全球老龄化的背景下,65岁及以上人群的数量快速增长,老年人群慢性病患病率急剧攀升,一人共患多种疾病的情况越来越严重[1]。共病(multimorbidity、comorbidity、multiple chronic conditions)是指2种及以上慢性病长期共存于同一个体,包括躯体疾病共存、躯体-精神心理疾病共存,以及躯体疾病/精神心理疾病-老年综合征共存[2]。而复杂共病(complex multimorbidity)则是指4种及以上慢性病长期共存于同一个体[3]。慢性病共病患者的不同疾病之间、疾病与治疗方案之间以及不同治疗方案之间相互影响,产生的不良结局远大于单个疾病的叠加[4]。共病增加老年人发生多重用药及药物不良反应风险,使医疗成本攀升,显著增加治疗相关不良事件的发生风险,降低患者生活质量且减少健康寿命年,并增加住院率和全因死亡率[5]。我国60岁及以上老年人中有1.8亿(81.1%)患有慢性病,共病老年人占比已超1/3[6]。根据中国健康与养老追踪调查(China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study, CHARLS)2015年发布的数据,在我国45岁及以上成年人中,共病和复杂共病的患病率分别为63.4%和38.6%;其中躯体-精神心理疾病共存的患病率为23.2%。共病的种类每增加1种,患者自费的医疗支出增加18.8%。其中,慢性肝病和糖尿病是患者自费医疗支出最多的2种慢性病[7]。因此,加强对老年人共病的认识并提升对共病患者的管理能力十分重要。
目前绝大多数临床研究及临床指南均针对单病种群体,而针对共病群体,尤其是复杂共病和老年共病人群的临床研究及临床指南极少,临床医师在管理共病患者时面临“无证可循”的窘况[8]。因此,本文对2000—2023年老年人共病相关研究进行文献计量学分析,探讨该领域研究现状、研究热点及发展趋势,以期提高我国临床医师对老年人共病的认识及管理。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 资料来源
计算机检索Web of Science核心合集数据库,纳入2000年1月1日—2023年10月24日的所有老年人共病相关文献[9]。检索策略如下:[TI=(“the aged” OR “the elderly” OR “older adults” OR “older people” OR “older patient” OR “geriatric”)AND TI=(“multimorbidity” OR “comorbidity” OR “multiple chronic conditions” OR “Chronic Conditions, Multiple” OR “Multiple Chronic Health Conditions” OR “Multiple Chronic Medical Conditions” OR “Multiple Chronic Illnesses” OR “Chronic Illnesses, Multiple”)OR(AK= (“the aged” OR “the elderly” OR “older adults” OR “older people” OR “older patient” OR “geriatric”)AND AK=(“multimorbidity” OR “comorbidity” OR “multiple chronic conditions” OR “Chronic Conditions, Multiple” OR “Multiple Chronic Health Conditions” OR “Multiple Chronic Medical Conditions” OR “Multiple Chronic Illnesses” OR “Chronic Illnesses, Multiple”) OR (KP=(“the aged” OR “the elderly” OR “older adults” OR “older people” OR “older patient” OR “geriatric”)AND KP=(“multimorbidity” OR “comorbidity” OR “multiple chronic conditions” OR “Chronic Conditions, Multiple” OR “Multiple Chronic Health Conditions” OR “Multiple Chronic Medical Conditions” OR “Multiple Chronic Illnesses” OR “Chronic Illnesses, Multiple”]。纳入标准:(1)以“老年人共病”为主题的相关文献;(2)语种为英文。排除标准:信件(Letter)、评论(Comment)、会议(Meeting)及其他类型文献。
1.2 数据分析
检索完成后导出文献信息,采用VOSviewer 1.6.18软件提取文献发表的期刊作者、关键词、机构、国家/地区、引文和出版日期等信息,并生成高产国家/地区(发文量≥30篇)、机构(发文量≥43篇)的合作网络图以及高频关键词(出现频次≥74次)的共现关系时间线图。其中,合作网络图由节点和连线组成,节点表示国家/地区、机构和关键词等被分析的元素,不同颜色表示不同的聚类,节点大小可表示不同元素出现的频次,节点之间的连线表示合作及共现关系。
1.3 统计学处理
采用Microsoft Office Excel 2021软件进行数据整理。采用VOSviewer 1.6.18软件对文献中的内容进行提取,并绘制高产国家/地区、机构的合作网络图及高频关键词共现关系时间线图[10]。采用CiteSpace 6.1.R6软件对作者、研究机构、国家等信息进行共现和聚类分析[11]。采用R语言“bibliometrix”包分析文献的关键词演变趋势[12]。
2. 结果
2.1 年发文量
经检索共获得老年人共病研究相关文献2590篇,包括Article 2230篇,Review 360篇。老年人共病研究文献的发文量及被引频次分布情况主要反映了该领域科学贡献度、关注度的年均表现和总体趋势,2000—2021年该领域的发文量总体呈快速上升趋势,并在2021年达到高峰(328篇),之后发文量逐渐趋于稳定。2023年由于仅统计了截至10月24日发表的文献,故2023年前的数据更具可信度。其中,在2016年、2018年和2020年显著增加。同时,文章被引频次也呈现逐年增长趋势,快速增长期出现于2018—2021年,详见图 1。对年累计发文量进行了多项式拟合,拟合公式为y=-0.0018x5+ 0.111x4-2.1312x3 +19.339x2-59.752x+ 66.225,拟合优度R2=0.9991。
2.2 国家/地区分布及合作情况
2590篇文献共来自87个国家和地区,发文量、连接强度及被引频次排名详见表 1。在老年人共病研究领域处于主导地位和输出中心前5位的国家分别是美国、英国、加拿大、意大利和荷兰。其中,美国的发文量(907篇)及被引频次(31 343次)均居首位。且美国在老年人共病研究领域与其他国家/地区的合作亦最为广泛和密切,主要与英国、加拿大、意大利、中国等国家合作,详见图 2。
表 1 发文量、连接强度、被引频次居前10位的国家Table 1. Top 10 countries in terms of number of publications, link strength and frequency of citations序号 国家 发文量(篇) 国家 连接强度 国家 被引频次(次) 1 美国 907 英国 396 美国 31 343 2 英国 240 美国 371 英国 10099 3 加拿大 228 意大利 323 意大利 9258 4 意大利 206 西班牙 300 荷兰 7193 5 荷兰 200 荷兰 278 加拿大 7191 6 德国 191 德国 254 德国 5782 7 中国 185 澳大利亚 243 瑞典 5086 8 西班牙 184 法国 193 瑞士 4462 9 澳大利亚 183 加拿大 170 西班牙 3944 10 瑞典 105 比利时 170 澳大利亚 3693 2.3 作者分布及合作情况
发文量排名居前4位的作者分别为Jenny Ploeg(32篇,加拿大麦克马斯特大学),Maureen Markle- Reid (29篇,加拿大麦克马斯特大学),Davide L.Vetrano(29篇,瑞典卡罗林斯卡学院)和Alessandra Marengoni (28篇,意大利布雷西亚大学)。其中Alessandra Marengoni也是该领域被引频次(3491次)和共被引频次(566次)最高的作者,提示其发文质量较高、在老年人共病领域具有较大的学术影响力(表 2)。
表 2 发文量、被引频次及共被引频次居前10位的作者Table 2. Top 10 authors in terms of number of publications, citation frequency and co-citation frequency序号 作者 发文量(篇) 作者 被引频次(次) 作者 共被引频次(次) 1 Jenny Ploeg 32 Alessandra Marengoni 3491 Alessandra Marengoni 566 2 Maureen Markle-Reid 29 Laura Fratiglioni 2794 Linda P Fried 496 3 Davide L.Vetrano 29 Susan M.Smith 1419 Martin Fortin 437 4 Alessandra Marengoni 28 Graziano Onder 1186 Mary E.Charlson 425 5 Cynthia M.Boyd 22 Martin Fortin 1123 World Health Organization 400 6 Amaia Calderon-Larranaga 22 Davide L.Vetrano 997 Cynthia M.Boyd 357 7 Graziano Onder 22 Cynthia M.Boyd 972 Karen Barnett 342 8 Laura Fratiglioni 21 Jenny Ploeg 963 Mary E Tinetti 335 9 Ai Koyanagi 17 Maureen Markle-Reid 815 Martine Exterman 293 10 Kathryn Fisher 16 Emma Wallace 799 Ronald C.Kessler 273 2.4 研究机构分布及合作情况
发文量、总连接强度和被引频次居前10位的研究机构详见表 3。其中加拿大多伦多大学是发文量最多的研究机构(67篇),其次为瑞典卡罗林斯卡学院(63篇),该学院同时也是被引频次最高的研究机构。加拿大麦克马斯特大学、美国约翰斯·霍普金斯大学等院校也对该领域贡献颇多。
表 3 发文量、总连接强度、被引频次居前10位的研究机构Table 3. Top 10 research institutions in terms of number of publications, total link strength and citation frequency序号 机构名称 发文量(篇) 机构名称 总连接强度 机构名称 被引频次(次) 1 多伦多大学 67 卡罗林斯卡学院 164 卡罗林斯卡学院 4128 2 卡罗林斯卡学院 63 多伦多大学 135 哥伦比亚大学 3640 3 麦克马斯特大学 53 斯德哥尔摩大学 125 布雷西亚大学 3552 4 约翰斯·霍普金斯大学 51 约翰斯·霍普金斯大学 117 约翰斯·霍普金斯大学 3343 5 华盛顿大学 50 杜克大学 115 斯德哥尔摩大学 3055 6 密歇根州立大学 49 加利福尼亚大学旧金山分校 114 斯德哥尔摩老年研究中心 2830 7 杜克大学 47 布雷西亚大学 102 伦敦卫生与热带医学院 2731 8 加利福尼亚大学旧金山分校 45 哈佛医学院 100 印第安纳大学 2653 9 悉尼大学 45 圣心天主教大学 96 拉德堡德大学 2570 10 伦敦国王学院 43 斯德哥尔摩老年研究中心 94 匹兹堡大学 2134 最密集的合作关系发生在美国约翰斯·霍普金斯大学、美国杜克大学、美国华盛顿大学等机构之间(红色聚类);瑞典卡罗林斯卡学院、英国伦敦国王学院等机构不仅在绿色聚类内连接紧密,同时也与瑞典斯德哥尔摩老年研究中心、意大利天主教圣心大学所代表的橙色聚类之间有合作关系;澳大利亚悉尼大学等院校(紫色聚类)则与其他研究方向的诸多院校有着广泛联系。整体而言,美国约翰斯·霍普金斯大学与瑞典卡罗林斯卡学院为合作强度最大的两所研究机构,详见图 3。
2.5 期刊分布情况
老年人共病领域发文量与被引频次居前10位的期刊详见表 4。其中发文量居前3位的期刊分别为BMC Geriatr(99篇)、J Am Geriatr Soc(67篇)和BMJ Open(56篇),被引频次最高的前4名期刊分别为J Am Geriatr Soc(4037次)、J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci(2164次)、J Am Med Assoc(2144次)以及J Clin Oncol(2105次)等。这些期刊的影响因子和JCR分区也可一定程度上反映学界对该领域的投入和关注度。在发文量居前10位的期刊中,仅有1种期刊处于Q3分区,其余均跻身前50%行列。被引用期刊则均处于Q1、Q2分区,包括New Engl J Med、Lancet、J Am Med Assoc等顶级期刊,表明老年人共病这一领域具有相当高的关注度与研究价值。
表 4 发文量、被引频次居前10位的期刊Table 4. Top 10 journals in terms of number of publications and frequency of citations序号 期刊 发文量(篇) 影响因子(JCR2022) JCR分区 共被引期刊 被引频次(次) 影响因子(JCR2022) JCR分区 1 BMC Geriatr 99 4.1 Q2 J Am Geriatr Soc 4037 6.3 Q1 2 J Am Geriatr Soc 67 6.3 Q1 J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2164 5.1 Q2 3 BMJ Open 56 2.9 Q2 J Am Med Assoc 2144 120.7 Q1 4 Arch Gerontol Geriatr 53 4 Q2 J Clin Oncol 2105 45.4 Q1 5 J Geriatr Oncol 53 3 Q3 Lancet 1829 168.9 Q1 6 PLoS One 50 3.7 Q2 PLoS One 1815 3.7 Q2 7 Age Ageing 46 6.7 Q1 J Clin Epidemiol 1781 7.2 Q1 8 Int J Environ Res Public Health 36 NA NA New Engl J Med 1431 158.5 Q1 9 J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 34 5.1 Q2 Age Ageing 1382 6.7 Q1 10 J Am Med Dir Assoc 33 7.6 Q1 Blood 1193 20.3 Q1 2.6 关键词分布情况
关键词代表了文献的主要研究方向或核心观点,可以精确地反映某一领域在某一时间段内的研究热点和前沿,并帮助研究者预测未来的热点方向。出现频次、总连接强度居前20位的关键词详见表 5。处于研究中心、出现频次较高的前2个关键词分别是“multimorbidity”(共病,1172次)和“older adults”(老年人,886次),与本研究主题契合。其次是“frailty”(衰弱,206次)、“aging”(衰老,153次)以及“polypharmacy”(多重用药,138次)。表明在老年人共病领域最受关注的是其与衰老的关系,以及与共病相关的衰弱和多重用药现象。其他高频关键词还包括“comprehensive geriatric assessment/ geriatric assessment” (老年综合评估/老年评估)、“quality of life”(生活质量)、“primary care”(初级卫生保健),提示上述内容也越来越受重视。
表 5 出现频次、总连接强度居前20位的关键词Table 5. Top 20 keywords in terms of frequency of occurrenceand total link strength序号 关键词 出现频次(次) 总连接强度 1 multimorbidity 1172 2194 2 older adults 886 1706 3 frailty 206 468 4 aging 153 301 5 polypharmacy 138 312 6 depression 137 294 7 chronic disease 134 302 8 mortality 124 261 9 geriatric assessment 83 200 10 quality of life 80 188 11 cancer 75 213 12 dementia 74 145 13 epidemiology 70 132 14 disability 68 145 15 comprehensive geriatric assessment 62 151 16 geriatrics 60 144 17 primary care 58 116 18 anxiety 54 118 19 geriatric oncology 46 123 20 geriatric 44 102 出现最早且最大的聚类及其关键词分别是geriatric assessment(老年评估)和older patients(老年患者);出现较早的聚类及其关键词分别是depression(抑郁)和disease(疾病)、mental disorders(精神障碍)。Heart disease(心脏病)是出现相对较晚的聚类,而共现频率较高、在时间线上靠后的关键词为multimorbidity(共病)中的“health care utilization”(医疗卫生资源使用)、“guideline”(指南)等。
2.7 文章被引频次分析
被引频次是对文章质量及影响力进行评估的重要指标之一,高被引频次的文章也是推动研究进展、反映研究趋势的关键因素之一。抑郁与躯体疾病/老年综合征共存是重要的共病类型,抑郁显著增加老年人发生躯体共病的风险[13]。被引频次最高的文献是Moussavi等于2007年发表于Lancet的Depression, chronic diseases, and decrements in health: results from the World Health Surveys(2586次),该文通过对比抑郁与其他4种常见慢性病(心绞痛、骨关节炎、哮喘、糖尿病),发现抑郁对健康结局的影响明显大于其他慢性病,并可能导致其他慢性病恶化。抑郁合并上述慢性病中的1种或多种对患者健康结局的影响亦远大于仅患有抑郁对患者的影响,认为应对抑郁与其他躯体共病之间的关系给予更多重视,并思考可能的应对措施[14]。抑郁还能促进并加速老年人共病的发生,一项前瞻性队列研究纳入3042例老年人,随访时间长达15年,在多种调整模型中,合并抑郁的老年人发生共病的速度及严重程度均明显升高(β=0.33,95% CI:0.06~0.61)[15]。另一篇被引频次超过2000次的文献是The PHQ-8 as a measure of current depression in the general population (2575次),仍围绕抑郁这一严重影响患者身心健康及生活质量的慢性病展开,阐述了8项患者健康问卷抑郁量表PHQ-8在人群中检测、筛选出抑郁患者的可行性,从而有利于抑郁的诊断和干预[16]。被引频次居第3位的文献为Aging with multimorbidity: A systematic review of the literature(1645次),系统回顾了1990—2010年间老年共病领域相关文献,就老年人共病的患病情况及影响因素、发病率及危险因素、临床结局(包括功能状态、死亡率、生活质量)、医疗卫生资源使用情况以及对共病患者的诊疗和照护模式进行总结分析,并提出针对老年人共病的研究应重点关注以下内容:(1)共病发生的危险因素和发病机制,包括遗传和生物学因素、生活方式以及这些因素间的相互影响。(2)环境因素,包括社会支持、社会经济状况、压力和应激对共病患者的影响。(3)在今后的临床研究中纳入共病患者,而非仅入选单病种患者,开展针对共病患者治疗/干预的临床研究,制订针对共病管理的指南。(4)针对共病人群的医疗照护模式,重点关注在初级卫生保健中对共病患者进行综合管理[17],详见表 6。
表 6 被引频次居前15位的文献Table 6. Top 15 cited articles序号 作者及发表时间 文章题目 期刊名称 被引频次(次) 文章类别 1 Moussavi S等(2007年) Depression, chronic diseases, and decrements in health: results from the World Health Surveys Lancet 2586 Article 2 Kroenke K等(2009年) The PHQ-8 as a measure of current depression in the general population J Affect Disord 2575 Article 3 Marengoni A等(2011年) Aging with multimorbidity: A systematic review of the literature Ageing Res Rev 1645 Review 4 Wolff JL等(2002年) Prevalence, expenditures, and complications of multiple chronic conditions in the elderly Arch Intern Med 1480 Article 5 Diniz BS等(2013年) Late-life depression and risk of vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of community-based cohort studies Br J Psychiatry 763 Review 6 Repetto L等(2002年) Comprehensive geriatric assessment adds information to Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status in elderly cancer patients: An Italian group for geriatric oncology study J Clin Oncol 676 Article 7 Salive ME(2013年) Multimorbidity in Older Adults Epidemiol Rev 669 Article 8 Lehnert T等(2011年) Health Care Utilization and Costs of Elderly Persons With Multiple Chronic Conditions Med Care Res Rev 468 Review 9 Hanlon P等(2018年) Frailty and pre-frailty in middle-aged and older adults and its association with multimorbidity and mortality: a prospective analysis of 493 737 UK Biobank participants Lancet Public Health 441 Article 10 Byers AL等(2010年) High Occurrence of Mood and Anxiety Disorders Among Older Adults The National Comorbidity Survey Replication Arch Gen Psychiatry 428 Article 11 Quoix E等(2011年) Carboplatin and weekly paclitaxel doublet chemotherapy compared with monotherapy in elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: IFCT-0501 randomised, phase 3 trial Lancet 417 Article 12 Diederichs C等(2011年) The measurement of multiple chronic diseases--a systematic review on existing multimorbidity indices J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 413 Review 13 Smith SM等(2012年) Managing patients with multimorbidity: systematic review of interventions in primary care and community settings BMJ 396 Article 14 Björgvinsson T等(2013年) Psychometric properties of the CES-D-10 in a psychiatric sample Assessment 389 Article 15 Smith SM等(2016年) Interventions for improving outcomes in patients with multimorbidity in primary care and community settings Cochrane DatabaseSyst Rev 384 Review 3. 讨论
共病给社会带来沉重的卫生经济学负担。根据2016—2019年美国医疗支出面板调查(medical expenditure panel survey, MEPS)结果,美国成年人中最常见的2种慢性病共存类型为高血压-高脂血症(估算患病人数占总人口的12.4%);最常见的3种慢性病共存类型为高血压-高脂血症-糖尿病(估算患病人数占总人口的4.6%),人均年度医疗支出最多的3种慢性病共存类型为糖尿病-骨关节炎-心血管疾病(23 850美元/年);最常见的5种慢性病共存类型为高血压-高脂血症-肌肉骨骼疾病-糖尿病-骨关节炎(估算患病人数占总人口的1.1%);在校正年龄、性别和种族后,糖尿病-关节炎-哮喘/慢性阻塞性肺病共病患者的健康自评结果最差[18]。CHARLS于2018年对3511例60岁及以上共病老年患者的调查显示,家庭总支出、自费医疗支出和家庭支付能力的中位数分别为19 900元、1500元和10 520元。共病患者灾难性医疗支出(catastrophic health expenditure, CHE)(即自费医疗支出≥家庭支付能力的40%)的发生率高达31.5%[19]。我国60岁及以上共病老年患者中患病率最高的3种共病类型分别为哮喘-慢性肺病,哮喘-骨关节炎/风湿性疾病-慢性肺病以及血脂异常-高血压-骨关节炎/风湿性疾病/心脏病[20]。
本研究显示,2000—2021年该领域发文量显著增加,目前处于相对稳定阶段,国内外学者逐渐重视老年人共病问题。美国对该领域贡献最大,发文量及总被引频次显著高于其他国家。在美国,50%以上的老年人同时罹患3种及以上慢性病[21]。早在2012年,美国老年医学会(American Geriatrics Society, AGS) 即根据系统性文献回顾和专家共识,发布了老年共病患者管理的指导建议[22]。2019年,AGS进一步发文介绍执行这些指导建议的具体步骤,包括询问患者关心的最主要问题,对共病患者的治疗方案进行完整的系统性回顾,考虑患者的意愿和依从性,充分考虑疾病情况与治疗间的相互作用,审慎权衡治疗方案的获益与风险,沟通并决定是否继续/停止某种干预/治疗措施,明确需要优先干预/治疗的疾病情况,并根据获益、可行性等对干预/治疗方案进行再评估[23]。
关键词分析显示,近年该领域备受关注的热点主要是衰老与共病的关系,以及与共病相伴随的衰弱和多重用药现象。人体衰老与老化相关疾病(如心血管疾病、神经退行性疾病、肿瘤)的发生存在很强的非随机关联[24]。寻找能够反映衰老过程、并能早期识别衰老过程中的共病和衰弱的理想生物标志物是老年学基础领域的研究热点[25]。针对2011—2019年入选美国国家健康和老龄化趋势研究(National Health and Aging Trends Study)的9450例老年人、中位随访4年的前瞻性队列研究显示,在随访期间,存在共病的老年人较无基础疾病老年人发生衰弱的风险增加1.68倍(95% CI: 1.04~2.73, P<0.05)[26]。另一项针对英国生物银行数据库(UK Biobank)中493 737例中年及老年人、中位随访7年的前瞻性队列研究显示,整体人群中衰弱的患病率为3%,但在合并4种及以上慢性病人群中,衰弱的患病率则高达18%。在校正合并慢性病情况、社会经济状况及生活方式后,衰弱显著增加队列人群的全因死亡率,研究认为应及早识别并干预存在共病的中年和老年患者的衰弱状态[27]。老年人衰弱与共病的密切关联反映了疾病状态对功能状态的相互和叠加影响。多重用药指患者同时使用5种药物,包括非处方药、中成药、保健品[28]。共病老年患者合并多重用药现象突出,多种药物的应用增加潜在的药物-药物及药物-疾病相互影响,显著增加药物不良反应风险和患者经济负担,亦使患者的治疗依从性明显下降。通过对共病老年患者进行药物重整(medication reconcillation)及处方精简以改善整体临床结局亦是近年的研究热点。
通过关键词分析还发现,老年综合评估/老年评估、初级卫生保健以及生活质量在老年人共病研究中也愈发受到重视。老年综合评估(comprehen-sive geriatric assessment, CGA)是指采用多学科方法评估老年人的躯体情况、功能状态、心理健康和社会环境状况等,并据此制订以维持和改善老年人健康及功能状态为目的的治疗计划,最大限度地提高老年人的生活质量。CGA是现代老年医学的核心技能之一,也是筛查老年综合征的有效手段[29]。英国国家健康与临床卓越研究所(National Institute for Health & Clinical Excellence, NICE)在其2017年发布的共病临床评估与管理指南中建议,对共病患者的管理应重点涵盖以下3个方面:(1)对共病患者进行系统性的健康评估,尤其注意衰弱的筛查和识别。(2)评估共病对患者的影响。包括共病对患者生活质量的影响,不同疾病和治疗方案间的相互影响;共病患者的用药情况,是否存在多重用药及不合理用药。(3)共病患者的管理方案。应明确当前和今后的治疗目标,包括制订预先医疗计划(advance care planing, ACP);明确负责共病患者综合管理的具体人员(如全科医师、老年科医师),并协调与专科医师的沟通/转诊;明确患者的随访间隔,以及发生急性医疗情况时的就诊渠道;梳理患者当前的用药和其他治疗方案,结合现有循证医学证据,充分/审慎权衡药物和治疗的风险及获益,结合风险/获益、患者预期生存及自主意愿,综合作出治疗决策。针对老年共病患者,建议在初级卫生机构中,通过CGA识别患者存在的疾病情况及老年综合征,以患者为中心,由患者的主诊医师牵头负责、由多学科团队参与,以有效的临床信息系统为依据,为共病老年患者制订个体化的治疗方案,并为患者安排规律随访。未来可围绕初级卫生保健和老年综合评估在老年人共病管理中的作用,以及维护共病老年患者的生活质量方面展开研究。
本研究利用文献计量学方法分析2000—2023年老年人共病领域的研究趋势,时间跨度大,对其发展态势进行了整体展现。针对老年患者,尤其是共病、衰弱老年患者的治疗和照护,过去以疾病为导向的医疗模式已难以为继,应尽早转向以患者为中心,全人、全程、全生命周期管理的人本医疗模式。基于老年综合评估和多学科团队的现代老年医学模式应是今后管理老年共病的新模式,其有效性和对患者生活质量、整体预后的影响尚有待大样本、多中心、长期随访临床研究的验证。
本研究局限性:首先,研究虽采用Web of Science核心合集数据库,但覆盖面较窄,未结合PubMed、Scopus等其他数据库进行分析。其次,本研究仅纳入了英文文献,可能遗漏部分高质量中文文献,未来可将中文数据库相关文献纳入分析,并进行国内外对比研究。
综上,目前对老年人共病的研究在世界范围内有着较高的热度,我国应大力开展相关研究,加强国际交流合作,以探索适合我国国情的老年患者全人管理新模式。
作者贡献:张丽负责研究方案设计、数据分析及论文撰写;康梅、陈中举、曹存巍、马玲、朱敏、金炎、夏云、褚云卓、刘文恩、郭大文、黄颖、段金菊、王俊瑞、徐雪松、马筱玲、李彬、廖康和朱鹏飞负责实验操作和数据采集;王瑶、徐英春和明亮负责数据审核及论文审校。利益冲突:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突 -
表 1 16 285例霉菌感染患者一般临床资料[n(%)]
项目 数值 性别 女性 6176(37.9) 男性 10 109(62.1) 年龄(岁) 0~1 96(0.6) 2~10 186(1.1) 11~20 302(1.9) 21~40 2000(12.3) 41~60 5678(34.9) 61~80 6841(42.0) ≥81 1182(7.3) 科室 内科 8297(50.9) ICU 2817(17.3) 外科 1520(9.3) 五官科 1086(6.7) 急诊科 920(5.6) 皮肤科 462(2.8) 儿科 188(1.2) 其他科室 995(6.2) 表 2 16 285株霉菌菌种构成及标本分布[n(%)]
项目 数值 菌种构成 曲霉属 13 806(84.8) 青霉属 831(5.1) 镰刀菌属 493(3.0) 毛霉目 206(1.3) 赛多孢霉 57(0.4) 其他 892(5.5) 标本类型 下呼吸道 13 305(81.7) 脓液及分泌物 1272(7.8) 耳部 300(1.8) 眼部 207(1.3) 组织 221(1.4) 体液 150(1.0) 血液 53(0.3) 其他 777(4.8) 表 3 曲霉属菌种构成[n(%)]
菌种 数值 烟曲霉 6819(49.4) 黄曲霉 3574(25.9) 黑曲霉 1645(11.9) 土曲霉 547(4.0) 构巢曲霉 160(1.1) 杂色曲霉 121(0.9) 棒曲霉 7(0.1) 灰绿曲霉 7(0.1) 其他曲霉属 926(6.6) 总计 13 806(100) 表 4 毛霉目种属构成[n(%)]
种属 数值 毛霉属 96(46.6) 根霉属 68(33.0) 根毛霉属 20(9.7) 横梗霉属 16(7.8) 小克银汉霉属 6(2.9) 总计 206(100) -
[1] Bongomin F, Gago S, Oladele RO, et al. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases: Estimate Precision[J]. J Fungi (Basel), 2017, 3: 57. DOI: 10.3390/jof3040057
[2] WHO fungal priority pathogens list to guide research, development and public health action[M]. World Health Organization, 2022.
[3] von Lilienfeld-Toal M, Wagener J, Einsele H, et al. Inva-sive Fungal Infection[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2019, 116: 271-278.
[4] Wang H, Wang Y, Yang QW, et al. A national survey on fungal infection diagnostic capacity in the clinical mycology laboratories of tertiary care hospitals in China[J]. J Microbiol Immunol Infect, 2020, 53: 845-853. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.016
[5] Xiao M, Chen SC, Kong F, et al. China Hospital Invasive Fungal Surveillance Net (CHIF-NET) Study Group. Five-year China Hospital Invasive Fungal Surveillance Net (CHIF-NET) study of invasive fungal infections caused by noncandidal yeasts: species distribution and azole susceptibility[J]. Infect Drug Resist, 2018, 11: 1659-1667.
[6] Wang Q, Cai X, Li Y, et al. Molecular identification, antifungal susceptibility, and resistance mechanisms of patho-genic yeasts from the China antifungal resistance surveillance trial (CARST-fungi) study[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13: 1006375. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1006375
[7] Firacative C. Invasive fungal disease in humans: are we aware of the real impact?[J]. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, 2020, 115: e200430. DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760200430
[8] Rotjanapan P, Chen YC, Chakrabarti A, et al. Epidemio-logy and clinical characteristics of invasive mould infections: A multicenter, retrospective analysis in five Asian countries[J]. Medical Mycol, 2018, 56: 186-196. DOI: 10.1093/mmy/myx029
[9] Wei L, Zhu P, Chen X, et al. Mucormycosis in Mainland China: A Systematic Review of Case Reports[J]. Mycopathologia, 2022, 187: 1-14. DOI: 10.1007/s11046-021-00607-4
[10] Vallabhaneni S, Benedict K, Derado G, et al. Trends in Hospitalizations Related to Invasive Aspergillosis and Mucormycosis in the United States, 2000—2013[J]. Open Forum Infect Dis, 2017, 4: ofw268. DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofw268
[11] Krishna V, Bansal N, Morjaria J, et al. COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Mucormycosis[J]. J Fungi, 2022, 8: 711. DOI: 10.3390/jof8070711
[12] Song Y, Liu X, Yang Z, et al. Molecular and MALDI-ToF MS differentiation and antifungal susceptibility of prevalent clinical Fusarium species in China[J]. Mycoses, 2021, 64: 1261-1271. DOI: 10.1111/myc.13345
[13] 孙声桃, 吕奇学, 韩雷, 等. 我国中原地区653株真菌性角膜炎分离镰刀菌的基因型及药物敏感性[J]. 中华眼科杂志, 2015, 51: 660-667. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2015.09.005 [14] 杨之辉, 余进, 李若瑜. 中国大陆地区赛多孢霉感染流行现状的回顾性分析[J]. 中国真菌学杂志, 2019, 14: 183-188, 192. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3827.2019.03.014 [15] Chen M, Zhu X, Cong Y, et al. Genotypic diversity and antifungal susceptibility of Scedosporium species from clinical settings in China[J]. Mycoses, 2022, 65: 1159-1169. DOI: 10.1111/myc.13507
[16] Paulussen C, Hallsworth JE, álvarez-Pérez S, et al. Ecology of aspergillosis: insights into the pathogenic potency of Aspergillus fumigatus and some other Aspergillus species[J]. Microb Biotechnol, 2017, 10: 296-322. DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.12367
[17] Jeong W, Keighley C, Wolfe R, et al. The epidemiology and clinical manifestations of mucormycosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case reports[J]. Clin Microbiol Infec, 2019, 25: 26-34. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.07.011
[18] Jing R, Yang WH, Xiao M, et al. Species identification and antifungal susceptibility testing of Aspergillus strains isolated from patients with otomycosis in northern China[J]. J Microbiol Immunol Infect, 2022, 55: 282-290. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmii.2021.03.011
[19] Gharaghani M, Seifi Z, Zarei Mahmoudabadi A. Otomycosis in Iran: A Review[J]. Mycopathologia, 2015, 179: 415-424. DOI: 10.1007/s11046-015-9864-7
[20] Lin Y, Zhang J, Han X, et al. A retrospective study of the spectrum of fungal keratitis in southeastern China[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10: 9480-9487. DOI: 10.21037/apm-21-1949

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS


 下载:
下载: