Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Novel Opinion of The 6th World Symposium on Pulmonary Hypertension
-
摘要: 2018年2月28日至3月1日在法国尼斯举办了第六次世界肺高血压大会。第十一工作组(Task Force 11)对近5年慢性血栓栓塞性肺高血压(chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, CTEPH)在定义、分类、病理机制、流行病学、诊断和治疗方面的更新进行了总结,并提出了慢性血栓性疾病的新定义及其与CTEPH的区别。CTEPH的诊疗需要多学科综合评估,随着肺动脉球囊成形术的不断改进,其疗效和安全性明显改善,目前已成为CTEPH的重要治疗方式之一,但其与药物治疗的对比研究尚在进行中,联合治疗疗效仍需长期随访。
-
关键词:
- 慢性血栓栓塞性肺高血压 /
- 慢性血栓性疾病 /
- 肺动脉球囊成形术 /
- 药物治疗 /
- 联合治疗
Abstract: The 6th World Symposium on Pulmonary Hypertension was held in Nice between February 28 and March 1, 2018. The major progress in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) in the past 5 years was reviewed by the experts of Task Force 11. The definition, classification, pathologic mechanisms, epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment were updated based on available evidence. Chronic thromboembolic disease (CTED) was defined and the difference between CTED and CTEPH was summarized. All CTEPH patients should be evaluated by a multidisciplinary team. Balloon pulmonary angioplasty (BPA), with improved efficacy and safety, plays an important role in CTEPH therapy. An ongoing study investigates patients with CTEPH who are not eligible for pulmonary endarterectomy and are randomized into medicine therapy or balloon pulmonary angioplasty (BPA), and compares the effects of the two therapies. The combination therapy for CTEPH needs the evidence of a long-term follow-up. -
糖尿病视网膜病变(diabetic retinopathy, DR)是2型糖尿病高度特异性的微血管并发症,约发生于30%的2型糖尿病患者,脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2(lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, LP-PLA2)是一种新型的动脉粥样硬化炎性标志物,与血脂水平有关[1],而25-羟维生素D[25-hydroxy vitamin D, 25(OH)D]与糖尿病的发生发展[2-5]及糖尿病血管并发症均有密切关系[6]。本文通过对2型糖尿病患者的分组研究,旨在探讨25(OH)D、LP-PLA2与DR的相关性。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
回顾性分析2014年5月至2017年1月沧州市中心医院内分泌科住院治疗的2型糖尿病患者临床资料。
纳入标准:(1)年龄≥18周岁;(2)符合美国糖尿病学会2013年修订的2型糖尿病诊断标准[7]:即空腹血糖(fasting plasma glucose, FPG) ≥7.0 mmol/L和(或)餐后2 h血糖≥11.1 mmol/L和(或)已确诊2型糖尿病并接受治疗者;(3)接受彩色眼底照相检查:使用免散瞳方法对眼底摄片。
排除标准:(1)1型糖尿病;(2)妊娠糖尿病;(3)合并严重心肝肾等脏器疾病;(4)急慢性感染性疾病;(5)糖尿病急性并发症;(6)风湿免疫性疾病;(7)恶性肿瘤;(8)其他眼部疾病;(9)近半年内服用过维生素D及影响骨代谢的药物。
选取本院同期进行体检的健康人作为对照组。
1.2 糖尿病视网膜病变程度及分组
由同一名眼科医生读取所有入选患者的眼底摄片,诊断标准参考2002年悉尼国际眼科学会制定的糖尿病性视网膜病变及糖尿病性黄斑水肿临床分级标准[8]。按照病情严重程度,将患者分为糖尿病不伴视网膜病变(no DR, NDR)组,背景期糖尿病伴视网膜病变(background DR, BDR)组,增殖期糖尿病伴视网膜病变(proliferative DR, PDR)组。
1.3 收集临床资料
收集并记录患者性别、年龄、病程、体质量指数(body mass index,BMI)、血压等一般临床资料;血总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、甘油三酯(triglyceride,TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)、FPG、糖化血红蛋白A1c(glycated hemoglobin A1c, HbA1c)、糖化白蛋白(glycated albumin, GA)、血清胱抑素C(serum cystatin C, Cys-C)、LP-PLA2、25(OH)D等血清学指标。TC、TG采用酶联免疫法检测(上海一研生物科技有限公司),HDL-C、LDL-C采用直接法检测(长春汇力生物技术有限公司),FPG采用葡萄糖氧化酶法检测(厦门海菲生物技术有限公司),HbA1c采用酶法检测[积水医疗科技(中国)有限公司],GA采用比色法检测(上海杰美基因医药科技有限公司),Cys-C采用增强免疫比浊法检测(武汉博迈特生物科技有限公司),LP-PLA2试剂盒采用双抗体夹心酶联免疫法(天津康尔克生物技术有限公司),25(OH)D采用电化学发光法(罗氏诊断产品上海有限公司)。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计学分析,计量资料采用均数±标准差表示,组间比较采用单因素方差分析和SNK-q检验,相关性采用Pearson相关分析与多元Logistic回归分析。P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般临床资料
共340例符合纳入和排除标准的2型糖尿病患者入选本研究,其中NDR组125例、BDR组118例、PDR组97例,健康对照组100例。4组患者性别、年龄、BMI、血压等一般资料比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),基线水平均衡可比;随着病情加重,NDR组、BDR组、PDR组的病程逐渐增长(P=0.003)(表 1)。
表 1 2型糖尿病视网膜病变患者与健康对照组一般临床资料比较指标 2型糖尿病视网膜病变患者 健康对照组(n=100) F值 P值 NDR组(n=125) BDR组(n=118) PDR组(n=97) 性别(男/女, n) 64/61 61/57 50/47 52/48 - - 年龄(x±s,岁) 56.8±5.4 57.3±6.2 57.8±5.8 58.1±6.5 1.564 0.353 病程(x±s,年) 2.9±1.1 7.1±1.7 9.2±2.4 - 16.112 0.003 BMI(x±s,kg/m2) 25.1±2.4 24.6±1.9 25.5±2.1 24.3±1.8 1.587 0.265 收缩压(x±s,mm Hg) 129.7±10.5 134.2±11.5 136.5±12.4 112.4±9.5 1.064 0.564 舒张压(x±s,mm Hg) 82.5±8.1 81.4±8.6 80.8±7.9 66.9±5.8 1.065 0.561 NDR:糖尿病不伴视网膜病变;BDR:背景期糖尿病伴视网膜病变;PDR:增殖期糖尿病伴视网膜病变;BMI:体质量指数 2.2 血清学指标
4组间的TC、TG、LDL-C、HDL-C、FPG差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05);NDR组、BDR组、PDR组HbA1c、GA、Cys-C、LP-PLA2、均显著高于健康对照组,25(OH)D显著低于对照组(P均<0.05);NDR、BDR、PDR组间两两比较,HbA1c、GA、Cys-C、LP-PLA2、25(OH)D差异亦均具有统计学意义(P均<0.05)(表 2)。
表 2 2型糖尿病视网膜病变患者与健康对照组血清学指标比较(x±s)指标 2型糖尿病视网膜病变患者 健康对照组(n=100) F值 P值 NDR组(n=125) BDR组(n=118) PDR组(n=97) TC(mmol/L) 4.92±1.03 4.99±1.08 5.13±1.14 3.86±0.45 1.045 0.620 TG(mmol/L) 1.81±0.76 1.75±0.72 1.88±0.84 1.13±0.15 1.024 0.625 LDL-C(mmol/L) 2.53±1.02 2.65±1.01 2.58±1.04 2.16±0.83 1.031 0.624 HDL-C(mmol/L) 1.46±0.65 1.38±0.57 1.33±0.61 1.75±0.79 1.611 0.264 FPG(mmol/L) 7.69±1.57 8.25±1.84 8.81±1.92 4.91±1.35 1.455 0.356 HbA1c(%) 7.2±1.8*# 8.6±2.1*# 10.4±2.5*# 5.3±1.4 3.325 0.027 GA(%) 21.46±3.27*# 22.51±3.72*# 23.77±4.12*# 16.74±2.15 6.711 0.012 Cys-C(mg/L) 0.94±0.13*# 1.15±0.14*# 1.35±0.19*# 0.62±0.12 4.529 0.025 LP-PLA2(μg/L) 135.68±28.53*# 151.73±31.66*# 173.59±34.16*# 71.46±14.72 6.283 0.016 25(OH)D(nmol/L) 45.3±5.8*# 31.5±5.1*# 20.4±4.6*# 60.5±7.9 3.161 0.036 NDR、BDR、PDR:同表 1;TC:总胆固醇;TG:甘油三酯;LDL-C:低密度脂蛋白胆固醇;HDL-C:高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;FPG:空腹血糖;HbA1c:糖化血红蛋白A1c;GA:糖化白蛋白;Cys-C:血清胱抑素C;LP-PLA2:脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2;25(OH)D:25-羟维生素D;*与健康对照组相比,P均<0.05;#NDR、BDR、PDR组间两两比较,P均<0.05 2.3 糖尿病视网膜病变的相关性分析
Pearson相关分析显示,糖尿病病程(r=0.391)、HbA1c(r=0.272)、GA(r=0.121)、Cys-C(r=0.248)及LP-PLA2(r=0.326)与DR呈正相关(P均=0.000),25(OH)D与DR呈负相关(r=-0.371,P=0.000)。
2.4 糖尿病视网膜病变的危险因素分析
多元Logistic回归分析显示,糖尿病病程、HbA1c、Cys-C、LP-PLA2及25(OH)D均与DR的发展有关,糖尿病病程、HbA1c、Cys-C、LP-PLA2是DR发病的独立危险因素,25(OH)D是DR的保护因素(P均<0.05)(表 3)。
表 3 糖尿病视网膜病变的危险因素分析危险因素 β值 SE值 Wald值 P值 OR值 95%CI 病程 1.713 0.562 9.514 0.000 6.093 1.763~18.253 HbA1c 1.802 0.571 9.565 0.000 6.184 1.865~18.731 GA 0.473 0.588 0.672 0.359 1.593 0.562~4.775 Cys-C 2.316 0.675 8.641 0.001 5.972 1.305~10.741 LP-PLA2 0.374 0.104 7.583 0.008 1.725 1.157~3.026 25(OH)D -0.601 0.142 16.248 0.000 0.129 0.031~0.391 HbA1c、GA、Cys-C、LP-PLA2、25(OH)D:同表 2 3. 讨论
DR是一种特异性的眼底病变,是临床糖尿病较为常见的慢性微血管并发症,其主要特点为微血管受损、微循环障碍。DR属于较为严重的疾病,对视力有严重伤害,甚至会引起失明,严重影响患者的生活质量[9-10]。DR发生发展的危险因素包括糖尿病病程、高血糖、高血压、高血脂等,但对于维生素D、LP-PLA2与DR的相关性研究较少。本研究结果显示,DR患者血清25(OH)D显著低于健康对照组,而LP-PLA2则显著高于健康对照组;进一步相关性分析显示,血清25(OH)D与DR呈负相关,而LP-PLA2与DR呈正相关。
维生素D是脂溶性类固醇衍生物,其主要功能是调节机体钙磷代谢,还可参与机体免疫调节和炎症防御[11]。1, 25-羟基维生素D [1, 25-(OH)2-D]虽是维生素D的活性形式,但其半衰期较短,不适合作为反映机体维生素D水平的指标[12],而25(OH)D亦是维生素D在机体内代谢产生的活性物质,是维生素D在血液循环中的主要形式,可与维生素D受体结合,从而发挥生理活性。其可有效反映内源及外源性维生素D总水平,在机体中水平稳定,且易于检测,因此可作为评价维生素D状态的有效指标。多项研究表明,25(OH)D与DR的发生发展及严重程度均有密切关系[13-14]。25(OH)D具有较强的抗氧化能力,可减少自由基、保护细胞膜,还可直接抑制机体炎性反应,减少白细胞介素-2、肿瘤坏死因子等炎症因子的分泌。若25(OH)D水平下降,对机体免疫功能的调控作用就会减弱,进而导致视网膜血管增殖,引发免疫反应,产生大量炎症因子,最终导致DR的进展[15]。本研究结果显示,BDR组、PDR组的25(OH)D水平显著低于NDR组(P<0.05);PDR组的25(OH)D水平显著低于BDR组(P<0.05),说明随着DR病情严重程度的加剧,25(OH)D水平不断下降。本研究Pearson相关性分析显示,25(OH)D与DR呈负相关(P<0.05)。多元Logistic回归分析证实,25(OH)D是DR的保护因素(P<0.05)。
LP-PLA2是磷酸酯酶PLA2超家族成员之一,具有水解血小板活化因子的作用。LP-PLA2主要由巨噬细胞、淋巴细胞分泌,可引起由单核巨噬细胞参与的慢性炎症反应。研究表明,LP-PLA2可促进动脉粥样硬化的发生发展,且与血脂水平密切相关,尤其与LDL-C水平的相关性最强[16]。LP-PLA2引发的慢性炎症反应及脂质代谢紊乱共同诱发了动脉粥样硬化。LP-PLA2可促进低密度脂蛋白的氧化代谢,生成溶血磷脂胆碱和氧化型游离脂肪酸,促使血管内皮细胞功能障碍,引发局部炎症反应,形成新的动脉粥样斑块[17]。DR与动脉粥样硬化的终点事件有相关性,两者具有类似的病理学病变,即均出现炎症反应、内皮功能异常、新生血管生成、细胞凋亡及高凝状态[18]。LP-PLA2是动脉粥样硬化的独立危险因素,而DR的发生与动脉粥样硬化关系密切,因此可以推断LP-PLA2与DR有关[19]。本研究结果中,BDR组、PDR组的LP-PLA2水平显著高于NDR组(P<0.05);PDR组的LP-PLA2水平显著高于BDR组(P<0.05),说明随着病情严重程度的加剧,LP-PLA2水平不断上升。Pearson相关性分析显示,LP-PLA2与DR呈正相关(P<0.01)。多元Logistic回归分析,LP-PLA2是DR的独立危险因素(P<0.05)。
综上,25(OH)D、LP-PLA2水平变化与DR的发生、发展有密切关系,25(OH)D是其保护因素,LP-PLA2是其危险因素。但本研究属于回顾性研究, 今后尚需大样本的前瞻性研究和随机对照研究进一步证实。
利益冲突 无 -
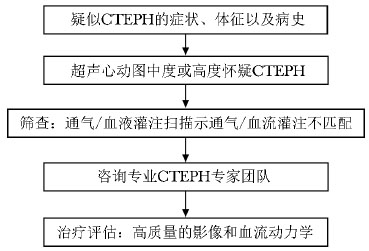
图 1 CTEPH多学科合作诊断流程
CTEPH:同表 1
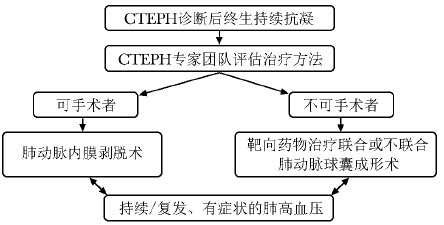
图 4 慢性血栓栓塞性肺高血压治疗流程
CTEPH:同表 1
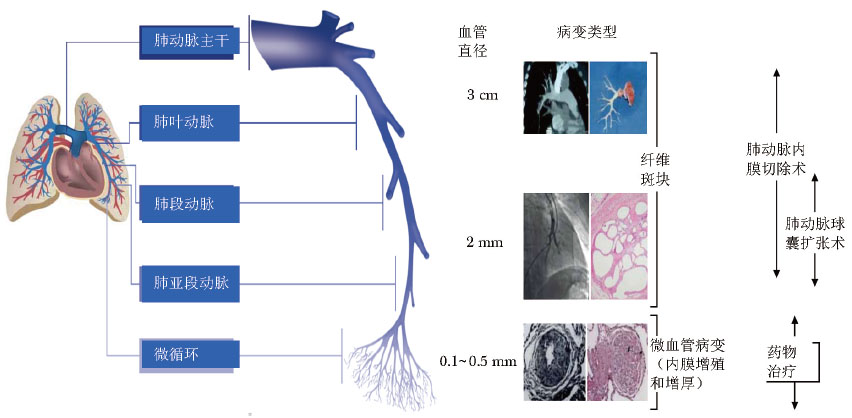
表 1 除CTEPH外的其他肺动脉阻塞性疾病分类
欧洲心脏协会/欧洲呼吸协会(2015) 第六次世界肺高血压大会(2018) 4.2.1 血管肉瘤 4.2.1 肉瘤(高度或中度)或者血管肉瘤 4.2.2 其他血管内肿瘤 4.2.2 其他恶性肿瘤 肾癌 子宫肿瘤 生殖细胞肿瘤 其他肿瘤 4.2.3 动脉炎 4.2.3 非恶性肿瘤 子宫肌瘤 4.2.4 先天性肺动脉狭窄 4.2.4 非结缔组织病的动脉炎 4.2.5 寄生虫(包虫病) 4.2.5 先天性肺动脉狭窄 4.2.6 寄生虫 包虫病 CTEPH:慢性血栓栓塞性肺高血压 表 2 CTEPH与CTED诊断比较
特点 CTEPH CTED ·症状 运动时呼吸困难 运动时呼吸困难 ·右心导管 mPAP≥25 mm Hg, PAWP≤15 mm Hg mPAP<25 mm Hg(通常为21~24 mm Hg), PAWP≤15 mm Hg ·运动右心导管 - PQ斜率>3 mm Hg/(L·min) ·通气/血流灌注扫描 通气/血流灌注不匹配 通气/血流灌注不匹配 ·血管造影 CTEPH的典型发现 CTEPH的典型发现 ·心肺功能运动试验 - 排除通气限制、缺少运动 ·经胸超声心动图 - 排除左心室心肌及瓣膜疾病 ·抗凝作用 至少3个月 至少3个月 mPAP:平均肺动脉压;PAWP:肺动脉楔压;CTED:慢性血栓栓塞性疾病;CTEPH:同表 1 表 3 肺动脉血栓内膜剥脱术手术获益与风险分析
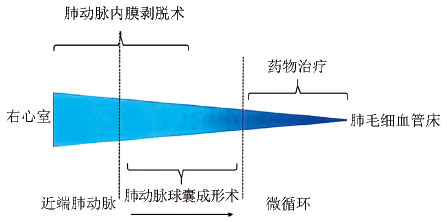
特点 低风险,可预测远期预后 高风险,不可预测远期预后 既往史 既往有深静脉血栓形成或肺栓塞 既往无深静脉血栓形成或肺栓塞 检查 无右心衰竭体征 有右心衰竭体征 伴随疾病 无 合并明确的肺部或左心疾病 心功能 心功能Ⅱ~Ⅲ级 心功能Ⅳ级 影像学 影像学表现与病变表现一致 影像学表现与病变表现不一致 疾病类型 双侧下叶病变 病变不位于下叶 血液动力学 PVR<12.5 WU, 与影像学上闭塞的部位和数量成比例,肺动脉压高 PVR>15 WU, 与影像学上闭塞的部位和数量不成比例, 肺动脉舒张压高 PVR:肺血管阻力 -
[1] Quarck R, Wynants M, Verbeken E, et al. Contribution of inflammation and impaired angiogenesis to the pathobiology ofchronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension[J]. Eur Respir J, 2015, 46:431-443. DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00009914
[2] Konstantinides SV, Vicaut E, Danays T, et al. Impact of Thrombolytic Therapy on the Long-Term Outcome of Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2017, 69:1536-1544. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=bdea978a70672ee25695ca711b3ce4dc
[3] Ende-Verhaar YM, Cannegieter SC, Vonk Noordegraaf A, et al. Incidence of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after acute pulmonary embolism: a contemporary view of the published literature[J]. Eur Respir J, 2017, 49:1601792. https://core.ac.uk/display/153431350
[4] Gopalan D, Blanchard D, Auger WR.Diagnostic Evaluation of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension[J]. Ann Am Thorac Soc, 2016, 13:S222-S239. DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201509-623AS
[5] Delcroix M, Lang I, Pepke-Zaba J, et al. Long-Term Outcome of Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Results from an International Prospective Registry[J]. Circulation, 2016, 133:859-871. DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016522
[6] Wiedenroth CB, Olsson KM, Guth S, et al. Balloon pulmonary angioplasty for inoperable patients with chronic thromboembolic disease[J]. Pulm Circ, 2018, 8:2045893217753122. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25869123
[7] Aoki T, Sugimura K, Tatebe S, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of balloon pulmonary angioplasty for inoperable chronic thrombo-embolic pulmonary hypertension: long-term effects and procedure-related complications[J]. Eur Heart J, 2017, 38:3152-3159. DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx530
[8] Hosokawa K, Abe K, Oi K, et al. Balloon pulmonary angioplasty-related complications and therapeutic strategy in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2015, 197:224-226. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.06.075
[9] Simonneau G, D'Armini AM, Ghofrani HA, et al. Riociguat for the treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a long-term extension study (CHEST-2)[J]. Eur Respir J, 2015, 45:1293-1302. DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00087114
[10] Ghofrani HA, D'Armini AM, Grimminger F, et al. Study Group. Riociguat for the treatment of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension[J]. N Engl J Med, 2013, 369:319-329. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1209657
[11] Ghofrani HA, Simonneau G, D'Armini AM, et al. MERIT study investigators.Macitentan for the treatment of inoperable chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (MERIT-1): results from the multicentre, phase 2, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2017, 5:785-794. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30305-3
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 桑丹卓嘎,郑松柏. 维生素D与老年疾病. 国际老年医学杂志. 2023(01): 82-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张雪姣,田华伟,孙子辉,余帆. 高血压患者视网膜病变与血清脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A_2的相关性研究. 中国社区医师. 2023(16): 89-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 苏志燕,刘薇,史婷婷,杨金奎. 无骨质疏松的男性2型糖尿病患者视网膜病变与25羟维生素D的关系. 临床内科杂志. 2022(02): 101-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 薛敏. 羟苯磺酸钙联合利拉鲁肽治疗糖尿病性视网膜病变的临床效果. 糖尿病新世界. 2022(05): 168-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 郑德莎,肖婷,陈玉,邵佩,画妍,苏向妮,尼春萍. 血清胱抑素C水平与糖尿病视网膜病变相关性的Meta分析. 国际检验医学杂志. 2021(01): 42-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张伟亚,卢宇,张佳思,何姣姣. 血浆Lp-PLA2与2型糖尿病视网膜病变的相关性分析. 糖尿病新世界. 2020(18): 146-147+150 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 侯益轩,吴丽萍,刘燕萍. 糖化白蛋白在妊娠期糖尿病监测中的研究进展. 协和医学杂志. 2019(06): 660-665 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 万芳. 血清25-羟维生素D3与老年糖尿病患者颈动脉内膜中层厚度的关系. 中国老年学杂志. 2019(23): 5677-5679 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 毛维维,董萍. 血清25-羟维生素D3、脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2与早期糖尿病肾病的相关性研究. 临床荟萃. 2019(10): 911-914 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: