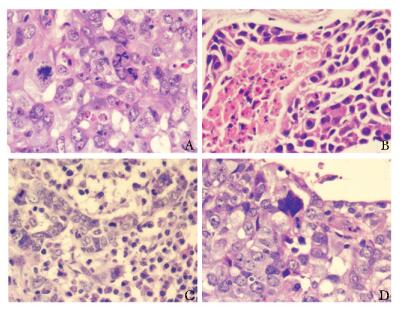
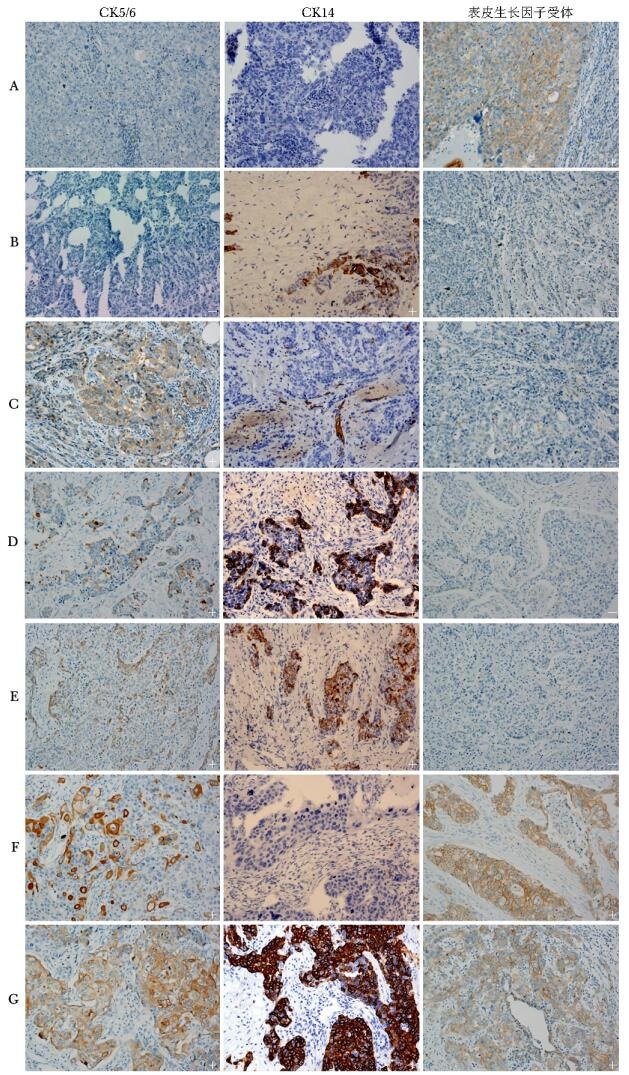
Combined Detection of CK5/6, CK14 and EGFR in Diagnosis of Basal-like Subtype Triple Negative Breast Cancer
-
摘要:目的 探讨联合检测CK5/6、CK14和表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR)对基底样三阴乳腺癌的诊断价值。方法 北京协和医院2000年1月至2011年12月经组织病理学证实的115例三阴乳腺癌患者, 收集其临床及病理资料。应用免疫组织化学法检测所有石蜡标本中CK5/6, CK14和EGFR的表达, 以此判定是否为基底样三阴乳腺癌。以三者联合检测结果作为金标准, 计算CK5/6, CK14和EGFR单独检测、两两联合检测的敏感性和特异性。进一步分析基底样三阴乳腺癌和非基底样三阴乳腺癌在年龄、肿瘤大小、组织学类型等临床及病理特征方面的差异。结果 115例三阴乳腺癌患者平均患病年龄为(50.7±13.6)岁。免疫组织化学结果显示, 单独检测CK5/6, 基底样三阴乳腺癌阳性率为29.6%(34/115), CK14为21.7%(18/83), EGFR为60.9%(70/115)。CK14, CK5/6和EGFR三者联合检测阳性率为67.8%(78/115)。将三者联合检测的阳性例数作为金标准, 则EGFR与CK5/6联合检测敏感性及特异性分别可达98.7%及100%。基底样三阴乳腺癌与非基底样三阴乳腺癌在组织学类型、分级, 淋巴结转移情况, 死亡率方面差异有统计学意义(P均 < 0.05), 基底样三阴乳腺癌总生存期显著缩短(HR=0.363, 95% CI:0.139~0.947)。结论 CK14、CK5/6和EGFR联合检测能够标识出最多数量的基底样三阴乳腺癌。基底样三阴乳腺癌预后比非基底样三阴乳腺癌预后更差, 病理识别很重要。
-
关键词:
- 三阴乳腺癌 /
- 基底样亚型 /
- CK5/6 /
- CK14 /
- 受体, 表皮生长因子
Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of combined detection of CK5/6, CK14 and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in diagnosing basal-like subtype triple negative breast cancer (TNBC).Methods The clinical and pathological data of 115 patients diagnosed with TNBC were recorded from January 2000 to December 2011. The expression of CK5/6, CK14 and EGFR were detected with immunohistochemical methods using paraffin specimens. Combined detection result of the three markers was used as gold standard, then the sensitivity and specificity of CK5/6, CK14 and EGFR were detected by single marker and two combined assays.The differences between basal-like and non basal-like subtype TNBC in age, tumor size, tumor histological type and other clinicopathological issues were compared.Results The mean age of 115 patients with TNBC was (50.7±13.6) years. Immunhistochemical result showed that single marker positivity was 29.6% (34/115), 21.7% (18/83), and 60.9% (70/115) for CK5/6, CK14, and EGFR, respectively. Combined detection of the three markers, the positive rate was 67.8% (78/115). Taking three markers combination as a golden standard, the sensitivity and specificity of EGFR and CK5/6 combination were 98.7% and 100%. There were significant differences between basal-like and non basal-like subtype TNBC in histological type, tumor grade, lymph node metastasis and mortality(all P < 0.05). Survival analysis showed that the overall survival period of basal-like subtype TNBC was significant shortened(HR=0.363, 95% CI:0.139~0.947).Conclusions Combined detection of CK5/6, CK14 and EGFR could identifiy the largest number of basal-like subtype TNBC. The prognosis of basal-like subtype TNBC is worse than that of non basal-like subtype TNBC, and it is important to identify the subtype.-
Keywords:
- triple-negative breast cancer /
- basal-like subtype /
- CK5/6 /
- CK14 /
- epidermal growth factor receptor
-
肝移植于1963年首次实施,至今仍是治疗终末期肝病最有效的方法,但患者术后常面临并发症高发、住院时间长、费用高等问题[1]。加速术后康复(enhanced recovery after surgery, ERAS)旨在优化围术期管理以最大限度减轻患者手术应激反应、减少术后并发症及住院时间[2]。越来越多的研究表明,ERAS融入肝移植围术期管理可改善上述问题,并强调了开发完整、国际公认、标准化肝移植ERAS管理方案的重要性[3]。我国学者曾发布《中国肝移植围手术期加速康复管理专家共识(2018版)》[4](下文简称“2018共识”),但未有证据质量和推荐意见分级,且多数证据发表时间较久远,未作进一步更新,而国内最新的ERAS临床实践指南(2021)[5]肝胆手术部分未包括肝移植术。近期,国际肝移植学会(International Liver Transplantation Society, ILTS)发布的首个基于循证医学证据的《肝移植手术加速康复共识建议》[6]具有重要意义,包括接受死亡后器官捐献和活体器官捐献的肝移植受者及活体肝移植供者术前评估和优化、术中监测及术后管理等内容。本文对该共识要点进行详细解读,以期为我国肝移植手术ERAS实践提供参考。
1. 共识制定概况
工作组遴选来自30个国家共273名肝移植领域的知名专家组成国际科学小组,研究32个肝移植ERAS相关的科学问题。先注册研究方案、完成系统文献综述,再采用GRADE系统将证据质量分为高(A)、中(B)、低(C)和极低(D)4个等级,并作出强推荐或弱推荐[7]。此外,本共识采用丹麦共识模式[8]制定,允许非专家团队的学者对意见协商过程提出建议,以减少制定过程中的专家偏倚,最终形成80条建议,推荐强度大多为强推荐。
2. 接受死亡后器官捐献的肝移植受者ERAS建议
此部分主要从术前评估与预康复、术中监测与管理、术后并发症预防三方面给予指导,强调应采取一切措施降低肝移植术后短期并发症的发生率。
2.1 术前准备
2.1.1 风险分层评估
多数罹患终末期肝病并接受肝移植的患者身体机能较差,存在营养不良、肌少症和虚弱等问题[9]。为提高受者对ERAS方案的耐受性,不同于2018共识建议设立严格纳入标准,本共识建议术前根据临床资源可及性,在Karnofsky功能状态评分、肝脏衰弱指数、腹部肌肉质量CT测量值和心肺运动测试4种评估工具中选择合适的工具来判断其是否实施ERAS方案,并纳入ERAS常规术前评估(B级证据,强推荐)。
Karnofsky功能状态评分可在所有环境下使用,但易受主观因素影响;肝脏衰弱指数是一种基于功能表现的衰弱评价指标,主要用于非卧床患者;腹部肌肉质量CT测量值常用于住院患者,可提供有关生理储备的信息;心肺运动测试可准确评估心肺健康,但对专业设备和人员有一定要求且无法在急症患者中实施[10]。综上,建议我国患者结合2018共识中肝移植ERAS的纳入与排除标准,根据实际情况选择合适的工具以进行更深入的术前评估。
2.1.2 运动预康复
本共识建议受者在术前进行合理的功能锻炼(D级证据,强推荐),指出多模式预康复方案应以患者为中心且内容全面。我国学者发现,肝移植受者移植等待期在专业人员监督下每周进行3次、每次40~70 min中等强度运动是一个合理的目标[11],包括有氧训练和抗阻训练等,但运动预康复的标准化指导方案仍需进一步循证支持。
2.1.3 营养干预
肝移植受者常伴有不同程度的营养不良,其营养状态是影响术后并发症发生率和死亡率的危险因素[12],本共识建议受者在术前优化营养状况(C级证据,强推荐)。基于我国人群体质特点,营养干预措施可参考国内《肝移植围手术期营养支持专家共识(2021版)》[13]。首先,使用评估工具联合人体测量参数等方法,动态筛查营养风险和评估营养不良程度。其次,营养支持途径首选口服,根据患者营养需求情况,考虑口服营养补充、经鼻胃管或空肠置管给予肠内营养以及联合肠外营养。患者应避免长期禁食,可少量多餐并夜间加餐。通常术前6 h禁食固态食物,术前2 h可饮用不超过400 mL含12.5%碳水化合物的清亮饮料,以防止不必要的饥饿和胃肠道应激。
2.1.4 心理干预
肝移植受者术前常出现焦虑、恐惧等心理,这与其对手术方式认知不足及缺乏社会支持有关,尤其是移植前抑郁、药物滥用、吸烟酗酒和依从性差易导致预后不良[14]。本共识建议术前对患者进行心理社会评估,并强调重点评估治疗依从性。此外,提供个性化干预有利于手术成功(C~D级证据,强推荐)。个体化宣教和护理访视是我国临床常采取的形式[4],对于解除患者及家属疑虑,获得其配合尤为重要。
2.2 术中措施
2.2.1 供肝准备
边缘供体如心脏死亡器官捐献(donation after cardiac death, DCD)或60岁以上捐赠者器官,在死亡后器官肝脏捐献供体中占重要比例。可通过器官灌注技术减轻器官获取、保存和再灌注过程中的损伤,并在使用前评估器官功能,从而降低移植相关风险[15]。现有证据表明,低温和常温机械灌注较静态冷保存,更利于预防再灌注后综合征和早期移植物功能障碍(early allograft dysfunction, EAD),缩短住院时间。因此,共识建议若医疗机构具备低温机械灌注基础应考虑使用边缘供肝(B级证据,强推荐),具备常温机械灌注技术应考虑脑死亡与心死亡供肝,具备常温局部灌注技术且符合当地管理条例的情况下,应根据可用性考虑所有DCD供肝(B~C级证据,弱推荐)。各移植中心应根据现有设备考虑可使用的供肝。
2.2.2 术中监测
本共识基于各种方式对重症监护时间、住院时间、并发症和EAD发生率的影响情况,提出了相关建议。首先,麻醉方式建议使用挥发性麻醉而非全静脉麻醉(D级证据,弱推荐),我国相关共识[16]则推荐选用静吸复合全身麻醉,且避免采用挥发性麻醉[17],因其可能导致受者术后早期出现恶心呕吐。尽管本共识推荐预防性使用止吐药(C级证据,弱推荐),但最佳麻醉方式仍有待进一步探究。
其次,本共识对麻醉监测措施提出了系统指导:可通过最低肺泡有效浓度与脑电图监测麻醉深度,常规使用有创动脉血压和中心静脉压行麻醉生命体征监测,肺动脉导管或经食管超声心动图亦可用于监测。中心静脉导管置管时常规使用超声引导,并选择颈内静脉等中心静脉(C~D级证据,强推荐)。对于血流动力学明显不稳定的患者,应考虑其外周血压和中心动脉血压监测值之间存在潜在差异(D级证据,弱推荐)。
此外,应注意维持术中正常体温。对于呼吸管理,本共识与国内共识意见[16]一致,采取避免过高吸氧浓度造成的肺泡萎陷、小潮气量通气和合适的呼气末正压通气策略(D级证据,强推荐),重点在于实施肺保护通气策略。
2.2.3 手术方式
关于供受体之间下腔静脉的重建一直存在争议。研究显示,与原位肝移植相比,背驮式肝移植手术时间和输血需求均减少,但二者术后早期并发症发生率、死亡率和住院时间相近[18],术中使用静脉转流结果亦类似,因此本共识未对腔静脉重建方式作具体推荐,但强调不常规使用静脉流转和临时门腔静脉分流术(D级证据,强推荐)。手术方式不存在孰优孰劣,应根据移植医师擅长的术式、移植中心配套设备、供肝情况、受者原发病和相应解剖情况选择最佳移植术式。
2.2.4 管路管理
受者是否常规置入T管和腹腔引流管尚存争议,虽然置入T管可减少胆管狭窄发生率,但因放置后胆道并发症发生趋势上升[19],故不常规放置T管(C级证据,强推荐)。基于患者安全考虑,高危人群可选择性置管。因缺乏证据,本共识未明确建议是否置入腹腔引流管。此外,尽管肝移植领域暂无专门关于腹腔引流管、中心静脉导管、导尿管或鼻胃管拔除时间的研究[20],但基于现有证据,本共识仍建议大多数患者应早期拔管(B级证据,强推荐),若术中放置腹腔引流管,应根据其引流液的量和性质,于术后第5天拔除(C级证据,强推荐)。若鼻胃管影响患者通气,术后第1天即可拔除;一旦患者无需循环支持,即可拔除中心静脉导管;一旦患者能活动,即可拔除导尿管(D级证据,强推荐)。综上,应依据患者的情况决定是否置管,并树立早期拔管理念。
2.2.5 输血和凝血监测
合并终末期肝病的肝移植受者常伴有凝血功能障碍,增加术中出血等并发症,肝缺血再灌注损伤将加重并发症情况。目前暂无最佳的血液制品替代策略或标准化输血方案[21],但本共识与2018共识均认为应减少输血,且推荐自体血液回收技术。不建议常规使用抗纤溶药物(C级证据,弱推荐),因其对输血率、受者及移植物预后或血栓形成无效。在指标监测方面,本共识推荐黏弹性测试(C级证据,强推荐)。我国凝血功能管理专家共识[22]亦提出黏弹性测试更适合移植术中凝血功能的监测与管理,同时术中注意既要防止出血倾向,又要避免对低凝状态过度纠正。
2.2.6 液体管理
本共识提出最佳策略是采用适当限制或替代液体疗法,特别是病肝切除阶段,同时避免无液体反应性、充盈压力升高和持续高血容量的情况(B级证据,强推荐),强调所有受者平均动脉压应高于60~65 mm Hg (1 mm Hg=0.133 kPa)(C级证据,强推荐)。此部分重点在于适当补液,避免液体过负荷,给予血管活性药物维持血液动力学稳定,并根据血容量的动态监测情况进行个性化液体治疗以达到最佳效果[16]。此外,本共识不建议使用130/0.4羟乙基淀粉,因其与受者肾功能衰竭和急性肾损伤的高发生率相关(C级证据,弱推荐),优先使用的特定胶体或晶体溶液有待深入探索。目前关于容量管理对肝移植预后影响的探索性研究较少,需进一步明确液体管理策略,以优化循环血量和局部微循环灌注,降低并发症的发生风险。
2.2.7 镇痛管理
充分和最佳的疼痛管理对促进受者及早苏醒和早期成功拔管至关重要。目前临床常采用多模式镇痛,包括阿片类、非阿片类镇痛药、胸段硬膜外镇痛和腹横肌平面阻滞等方式[4]。研究显示术中避免使用阿片类药物可缩短拔管及重症监护时间,降低术后疼痛评分和恶心呕吐风险[23],因此术中避免使用阿片类药物,扑热息痛、加巴喷丁、氯胺酮、曲马多和局部麻醉等药物可代替或辅助阿片类药物用于镇痛(B级证据,弱推荐)。需注意的是,此时使用加巴喷丁应警惕患者呼吸抑制风险,特别是老年患者[17]。此外,尽管本共识提供更多镇痛药物的选择,但终末期肝病患者病情复杂,常伴有药代动力学改变,应注意用药适应证、禁忌证与剂量的把控,并及时行镇痛后评估。
本共识还建议腹横肌平面阻滞和伤口局部浸润作为保留阿片类药物镇痛管理模式的一部分(D级证据,弱推荐),虽然目前研究相对较少,降低了证据质量,但为进一步探索多模式镇痛管理方法奠定了基础。
2.3 术后措施
2.3.1 预防血栓
本共识强调若发现受者有肝动脉和门静脉血栓形成风险,应高度重视血栓预防,并对不同部位血栓预防提出建议。首先,非高危患者不建议常规使用治疗或预防剂量药物预防新生门静脉血栓(B级证据,弱推荐),但缺乏实质性数据支持,我国亦少有研究关注非高危患者的血栓预防。其次,推荐使用阿司匹林预防肝动脉血栓,因其无论剂量多少,均能显著降低肝动脉血栓发生率且不增加出血风险。最后,建议术后早期慎用预防性剂量的肝素预防深静脉血栓或肺栓塞(均为B级证据,强推荐),这与2018共识存在意见分歧。可见,预防性使用肝素来预防深静脉血栓的可行性和安全性仍需进一步研究明确。需注意,多数研究中的抗凝药物是用于具有血栓预防特定指征的受者[24],因此仍需关注受者凝血或血流量等指标,及早采取预防措施。
2.3.2 预防感染
终末期肝病患者术后细菌、真菌和病毒感染的风险增加,包括多重耐药细菌和免疫抑制引起的机会性感染。本共识倡导提前预防,建议术后对所有受者个体化使用抗生素以预防细菌感染,使用持续时间一般不超过24 h(C级证据,弱推荐),应探究适合我国受者抗生素预防的最佳持续时间。侵袭性真菌感染风险高的受者应进行抗真菌预防治疗,药物选择取决于医院诊疗模式(A级证据,强推荐)。巨细胞病毒是肝移植受者最常见的病毒感染,可导致移植物排斥反应、胆道或血管并发症[25],建议采取普遍预防或抢先治疗,策略的选择取决于医疗资源以及供体和受体的病毒抗体血清状态(C级证据,强推荐)。此外,国内专家强调应预先隔离,从筛查和隔离两方面进行多重耐药菌防控[26]。
2.3.3 康复治疗
本共识指出受者术后进行康复治疗可改善机体功能(C级证据,强推荐)。目前肝移植受者术后早期入住ICU,情况平稳后转回普通病房,这两个阶段均可根据受者的意识状态、肌力等级、配合能力制订分级活动计划[27],总原则是尽早安全地开展康复锻炼,需与镇痛管理、营养支持、早期拔管等ERAS措施配合。
2.3.4 最佳免疫抑制策略
肝移植术后免疫抑制治疗尚无统一标准,但有必要在预防急性细胞排斥反应和最小药物副作用之间探索最佳免疫抑制策略[28]。本共识特别指出他克莫司在免疫抑制中的作用,建议其作为术后标准免疫抑制剂,可与皮质类固醇、霉酚酸酯和抗IL-2受体抗体诱导剂联合使用,既不会增加感染,且低剂量或延迟使用钙调蛋白类抑制剂可降低急性肾损伤发生率(C级证据,强推荐)。对此国内外专家意见较一致,应密切监测受者的生命体征和肝功能,正确评估其免疫状态,针对性地制订免疫抑制策略,并尽可能减少免疫抑制剂的种类和剂量。免疫抑制个体化治疗是目前肝移植术后维持移植物功能平稳的难点和努力方向[29]。
2.3.5 识别EAD
EAD是移植物存活率较差的重要危险因素和受者发生并发症、死亡的重要原因,应早识别、早干预。研究发现,术中或术后乳酸水平立即升高是EAD的重要标志,灵敏度高达86%,特异度高达83%。而其他标志物如V因子、总胆固醇、尿酸等预测能力较低,灵敏度或特异度差异较大[30]。因此,本共识更推荐将乳酸水平作为预测术后EAD的早期观察指标(B级证据,强推荐),但乳酸水平升高的界值需进一步明确。
2.3.6 出院指导
目前少有证据明确指出肝移植术后受者的最佳出院时间,故本共识仅给出一般性建议:在具备强有力的门诊随访支持及出院清单的指导下,受者可于术后8 d内安全出院(C级证据,弱推荐)。各移植中心可以8 d为参考,制订以患者安全为基础,可量化、可操作的出院标准[31]。由于肝移植手术特殊,有必要深入探索受者出院准备方案,加强院外随访,并建立明确的再入院“绿色通道”。
3. 活体肝移植供者ERAS建议
死亡后器官捐献供体稀缺导致对活体供肝依赖增加。活体肝移植供者作为健康个体,未从手术中获得健康益处,反而因手术创伤面临相关并发症,应密切关注其康复情况。本共识主要从术前评估、术中手术方式、出院准备三方面提出建议。
3.1 术前评估
3.1.1 供者评估
2016年ILTS活体肝移植指南[32]提到公认的捐献者年龄一般为18~60岁,但本共识认为高龄(60~69岁)人群亦可进行肝脏捐赠(C级证据,弱推荐),扩大了供者年龄范围,并强调所有候选供者应进行基本的生理检查(如麻醉评估、血液检测、超声心动图和胸部X线检查等),高风险的候选供者需进行更全面的检查,并考虑不同人群匹配概率(C级证据,强推荐)。本共识还关注到供者体质量指数(body mass index, BMI),但因研究中BMI对术后并发症的影响相互矛盾[33],故未作出具体阈值建议。此外,有必要为活体肝移植供者提供全面的术前宣教(B级证据,强推荐)。我国尤其关注活体肝移植的伦理问题,首要原则是保证供者安全,其次是自愿原则,应让供者知晓手术过程及风险,并主动签署知情同意书[34]。
3.1.2 供肝评估
术前必须评估供肝以明确其是否存在潜在慢性肝病,本共识就检测技术和供肝体积给出以下建议:(1) 初步检测肝脂肪变性宜采用影像学技术,首选MRI筛查,其灵敏度和预测价值较高(C级证据,强推荐)。(2)对影像学上怀疑有10%及以上肝脂肪变性的供者行经皮超声引导细针穿刺活检(C级证据,弱推荐),因为肝脂肪变性可影响肝脏再生能力,增加供者并发症[34],而肝活检是量化和明确肝脂肪变性以及检测其他肝病的唯一方法。(3) 移植物与受体重量比(graft to recipient weight ratio, GRWR)需大于0.8%。相较于2016年ILTS指南,本共识更精确地指出考虑脂肪变性、年龄和性别等因素,应为供者保留至少30%的残余肝体积以确保肝功能充足(C级证据,强推荐)。(4)活体肝移植需高度重视肝血管和胆道解剖结构,本共识推荐磁共振胰胆管造影和CT血管造影,不常规使用导管血管造影(C级证据,强推荐)。国内专家亦表示对于供肝评估,术前影像学评估是核心,尤以术中胆道造影及超声检查价值较高[34]。
3.2 术中手术方式与疼痛管理
同2016年ILTS指南意见一致,本共识建议优先考虑左肝切除术,因其与右肝切除术相比,供者总体并发症减少,住院时间缩短[35]。实施右侧供肝切除术可伴或不伴肝中静脉,两种手术结果相同(B级证据,弱推荐),这解决了一直以来关于右肝移植物是否包含肝中静脉的争议。由于可用证据较少,本共识未指出手术入路是微创或开放。随着手术技术和器械的发展,腹腔镜活体供肝切取术具有创伤小、供者恢复迅速、心理负担轻等优点,在我国展现出良好的应用前景[36],但手术团队需拥有丰富的腹腔镜肝切除和活体供肝切取经验。因此,各移植中心应根据实施的经验和专业程度决定手术方式。
本共识新增切口类型的建议,指出中线切口较肋下切口更有利于改善供者的自信评分及长期预后(C级证据,弱推荐)。此外,活体肝移植供者术中疼痛管理策略与受者一致,均应提供多模式镇痛策略,减少阿片类药物的使用(C级证据,强推荐)。
3.3 出院准备
为保障供者安全出院,本共识推荐设立出院检查清单,包含疼痛和饮食管理、拔除所有置管、预防深静脉血栓及常规影像检查(CT或肝脏超声)等,并强调监测肝功能(C级证据,强推荐),因供者右肝切除术后常发生短暂的肝功能受损(由胆红素升高和国际标准化比值定义),在术后第5天可呈恢复趋势。深静脉血栓预防方面,本共识不仅推荐应积极采取有关化学措施,更明确指出术后使用普通或低分子肝素预防血栓至少10 d(C级证据,弱推荐),因研究显示50%的供者术后10 d血液呈持续高凝状态[37]。国内同样倡导应积极预防深静脉血栓,对于预防策略、药物预防使用时间需进一步探索及对比。
此外,2016年ILTS指南建议供者出院后至少随访2年,密切监测肝功能和血小板计数至少1年,有条件者终身随访。目前国内关于活体肝移植供者的研究较少,有待建立并完善适合我国活体肝移植供者的出院检查清单及延续护理体系,以保障供者的出院安全。
4. 接受活体肝移植的受者ERAS建议
前文已有较全面的接受死亡后器官捐献的肝移植受者ERAS建议,此部分共识从术前危险因素评估和术中门静脉流量调节两方面给出建议。
首先,本共识强调重点评估受者的疾病情况和GRWR:(1)终末期肝病评分>25~30,合并一个或多个不良因素(肾功能不全和肌肉减少症)的患者,需进行多学科综合评估。同我国专家意见[38]一致,术前详细的检查与准备可有效降低术后并发症及死亡风险。(2)受者近期感染并非活体肝移植的禁忌,因其并不会增加术后死亡风险。但我国指南[38]指出难以控制的感染是绝对禁忌证,故需注意评估受者的感染程度。(3)GRWR≥0.8%符合ERAS要求(C级证据,强推荐)。研究显示,GRWR阈值在0.6%~0.8%之间可避免受者出现小肝综合征(small-for-size syndrome, SFSS)。本共识还提到GRWR<0.8%的供肝亦可使用,但对受者选择、医护人员手术技术与围术期管理能力要求更高[39]。
其次,术前和术中监测实际供肝重量、门静脉压力和血流量可综合评估供肝情况,发现潜在的小体积供肝。但本共识指出小体积供肝并非完全不可使用,门静脉压力和流量调节是手术成功的关键,具体措施包括各种药物干预(如特利加压素、生长抑素)和手术操作(如脾动脉结扎)以减少或部分转移门静脉流量,避免高灌注和SFSS(B级证据,强推荐)。药物调节可改善受者早期肾功能,使用脾动脉结扎而非脾切除术可避免受者过多损伤[40]。综上,需注意关注受者的疾病情况和GRWR,GRWR≥0.8%更有利于实施ERAS。对于小体积供肝,术中有效的门静脉流量调节是关键。
5. 小结与展望
本共识基于临床最新研究证据和丹麦共识模式制定,过程规范科学,涉及围术期评估、监测、干预等方面,广度和深度兼具,大多数建议为强推荐,对接受死亡后器官捐献或活体肝移植的受者,以及活体肝移植供者ERAS实践均有重要参考价值,值得推广与学习。然而该共识未对禁食禁饮要求、术后营养支持、早期活动等作具体推荐,这也为未来研究指明了方向。为此,广大学者应共同努力,积极探索肝移植围术期综合管理策略,丰富肝移植ERAS的证据支持。此外,本共识证据多源于国外研究,国内学者应注意结合我国诊疗现况与国民身体特质对相关建议进行本土化调适,以开展更贴合我国国情的肝移植手术ERAS临床实践,提高肝移植患者的生存质量。
-
表 1 CK5/6、CK14和EGFR免疫组织化学染色条件
抗体名称 克隆号 稀释倍数 公司 阳性部位 阳性对照 界值 热抗原修复
[1 mmol/L EDTA溶于10 mmol/
LTris缓冲液(pH=8.5)]孵育温度及时间 CK5/6 小鼠单抗(D5/16 B4) 即用型 Dako 膜或浆阳 间皮瘤 ≥5% 100 ℃30 min 37 ℃16 min CK14 兔单抗(SP44) 即用型 Novus 膜或浆阳 头颈癌 >5% 100 ℃60 min 37 ℃16 min EGFR 兔单抗(5B7) 即用型 Ventana 膜或浆阳 皮肤 >10% 100 ℃30 min 37 ℃16 min EGFR:表皮生长因子受体 表 2 CK5/6、CK14、EGFR分别及联合检测基底样三阴乳腺癌的敏感性及特异性
免疫标记物 阳性例数(n) 阴性例数(n) 敏感性(%) 特异性(%) CK5/6 34 81 43.6 45.7 CK14* 18 65 30.5 37 EGFR 70 45 89.7 82.2 EGFR和/或CK5/6 77 38 98.7 100 EGFR和/或CK14 73 42 93.5 88.1 CK5/6和/或CK14 42 73 53.8 50.7 EGFR和/或CK5/6和/或CK14 78 37 100 100 *因组织标本过少,32例无法获取CK14数据;EGFR:同表表 1 表 3 基底样三阴乳腺癌与非基底样三阴乳腺癌临床及病理特征比较
临床及病理指标 病例数(n) 三阴乳腺癌(n) 基底样 非基底样 P值 年龄 <40岁 26 20 6 0.188 ≥40岁 89 58 31 <50岁 62 43 19 0.428 ≥50岁 53 35 18 肿瘤大小* ≤3 cm 77 55 22 0.216 >3 cm 37 23 14 P53 阳性 48 36 12 0.116 阴性 67 42 25 Ki-67指数** >14% 65 47 18 0.315 ≤14% 16 10 6 组织学类型 浸润性导管癌(非特殊类型) 97 70 27 0.023 其他 18 8 10 浸润性导管与小叶混合性癌 3 1 2 髓样癌 4 3 1 黏液癌 2 2 0 浸润性微乳头状癌 2 0 2 浸润性小叶癌 5 1 4 腺鳞癌 2 1 1 分级 1级 10 2 8 2级 35 21 14 0.001 3级 70 55 15 0.001 淋巴结转移情况 阳性 47 37 10 0.029 阴性 68 41 27 复发 有 55 40 15 0.190 无 60 38 22 生存状况 存活 84 52 32 0.019 死亡 31 26 5 *1例肿瘤大小数据缺失;* *由于组织块局限性,34例无法获取Ki-67数据 -
[1] Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours[J]. Nature, 2000, 406:747-752. DOI: 10.1038/35021093
[2] Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2001, 98:10869-10874. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.191367098
[3] Sotiriou C, Wirapati P, Loi S, et al. Gene expression profiling in breast cancer:understanding the molecular basis of histologic grade to improve prognosis[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2006, 98:262-272. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djj052
[4] Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, et al. Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100:8418-8423. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0932692100
[5] Sotiriou C, Neo SY, McShane LM, et al. Breast cancer classification and prognosis based on gene expression profiles from a population based study[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2003, 100:10393-10398. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1732912100
[6] Rakha EA, Ellis IO. Triple-negative/basal-like breast cancer:review[J]. Pathology, 2009, 41:40-47. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S003130251632061X
[7] Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, et al. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10:5367-5374. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0220
[8] Leidy J, Khan A, Kandil D.Basal-like breast cancer:update on clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical and moleculr features[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2014, 138:37-43. DOI: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0439-RA
[9] National Health Service Breast Screening Programme (NHSBSP) and The Royal College of Pathologists. Pathology Reporting of Breast Disease[M]. Sheffield:NHSBSP and The Royal College of Pathologists, 2005:58.
[10] Weigelt B, Baehner FL, Reis-Filho JS. The contribution of gene expression profilingto breast cancer classification, prognostication and prediction:a retrospective of the last decade[J]. J Pathol, 2010, 220:263-280. DOI: 10.1002/path.2648
[11] Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, et al.Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10:5367-5374. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0220
[12] Cheang MC, Voduc D, Bajdik C, et al. Basal-like breast cancer defined by five biomarkers has superior prognostic value than triple-negative phenotype[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14:1368-1376. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1658
[13] Badve S, Dabbs DJ, Schnitt SJ, et al. Basal-like and triple-negative breast cancers:a critical review with an emphasis on the implications for pathologists and oncologists[J]. Mod Pathol, 2011, 24:157-167. DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.2010.200
[14] Perou CM. Molecular Stratification of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers[J]. Oncologist, 2011, 16:61-70. DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-S5-39
[15] Kim MJ, Ro JY, Ahn SH, et al. Clinicopathologic significance of the basal-like subtype of breast cancer:a comparison with hormone receptor and Her2/neu-overexpressing phenotypes[J]. Hum Pathol, 2006, 37:1217-1226. DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2006.04.015
[16] Livasy CA, Karaca G, Nanda R, et al. Phenotypic evaluation of the basallike subtype of invasive breast carcinoma[J]. Mod Pathol, 2006, 19:264-271. DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.3800528
[17] Rakha EA, Elsheikh SE, Aleskandarany MA, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer:distinguishing between basal and nonbasal subtypes[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2009, 15:2302-2310. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2132
[18] Jumppanen M, Gruvberger-Saal S, Kauraniemi P, et al.Basal-like phenotype is not associated with patient survival in estrogen-receptornegative breast cancers[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2007, 9:R16. DOI: 10.1186/bcr1649
[19] Bertucci F, Finetti P, Cervera N, et al. How basal are triple-negative breast cancers?[J].Int J Cancer, 2008, 123:236-240. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.23518
[20] Tischkowitz M, Brunet JS, Begin LR, et al. Use of immunohistochemical markers can refine prognosis in triple negative breast cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2007, 7:134. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-134
[21] Bidard FC, Conforti R, Boulet T, et al. Does triple-negative phenotype accurately identify basal-like tumour? An immunohistochemical analysis based on 143 'triple-negative' breast cancers[J]. Ann Oncol, 2007, 18:1285-1286. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdm360
[22] Tan DS, Marchio C, Jones RL, et al. Triple negative breast cancer:molecular profiling and prognostic impact in adjuvant anthracyclinetreated patients[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2008, 111:27-44. DOI: 10.1007/s10549-007-9756-8
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: