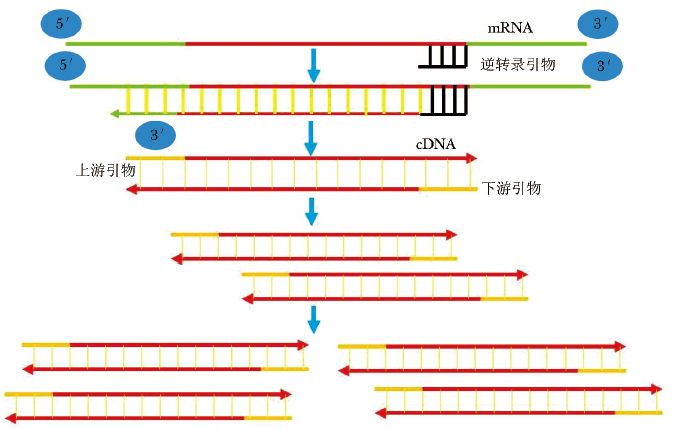
mRNA Expression of Methylase and Methyl-CpG Binding Protein in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells from Patients with Generalized Pustular Psoriasis
-
摘要:目的 观察泛发性脓疱型银屑病(generalized pustular psoriasis,GPP)患者外周血单个核细胞(peripheral blood mononuclear cell,PBMC)中DNA甲基转移酶及甲基化CpG结合蛋白(methyl-CpG binding protein,MeCP)mRNA的表达情况,初步探讨DNA甲基化在GPP中可能的作用机制。方法 回顾性收集2015年12月至2016年12月在北京协和医院皮肤科门诊或住院治疗的9例GPP患者临床资料;随机选取10例同期在医院接受健康体检的健康人做为对照,年龄和性别与GPP患者相匹配。分别留取10 ml肘正中静脉血,采用密度梯度离心法分离PBMC,应用Trizol法提取PBMC总RNA,采用实时PCR法检测DNMT1、DNMT3a、DNMT3b、MBD1、MBD2、MBD3、MBD4及MeCP2的mRNA表达水平,并分析年龄及病情严重程度与mRNA表达水平的相关性。结果 GPP患者PBMC中DNMT3a、DNMT3b、MBD1、MBD2、MBD4的mRNA表达水平较健康对照组升高[DNMT3a:0.000 17(0.000 06, 0.001 15)比0.000 03(0.000 02,0.000 04);DNMT3b:0.000 04±0.000 02比0.000 02±0.000 01;MBD1:为0.001 01±0.000 45比0.000 46±0.000 15;MBD2:0.002 61±0.000 39比0.001 85±0.000 52;MBD4:0.004 29±0.001 60比0.001 57±0.000 55, P均<0.05], 年龄及疾病严重度与上述因子mRNA的相对表达水平无相关性(P均>0.05)。结论 GPP患者体内甲基化相关调控基因表达异常,但与年龄和疾病严重程度不相关。
-
关键词:
- DNA甲基转移酶 /
- 甲基化CpG结合蛋白 /
- 泛发性脓疱型银屑病
Abstract:Objective The aim of this study was to observe the mRNA expression of DNA methyl-transferase(DNMT) and methyl-CpG binding protein(MeCP) in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells from GPP patients, and to explore the potential role of DNA methylation in the pathogenesis of GPP.Methods Clinical data of 9 GPP patients admitted or hospitalized at the Department of Dermatology of Peking Union Medical College Hospital from December 2015 to December 2016 were retrospectively collected. Ten healthy people who underwent a physical examination in the same hospital during the same period were randomly selected as the control group; their age and gender were matched with those of GPP patients. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from 10 ml blood of the elbow median vein using density gradient centrifugation. Total RNA was extracted from peripheral blood mononuclear cells by Trizol method; mRNA expression levels of DNMT1, DNMT3a, DNMT3b, MBD1, MBD2, MBD3, MBD4, and MeCP2 were detected by real-time PCR. The correlation of age and GPP severity with the expression level of these mRNAs was observed and analyzed.Results Compared with the healthy subjects, the relative expressions of DNMT3a, DNMT3b, MBD1, MBD2, and MBD4 mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from GPP patients were higher than those from the healthy controls [DNMT3a:0.000 17(0.000 06, 0.001 15) vs. 0.000 03(0.000 02, 0.000 04), DNMT3b 0.000 04± 0.000 02 vs. 0.000 02±0.000 01, MBD1 0.001 01±0.000 45 vs. 0.000 46±0.000 15, MBD2 0.002 61±0.000 39 vs. 0.001 85±0.000 52; and MBD4 0.004 29±0.001 60 vs. 0.001 57±0.000 55, all P < 0.05]. There was no correlation between age and GPP severity with the mRNA expression of the above factors (all P > 0.05).Conclusions Methylation related regulatory genes are abnormally expressed in GPP patients, and do not correlate with age or the disease severity. -
早期胃癌的定义是指局限于黏膜层或黏膜下层的胃癌,无论是否有淋巴结转移[1]。近年来,随着早期胃癌内镜下治疗的开展,对于早期胃癌浸润深度的判断有了更高要求。早期胃癌的内镜下治疗,包括内镜下黏膜切除术(endoscopic mucosal resection,EMR)和内镜下黏膜下层剥离术(endoscopic submucosal disection, ESD),对于没有淋巴结转移的早期胃癌患者可以达到根治性切除的目的,相比于传统的外科手术,疗效相当,并具有创伤小、保存胃正常解剖及功能的优点,目前已经作为早期胃癌的标准治疗方案之一[2-5]。早期胃癌的淋巴结转移与其病变的浸润深度有关,日本Gotoda等[2]报道黏膜下层浸润深度在500 μm以内的早期分化型胃癌如果病理证实没有脉管浸润,则淋巴结的转移率为0,该研究组随后的研究发现局限在黏膜层且直径小于2 cm的未分化型腺癌,如果没有脉管浸润,最终淋巴结的转移率也为0[6],意味着这类患者采用内镜治疗完全能够达到根治性切除的目的。因此,准确判断病变的浸润深度对于决定早期胃癌的治疗方式非常重要。
内镜超声(endoscopic ultrasonography, EUS),尤其是能够清晰地展示胃壁各层结构的高频超声小探头EUS,已经被广泛应用于胃癌的术前分期评价,对所有胃癌的T分期和N分期评价总准确性为78%~92%和63%~78%,对进展期胃癌评价的准确性比早期胃癌更高[7-8]。目前已经有很多研究报道EUS评估早期胃癌浸润深度的准确性,但结果相差较大。目前认为,影响判断准确性的主要因素有:病变部位、病变的内镜特点(大体形态,是否合并溃疡)、病变大小;另一方面,研究的设计对结果也有较大影响[8-10]。本研究旨在通过回顾性研究,评价小探头EUS对早期胃癌浸润深度的诊断价值,并分析影响其诊断准确性的因素。
资料和方法
资料
2010年3月1日至2012年12月31日于北京协和医院接受诊治的早期胃癌患者共64例,回顾性分析其中资料完整者59例。所有患者经普通内镜或放大色素内镜检查发现病变,活检证实为胃癌,在治疗前接受小探头EUS检查并评估病变浸润深度,之后40例接受ESD,其余19例进行外科手术治疗,ESD及外科手术标本经病理学检查证实为累及黏膜层或黏膜下层的早期胃癌。
研究方法
患者在检查前签署知情同意书,行利多卡因胶浆口咽部局部麻醉后接受EUS检查,检查采用超声高频小探头(UM-DP12-25R, 频率为12 MHz, 主机为EU-M2000,Olympus, Tokyo, Japan),检查时先观察病变的部位、大体形态及内镜下特点,然后在胃腔内注入200~500 ml不含气水,在内镜直视下将超声小探头通过活检孔道插入达病变上方进行EUS检查,记录清晰的超声图像并判断局部浸润深度,所有检查均由同一组有经验的超声内镜医生完成。
高频超声小探头可以清晰地显示胃壁的五层结构[11],由里向外第一层高回声代表黏膜层(M层),第二层低回声结构为黏膜肌层(MM层),第三层高回声结构为黏膜下层(SM层),第四层低回声结构为固有肌层(MP层), 第五层强回声代表浆膜下及浆膜层(SS层)(图 1)。当低回声病变仅累及第一层和第二层时判断为M层受累,如果累及1~3层则判断为SM层浸润。沿胃长轴将胃分为上、中、下1/3以记录病变的位置,上1/3包括胃底、贲门及胃体的近段1/3,中1/3包括胃体中下1/3及胃角,下1/3包括胃窦及幽门区。病变大体形态根据巴黎分型[12],将早期胃癌分为隆起型(0-Ⅰ)、平坦型(0-Ⅱ)和凹陷型(0-Ⅲ), 其中0-Ⅱ型根据形态又可以分为表浅隆起型(0-Ⅱa)、平坦型(0-Ⅱb)和表浅凹陷型(0-Ⅱc)3个亚型。
统计学处理
分别计算EUS判断M层和SM层浸润的敏感性、特异性及准确性,并用卡方检验对两组进行比较,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。同时比较不同内镜及病理特点病变EUS诊断的准确性,评价影响EUS准确性的因素。
结果
患者临床及病理资料
59例患者中男性39例,女性20例,男:女为1.95: 1,平均年龄(62.2±8.4)岁(43~85岁)。59例患者共发现病变59处,其中位于胃下1/3者最多,中1/3者次之;病变最大直径范围在0.7~5.5 cm之间;大体形态以0-Ⅱc型最多,其次为0-Ⅱa型。病理组织学检查证实大多数局限于M层,分化型腺癌占绝大多数,仅6例为未分化型腺癌或有印戒细胞成分(表 1)。
表 1 59例早期胃癌病变的内镜和病理检查特点特点 例数 构成比(%) 病变部位 上1/3 10 16.9 中1/3 22 37.3 下1/3 27 45.8 病变大小 >2 cm 21 35.6 ≤2 cm 38 64.4 大体形态 0-Ⅰ 4 5.8 0-Ⅱa 13 22.0 0-Ⅱb 5 8.5 0-Ⅱc 30 50.8 0-Ⅲ 7 11.9 合并溃疡 有 6 10.2 无 53 89.8 病变浸润深度 M层 49 83.1 SM层 10 16.9 病变分化类型 分化型 53 89.8 未分化型 6 10.2 0-Ⅰ:早期隆起型;0-Ⅱa:早期表浅隆起型;0-Ⅱb:早期平坦型;0-Ⅱc:早期表浅凹陷型;0-Ⅲ:早期凹陷型;M层:黏膜层;SM层:黏膜下层 EUS判断早期胃癌病变深度的诊断价值
59例早期胃癌EUS诊断病变深度和病理诊断最终结果比较见表 2。早期胃癌EUS诊断M层病变深度的敏感性为66.1%,特异性为80.0%,准确性为79.7%,诊断SM层病变的敏感性为80.0%,特异性为81.6%,准确性为81.4%,两组之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);总体病变诊断的敏感性为79.7%,特异性为81.4%,准确性为79.7%。图 2示1例早期胃癌EUS确定病变为M层并经病理证实。
早期胃癌不同内镜及病理特点下EUS诊断病变深度的准确性见表 3,早期胃癌诊断总体准确性为79.7%,位于胃上1/3和中1/3、大体形态为隆起型(0-Ⅰ及0-Ⅱa)以及合并溃疡的病变诊断的准确性相对较低;过高分级的比例为16.9%,位于胃上1/3和中1/3、大体形态为隆起型(0-Ⅰ及0-Ⅱa)(图 3)以及合并溃疡的病变容易过高分级;过低分级的比例为3.4%。
表 3 早期胃癌不同内镜及病理特点下EUS诊断病变深度的准确性特点 例数 EUS诊断病变
深度准确性
(%)过高分级
比例(%)过低分级
比例(%)总体病变 59 79.7 16.9 3.4 病变部位 上1/3 10 70.0 20.0 10.0 中1/3 22 68.2 27.3 4.5 下1/3 27 92.6 7.4 0 病变大小 >2 cm 21 80.9 14.3 4.8 ≤2 cm 38 78.9 18.5 2.6 大体形态 0-Ⅰ 4 75.0 25.0 0 0-Ⅱa 13 61.5 38.5 0 0-Ⅱb 5 100 0 0 0-Ⅱc 30 86.7 10.0 3.3 0-Ⅲ 7 71.4 14.3 14.3 合并溃疡 有 6 66.7 33.3 0 无 53 81.1 15.1 3.8 病变分化类型 分化型 53 79.2 17.0 3.8 未分化型 6 83.3 16.7 0 EUS:同图 1; 0-Ⅰ、0-Ⅱa、0-Ⅱb、0-Ⅱc、0-Ⅲ:同表 1 讨论
日本Gotoda[13]提出的早期胃癌内镜下治疗扩大适应证目前已经被广泛接受,包括:(1)黏膜内癌,分化型腺癌,无脉管浸润,无溃疡,病变大小不限;(2)黏膜内癌,分化型腺癌,无脉管浸润,合并溃疡,病变小于3 cm;(3)黏膜下层浅层浸润(深度小于500 μm),分化型腺癌,无脉管浸润,无溃疡,病变小于3 cm;(4)黏膜内癌,未分化型腺癌,无脉管浸润,无溃疡,病变小于2 cm。此类早期胃癌淋巴结转移率极低,内镜下治疗可以达到治愈性切除的目标,获得与外科手术相近的预后结果,创伤小,操作相对简便,能尽可能保存胃原有的结构及功能。对于超出此类适应证之外的病变,淋巴结转移的比例大大增加,单纯的内镜切除常常不能达到根除胃癌的目的,需要追加外科手术。
因此,对于早期胃癌患者,在制定治疗决策之前,必须明确病变的大体形态、大小、是否存在溃疡、组织学类型及病变的浸润深度等。前几种特征通过仔细的内镜检查及精确活检病理检查通常能获得明确的答案,而针对病变的浸润深度,尽管某些内镜下特点对于判断病变黏膜下层浸润有一定帮助,但不同内镜医生判断的准确性差异很大[14],活检病理也很难提供黏膜下层浸润的信息,因而常常依赖于影像学检查。由于胃是空腔脏器,胃壁很薄且有很大的延展性,传统的CT和MRI对于胃癌局部浸润的T分期诊断价值都有限,常常作为评价淋巴结转移(N分期)和远处转移(M分期)的手段[15-17]。EUS能够清晰地展示胃壁各层结构,已经被广泛应用于胃癌的术前分期评价,目前被公认为评价胃癌局部浸润深度的最佳手段[17-19]。但是对于早期胃癌,EUS诊断浸润深度的准确性不如进展期胃癌[7-8, 10, 18]。
关于EUS对胃癌局部分期的研究很多,不同研究其准确性差异很大,大多波动于65%~92%[7-9, 16-19]。本研究采用了12 MHz的超声小探头对早期胃癌病变进行扫查,诊断的总体准确性为79.7%,敏感性为79.7%,特异性为81.4%,与已有文献报道一致[7-9, 16-19]。同时本研究分别计算了M层和SM层病变EUS的诊断敏感性、特异性和准确性,M层分别为66.1%、80.0%和79.7%,SM层分别为80.0%、81.6%和81.4%,两者均在上述文献[7-9, 16-19]的报道范围之内,但SM层病变的结果要略优于M层,尤其是敏感性有所提高,两者之间差异没有统计学意义,可能是由于SM层病变例数太少所致,该结果有待更多纳入SM层病变的研究来证实。
Kwee等[20]进行了一项关于EUS区分M层及M层以下病变诊断价值的荟萃分析,共纳入18个研究,每个研究的样本数在30~226例(平均89.5例),结果发现各项研究的敏感性为18.2%~100% (平均87.8%),特异性34.7%~100% (平均80.2%),存在显著差异(P<0.0001)。影响研究结果的因素很多,包括采用检查设备、操作者经验、入选病例等,病变的内镜和病理特点对于诊断结果也有很大影响。目前认为与病变相关的可能影响因素包括:病变部位、大小、大体形态、是否合并溃疡以及组织学分型[8-9, 14, 18-19, 21]。本研究也探讨了不同内镜和病理特点病变EUS诊断的准确性和错误分级的情况。针对部位而言,之前的报道大多以胃上1/3病变准确率最低[9, 14, 18, 22],与超声小探头不易接近病变有关,另外胃底的SM层较薄,有较多的血管和纤维组织,也会影响诊断结果[22]。本研究发现位于胃中1/3的病变准确率最低(68.2%),上1/3病变次之(70.0%),两者结果非常接近,原因可能是:(1)22例胃中1/3病变中有15例为胃角附近的病变,超声小探头不易接近并进行标准切线位扫查,影响诊断结果;(2)胃上1/3病变例数相对较少。另外,本研究结果提示大体形态为隆起型(0-Ⅰ及0-Ⅱa,分别为75.0%和61.5%)以及合并溃疡的病变(66.7%)诊断的准确性相对较低,与Akashi等[21]的研究结果类似。隆起型病变区域较厚,位于病变上方的高频超声小探头产生的声波在SM层以上被反射,因而SM层声像显示不够清楚,影响诊断的准确性,换用更低频率的小探头扫查或者用普通超声内镜直接扫查可能会有帮助。溃疡底部通常会有炎症、水肿以及纤维化,也会影响超声检查结果。本研究结果显示不同大小病变EUS诊断的准确性接近,分化型和未分化型腺癌的EUS诊断准确性也没有明显差异,但由于未分化型腺癌的例数较少,结果可靠性有待更大样本研究证实。
本研究结果提示,对于早期胃癌,EUS判断病变深度时容易出现过高分级(16.9%),主要发生在位于胃上1/3(20.0%)和中1/3(27.3%)、大体形态为隆起型(0-Ⅰ:25.0%,0-Ⅱa:38.5%)以及合并溃疡(33.3%)的病变中,提示对于这类病变,小探头EUS判断病变深度的价值有局限,可能会作出错误的判断,导致部分患者因过高分级失去内镜切除病变的机会,因而需要结合病变内镜特点(有无SM层浸润改变)、黏膜下注射抬举征是否阳性或换用普通超声内镜检查进行综合判断,以作出正确的治疗决策。过低分级的比例较低,仅为3.4%,这个结果可能与SM层病变例数较少有关,可靠性有待进一步确认。
本研究是回顾性分析,存在一定的局限性,主要在于样本量较小,按内镜和病理特点分层后数据分布不均,个别组例数过少,得出的结果未能进行统计学分析判断差异的显著性。另外,由于病理检查结果未能测量SM层病变的浸润深度,无法对SM层病变进行更深层次的分析(区分SM浅层浸润及深层浸润)。要获得EUS对早期胃癌浸润深度诊断价值更为精确可靠的结果,需要更大样本量的研究,尤其要纳入更多累及SM层的病例,并对SM浅层及深层浸润进行区分。
综上,小探头EUS对于判断早期胃癌浸润深度有较高的准确性,有助于作出适当的治疗决策,病变部位、大体类型及溃疡的存在会影响EUS的准确性,胃上1/3和中1/3、大体形态为隆起型(0-Ⅰ和0-Ⅱa)以及合并溃疡的病变更易出现过高分级,判断病变深度时需要综合考虑其内镜下特点,必要时采用其他检查手段。
志谢: 衷心感谢参与本项研究的GPP患者及全体工作人员。利益冲突 无 -
表 1 GPP患者甲基化相关调控基因引物序列
基因名称 上游引物(5′→3′) 下游引物(5′→3′) DNMT1 5′-GAGCTACCACGCAGACATCA-3′ CGAGGAAGTAGAAGCGGTTG DNMT3a 5′-CCGGAACATTGAGGACATCT-3′ CAGCAGATGGTGCAGTAGGA DNMT3b 5′-CCCATTCGAGTCCTGTCATT-3′ GGTTCCAACAGCAATGGACT MBD1 5′-CACCCTCTTCGACTTCAAACAAG-3′ CAACCTGACGTTTCCGAGTCTT MBD2 5′-AACCCTGCTGTTTGGCTTAAC-3′ CGTACTTGCTGTACTCGCTCTTC MBD3 5′-CCGCTCTCCTTCAGTAAATGTAAC-3′ GGCTGGAGTTTGGTTTTCAGAA MBD4 5′-TGGTGGTGCATGCCTGTAAT-3′ TGAGACAGGGTCTCTCTCTGTCAT MeCP2 5′-CCCCACCCTGCCTGAA-3′ GATGTGTCGCCTACCTTTTCG GPP:泛发性脓疱型银屑病;DNMT:DNA甲基转移酶;MBD:甲基化CpG结合域; MeCP:甲基化CpG结合蛋白 表 2 GPP患者及健康人外周血单个核细胞中DNMT和MeCP mRNA相对表达量的比较
基因 GPP组(n=9) 健康对照组(n=10) t/Z值 P值 DNMT1 0.001 77±0.000 76 0.001 83±0.002 00 -0.097 0.924 DNMT3a 0.000 17
(0.000 06, 0.001 15)0.000 03
(0.000 02, 0.000 04)-2.598 0.009 DNMT3b 0.000 04±0.000 02 0.000 02±0.000 01 2.326 0.021 MeCP2 0.002 08±0.000 84 0.001 79±0.000 83 0.716 0.487 MBD1 0.001 01±0.000 45 0.000 46±0.000 15 3.060 0.000 MBD2 0.002 61±0.000 39 0.001 85±0.000 52 3.284 0.005 MBD3 0.000 02±0.000 01 0.000 03±0.000 01 -1.828 0.088 MBD4 0.004 29±0.001 60 0.001 57±0.000 55 4.447 0.003 GPP、DNMT、MBD、MeCP:同表 1 表 3 GPP患者年龄和疾病严重程度与DNMT及MeCP mRNA表达水平的相关分析
风险因素 基因 r值 P值 年龄 DNMT1 -0.319 0.402 DNMT3a -0.067 0.864 DNMT3b -0.487 0.183 MBD1 -0.235 0.542 MBD2 -0.252 0.513 MBD3 -0.328 0.389 MBD4 -0.202 0.603 MeCP2 0.050 0.897 病情严重程度 DNMT1 -0.134 0.732 DNMT3a 0.098 0.802 DNMT3b -0.241 0.533 MBD1 -0.241 0.533 MBD2 -0.009 0.982 MBD3 -0.178 0.646 MBD4 -0.134 0.732 MeCP2 -0.285 0.457 GPP、DNMT、MBD、MeCP:同表 1 -
[1] Reich A. Interleukin-17 blockade in generalized pustular psoriasis-new hope for severely ill patients [J]. Br J Dermatol, 2017, 176: 572-573. DOI: 10.1111/bjd.14987
[2] Marrakchi S, Guigue P, Renshaw BR, et al. Interleukin-36-receptor antagonist deficiency and generalized pustular psoriasis [J]. N Engl J Med, 2011, 365: 620-628. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1013068
[3] Jordan CT, Cao L, Roberson ED, et al. PSORS2 is due to mutations in CARD14 [J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2012, 90: 784-795. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e523f113631af97f465990c9cd244b11
[4] Sugiura K, Takemoto A, Yamaguchi M, et al. The majority of generalized pustular psoriasis without psoriasis vulgaris is caused by deficiency of interleukin-36 receptor antagonist [J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2013, 133: 2514-2521. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=77c0318cba979d3142142b831c593252
[5] Korber A, Mssner R, Renner R, et al. Mutations in IL36RN in patients with generalized pustular psoriasis [J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2013, 133: 2634-2637. DOI: 10.1038/jid.2013.214
[6] Sharma U, Rando OJ. Metabolic inputs into the epigenome [J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 25: 544-558. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.02.003
[7] Chen SH, Lv QL, Hu L. DNA methylation alterations in the pathogenesis of lupus [J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2017, 187: 185-192. DOI: 10.1111/cei.12877
[8] 桂欣钰, 晋红中.异常DNA甲基化与免疫性皮肤病[J].协和医学杂志, 2017, 8: 46-49. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9081.2017.03.009 [9] Elhamamsy AR. Role of DNA methylation in imprinting disorders: an updated review [J]. J Assist Reprod Genet, 2017, 34:549-562. DOI: 10.1007/s10815-017-0895-5
[10] Gowher H, Liebert K, Hermann A, et al. Mechanism of stimulation of catalytic activity of Dnmt3A and Dnmt3B DNA- (cytosine-C5)-methyltransferases by DNMT3L [J]. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280: 13341-13348. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M413412200
[11] Lopez-Serra L, Esteller M. Proteins that bind methylated DNA and human cancer: reading the wrong words [J]. Br J Cancer, 2008, 98: 1881-1885. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604374
[12] Umezawa Y, Ozawa A, Kawasima T, et al. Therapeutic guidelines for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) based on a proposed classification of disease severity [J]. Arch Dermatol Res, 2003, 295 Suppl 1: S43-S54. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6cfa5fec4d91fd205e6df0a095ddfacc
[13] Onoufriadis A, Simpson MA, Pink AE, et al. Mutations in IL36RN/IL1F5 are associated with the severe episodic inflammatory skin disease known as generalized pustular psoriasis [J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2011, 89: 432-437. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.07.022
[14] Sugiura K, Muto M, Akiyama M. CARD14c.526G4C(p.Asp176His) is a significant risk factor for generalized pustular psoriasis with psoriasis vulgaris in the Japanese cohort [J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2014, 134: 1755-1757. DOI: 10.1038/jid.2014.46
[15] Bestor TH. The DNA methyltransferases of mammals [J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2000, 9: 2395-2402. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/9.16.2395
[16] Tajima S, Suetake I, Takeshita K, et al. Domain structure of the DNMT1, DNMT3a, and DNMT3b DNA methyltrans-ferases [J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2016, 945: 63-86. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/27826835
[17] Wood KH, Johnson BS, Welsh SA, et al. Tagging methyl-CpG-binding domain proteins reveals different spatiotemporal expression and supports distinct functions [J]. Epigenomics, 2016, 8: 455-473. DOI: 10.2217/epi-2015-0004
[18] Pandey S, Pruitt K. Functional assessment of MeCP2 in Rett syndrome and cancers of breast, colon and prostate [J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2017, 95: 368-378. DOI: 10.1139/bcb-2016-0154
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 周红,郭春光,陈应泰,窦利州,张月明,王贵齐,赵东兵. 早期胃癌非治愈性内镜黏膜下剥离术后的治疗策略研究. 中华肿瘤杂志. 2019(11): 865-866-867-868-869 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 阮江,殷云勤,梁晓珍,殷鹏宇,尹馥梅. 小探头超声内镜诊断早期胃癌浸润深度准确性的Meta分析. 中华消化病与影像杂志(电子版). 2018(03): 127-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈梦雪,曹景莹,周宇,梁坚. 小探头超声内镜对消化道类癌的诊疗价值. 中国现代药物应用. 2017(01): 32-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(10)

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS


 下载:
下载: