Clinical Characteristics of Gleason Score 10 Prostate Cancer on Core Biopsy without Distant Metastases at Initial Diagnosis
-
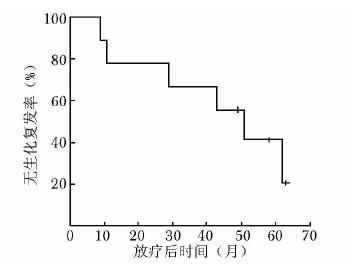
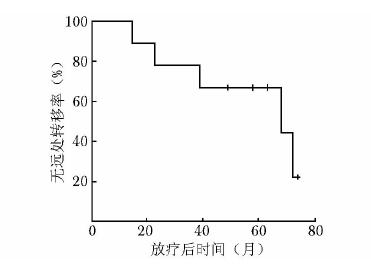
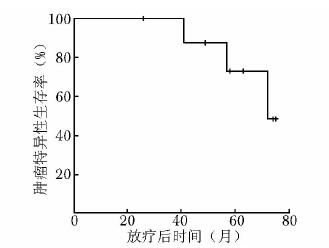
摘要:目的 分析初诊无远处转移的穿刺病理Gleason评分为10分前列腺癌的临床特点并探讨外放疗联合内分泌治疗的疗效。方法 2003年1月至2014年3月北京协和医院收治初诊无远处转移的Gleason评分10分前列腺癌患者9例。所有患者均接受全盆腔外放疗联合长期内分泌治疗。全盆腔外放疗的照射剂量为50.0 Gy, 前列腺、双侧精囊腺及区域阳性淋巴结加量至76.2~78.0 Gy。内分泌治疗采用最大限度雄激素阻断:口服抗雄激素药物加每月注射一次黄体生成素释放激素类似物。分析患者临床特点及联合治疗效果, 并运用Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线。结果 患者中位随访时间为4.8年(26~75个月)。治疗前中位血清前列腺特异性抗原(prostate specific antigen, PSA)为11.2 μg/L, 其中6例低于20 μg/L, 3例高于70 μg/L。中位穿刺活检针数阳性率为90.9%。TNM分期:3例T2c, 4例T3a, 2例T3b; 6例N0, 3例N1; 9例M0。随访期间, 6例患者出现生化复发, 其中5例进一步发展为转移性前列腺癌; 4例患者死亡, 其中3例死于前列腺癌。5年无生化复发率、无远处转移率、肿瘤特异性生存率及总体生存率分别为28.6%、57.1%、66.7%和57.1%。5例出现1~2级早期放疗胃肠道不良反应, 6例出现1~2级早期泌尿系统不良反应, 无晚期胃肠道及泌尿系统不良反应。无骨折、心血管意外等严重内分泌治疗并发症。结论 初诊无远处转移的穿刺病理Gleason评分10分前列腺癌常伴穿刺阳性范围大、肿瘤分期偏晚等高危因素, 患者通常预后不良, 放疗联合内分泌治疗等及时和积极的综合治疗方案往往是必需的。Abstract:Objective To analyze the clinical characteristics of patients with Gleason score 10 prostate cancer on core biopsy and without distant metastases when first diagnosed, and to evaluate the effectiveness of external radiotherapy combined with hormone therapy in these patients.Methods From January 2003 to March 2014, 9 patients were identified as Gleason score 10 prostate cancer without distant metastases when first diagnosed at Peking Union Medical College Hospital. All the patients were treated by whole pelvic external radiotherapy and long-term hormone therapy. The whole pelvic radiation dose was 50.0 Gy, the boost dose for the whole prostate, bilateral seminal vesicles, and regional positive lymph nodes ranged from 76.2 to 78.0 Gy. The hormone therapy used maximal androgen blockade, i.e. oral anti-androgen drugs plus monthly injection of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogs. We assessed the clinical characteristics of the patients and the treatment outcomes of the combination therapy. Survival curves were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method.Results The median follow-up was 4.8 years (26-75 months). The median pre-treatment serum prostate specific antigen (PSA) level was 11.2 μg/L. The pre-treatment PSA levels were lower than 20 μg/L in 6 patients, and higher than 70 μg/L in 3 patients. The median percentage of positive biopsy cores was 90.9%. In TNM staging, 3, 4, and 2 cases were classified as T2c, T3a, and T3b, respectively; 6 and 3 cases were classified as N0 and N1, respectively; and all the 9 cases were classified as M0. Six patients developed biochemical failure, 5 of which progressed into distant metastasis. Four patients died during the follow-up period, 3 of which died of prostate cancer. The 5-year biochemical failure-free survival (BFFS), distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS), and overall survival (OS) were 28.6%, 57.1%, 66.7%, and 57.1%, respectively. Five patients experienced grade 1-2 acute gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity and 6 patients developed grade 1-2 acute genitourinary (GU) toxicity due to radiotherapy. No late GI or GU toxicity was reported. No bone fracture, cardiovascular event, or other severe hormone therapy-related complications was detected.Conclusions Gleason score 10 prostate cancer without distant metastases when first diagnosed may be often combined with high risk factors such as high percentage of positive biopsy cores, and advanced tumor stage. Timely and active comprehensive treatments including external radiotherapy and hormone therapy are usually necessary because these patients generally have unfavorable prognosis.
-
Keywords:
- prostate cancer /
- biopsy pathology /
- combined therapy /
- treatment effect
-
新型冠状病毒肺炎(coronavirus disease 2019,COVID-19)是由新型冠状病毒(severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2,SARS-CoV-2)感染引起的呼吸系统传染病。重症COVID-19患者多在发病一周后出现呼吸困难或低氧血症,并可快速进展为急性呼吸窘迫综合征、感染性休克及多器官功能衰竭,病死率高[1]。在重症COVID-19患者治疗过程中,常需建立外周动脉导管进行连续血流动力学监测和血气分析采样[2]。传统触诊法留置外周动脉导管通常需多次尝试,在低血压、水肿或血流动力学不稳定的重症患者中更是如此[3]。多次尝试易致患者不适和应激,其引起的动脉痉挛进一步增加了置管难度。在三级防护下,由于防护服较厚重、穿戴多层手套导致触感下降,采用传统触诊法留置外周动脉导管更加困难。随着超声技术的发展,重症超声逐渐应用于血管穿刺中[4]。既往研究显示,由于超声具有可视化的优点,超声引导外周动脉置管可提高首次穿刺成功率,减少不良反应[3, 5]。本研究探讨超声引导技术在重症COVID-19患者外周动脉导管留置中的价值,旨在为重症COVID-19患者的救治提供借鉴。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象及分组
1.1.1 研究对象
本研究为回顾性病例对照研究。2020年2月至4月北京协和医院援鄂医疗队整建制接管了武汉同济医院中法新城院区ICU病房,收集并分析病房收治的确诊为重症COVID-19[6]且留置动脉导管的所有患者临床资料。排除标准:(1)转入时已留置动脉导管;(2)在桡动脉以外部位留置外周动脉导管的患者。
1.1.2 分组
前期因病房条件所限采用传统触诊法进行外周动脉置管的患者为对照组,后期条件改善后采用超声引导下外周动脉置管的患者为研究组。
由于COVID-19疫情属于突发公共卫生事件,本研究免除伦理审查。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 建立动脉穿刺小组
(1) 成员:动脉穿刺小组由医疗队中重症护理工作经验≥3年的12名护士组成。小组成员均完成超声引导下动脉穿刺技术的规范化培训,且具有≥1年的临床相关经验。穿刺过程由具有重症工作经验的医师进行质量控制。(2)培训:动脉穿刺小组在武汉均通过集体授课与视频学习等形式再次接受常规动脉穿刺与超声引导下动脉穿刺培训,保证操作的一致性。(3)排班:由于COVID-19疫情的特殊性,临床工作中共设7个护理组,采取轮班制按组别顺序循环值班开展工作,每组在污染区工作4 h。每个护理组配备1~2名具有超声工作经验的护士。
1.2.2 动脉穿刺方法
(1) 传统触诊法:患者手心朝上、手腕下部垫高,使手掌与手臂至少成45°角,碘伏消毒。穿刺者左手寻找患者桡动脉搏动最强位置,右手持针,30°角进针,见回血后将动脉针放平,退针芯并将动脉留置针管送入血管,连接密闭式采血套装,回抽见回血且通畅为置管成功。若穿刺不成功,拔除动脉针,按压至穿刺点不再渗血,更换动脉针重新穿刺,穿刺大于3次仍不成功者考虑更换其他部位进行置管。
(2) 超声引导下外周动脉置管:患者姿势同对照组。应用Venue ultrasound system超声仪(美国GE公司),血管探头(探头频率5~10 MHz)用无菌手套包裹,探头标志点朝向患者右侧。操作者左手用超声探头平面外(短轴)定位桡动脉(图 1A),右手30°角进针,随着进针深入,逐渐向后移动探头,使针尖持续显示在超声声像中。当超声声像示针尖进入动脉(图 1B)或见回血时,超声探头逆时针旋转90°(图 1C),探头标志点朝向远心端,左右滑动探头,见平面内(长轴)图像(图 1D)。放平动脉针,观察超声声像,继续送针,超声声像可见动脉针持续向动脉内前行,将针体的2/3完全送入血管内,退针芯并连接密闭式采血套装,回抽见回血且通畅为置管成功。若穿刺不成功,拔除动脉针,按压至穿刺点不再渗血,更换动脉针重新穿刺,穿刺大于3次仍不成功者,考虑更换其他部位进行置管。
1.3 评价指标
首次置管成功率:首次置管成功为第一针穿刺即见回血,送入导管过程顺利,无受阻感,连接密闭式采血装置后回抽见回血且通畅。首次置管成功率=首次置管成功例数/置管总例数×100%。
穿刺次数:穿刺针未触及桡动脉,或退至皮下重新进针即计一次,直至置管成功。记录每例患者穿刺次数。
总穿刺成功率:总穿刺成功率=穿刺成功次数/穿刺总次数×100%。1.3.4并发症:(1)导管留置24 h内是否失用,回抽导管无回血且监护仪无动脉波形即为失用。(2)有无局部血肿、导管阻塞曲折等情况。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS 24.0软件进行统计分析。穿刺次数、总穿刺成功率符合正态分布,以均数±标准差表示,组间比较采用两独立样本t检验;首次置管成功率、并发症发生率的比较采用χ2检验或Fisher精确概率法。双侧检验,以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般临床资料
共60例符合纳入和排除标准的重症COVID-19患者入选本研究(图 2)。其中研究组30例、对照组30例。两组患者年龄,性别,穿刺前无创血压、心率、水肿情况及基础疾病等情况见表 1。
表 1 两组患者一般资料项目 研究组(n=30) 对照组(n=30) 男性[n(%)] 17(56.7) 19(63.3) 年龄(x±s,岁) 66.47±10.70 66.50±8.66 收缩压(x±s,mm Hg) 110.63±22.35 115.83±22.38 舒张压(x±s,mm Hg) 73.13±11.85 74.27±11.32 心率(x±s,次/min) 78.83±18.48 79.30±18.63 水肿[n(%)] 7(23.3) 5(16.7) 基础疾病[n(%)] 高血压 6(20.0) 12(40.0) 糖尿病 4(13.3) 5(16.7) 冠心病 1(3.3) 1(3.3) 2.2 两组患者外周动脉置管情况比较
研究组外周动脉首次置管成功率、总穿刺成功率高于对照组(P均<0.05),穿刺次数少于对照组(P<0.05)(表 2)。
表 2 两组患者外周动脉置管情况比较组别 首次成功例数
[n(%)]穿刺次数
(x±s, 次)总穿刺成功率
(x±s, %)研究组(n=30) 19(63.3) 1.43±0.56 79.43±25.79 对照组(n=30) 8(26.7) 2.50±1.28 53.07±30.21 P值 0.004 <0.001 <0.001 2.3 两组患者外周动脉穿刺并发症比较
研究组外周动脉导管留置的24 h失用率及局部血肿、导管阻塞曲折发生率均低于对照组(P均<0.05)(表 3)。
表 3 两组患者外周动脉置管并发症比较[n(%)]组别 24 h失用 局部血肿 导管阻塞曲折 研究组(n=30) 2(6.7) 3(10.0) 1(3.3) 对照组(n=30) 9(30.0) 11(36.7) 12(40.0) P值 0.020 0.015 0.001 3. 讨论
本研究结果显示,研究组外周动脉首次置管成功率(63.3%比26.7%)、总穿刺成功率[(79.43± 25.79)%比(53.07±30.21)%]均高于对照组(P均<0.05),穿刺次数[(1.43±0.56)次比(2.50±1.28)次]、外周动脉导管留置的24 h失用率(6.7%比30.0%)及局部血肿(10.0%比36.7%)、导管阻塞曲折发生率(3.3%比40.0%)均低于对照组(P均<0.05)。
重症COVID-19患者需进行血常规、血生化、动脉血气、血流动力学等指标的监测[2]。留置外周动脉导管是最常见的操作。在隔离病房中,操作者由于穿戴多层防护,导致动脉穿刺触感下降,加之重症患者循环较差,常规定位和穿刺成功率均受到较大影响。床旁超声使得整个置管过程可视化,不仅可清晰显示血管位置与走形,能更加精准地对动脉血管进行定位[7],且可动态引导穿刺针进入血管,进而提高首次置管成功率。本研究结果显示,超声动态引导下进行外周动脉置管相比传统的触摸定位法,重症COVID-19患者的首次置管成功率及总穿刺成功率均显著提高,提示三级防护下应用超声动态引导进行动脉穿刺置管具有绝对优势。
本研究显示,应用超声平面外(短轴)联合平面内(长轴)技术进行外周动脉置管可减少总穿刺次数,进而减少对患者的刺激。平面外(短轴)技术可以观察到进针方向与血管之间的位置关系,有助于找到最佳穿刺点,提高进针的准确性[8];同时平面内(长轴)技术可在超声图像上观察穿刺针与动脉的走向[3]。三级防护下,即使动脉针针尖进入血管,在送入针体时由于佩戴多层手套降低操作者手感仍然可能会导致置管失败。因此两种技术结合可动态观察整个穿刺过程,提高穿刺成功率。
本研究中,研究组外周动脉导管留置的24 h失用率及局部血肿、导管阻塞曲折发生率均降低,与Tang等[5]的Meta分析结果一致,提示超声引导外周动脉置管可降低重症COVID-19患者穿刺并发症。传统触诊法置管可出现仅导管尖端在动脉中,当患者体位变化时易发生导管异位、移出动脉而失用的情况,而超声可视化技术可确认导管完全进入动脉。据报道,桡动脉起始位置或走形存在变异的比率为9.6%~15.4%[9]。虽然传统触诊法留置外周动脉导管通常是安全的,但血肿等并发症仍然不可避免(发生率约5%)[10]。对于重症COVID-19患者,多层防护影响穿刺者操作,可导致穿刺并发症发生率显著增加(本研究约为40%)。超声的可视化优点能充分展示动脉与其他组织的位置关系[5],有助于减少穿刺过程中不必要的置管并发症[5],对有解剖变异的患者尤其重要。国际超声引导血管通路操作指南[11]建议将超声引导重症患者进行动静脉置管技术列为常规操作,且初学者练习超声引导桡动脉穿刺置管约14次即可掌握该项操作技能[12]。本研究亦证实了重症医疗工作者掌握该项操作技能的必要性。
本研究存在以下局限性:第一,由于疫情的特殊性,本研究很难进行平行对照设计,对照组为历史对照,可能存在未能平衡的混杂因素。第二,受限于样本量,未对潜在混杂因素进行校正,报告的效应为未校正的粗效应,结果可能存在一定偏倚。
综上,三级防护下,利用超声的可视化特性,采用平面外(短轴)技术联合平面内(长轴)技术对重症COVID-19患者进行外周动脉置管,可提高首次置管成功率,减少穿刺次数,降低穿刺并发症的发生率。
-
[1] 那彦群, 叶章群, 孙颖浩, 等.中国泌尿外科疾病诊断治疗指南[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2014:65. [2] Hu XH, Cammann H, Meyer HA, et al. Risk prediction models for biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy using prostate-specific antigen and Gleason score[J]. Asian J Androl, 2014, 16:897-901. DOI: 10.4103/1008-682X.129940
[3] McGuire BB, Helfand BT, Loeb S, et al. Outcomes in patients with Gleason score 8-10 prostate cancer:relation to preoperative PSA level[J]. BJU Int, 2012, 109:1764-1769. DOI: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10628.x
[4] Krauss DJ, Hayek S, Amin M, et al. Prognostic significance of neuroendocrine differentiation in patients with Gleason score 8-10 prostate cancer treated with primary radiotherapy[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2011, 81:119-125. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21596486
[5] Stock RG, Cesaretti JA, Hall SJ, et al. Outcomes for patients with high-grade prostate cancer treated with a combination of brachytherapy, external beam radiotherapy and hormonal therapy[J]. BJU Int, 2009, 104:1631-1636. DOI: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08661.x
[6] Ellis CL, Partin AW, Han M, et al. Adenocarcinoma of the prostate with Gleason score 9-10 on core biopsy:correlation with findings at radical prostatectomy and prognosis[J]. J Urol, 2013, 190:2068-2073. DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.05.056
[7] Humphrey PA. Gleason pattern 5 adenocarcinoma in prostate needle biopsy[J]. J Urol, 2012, 188:1341-1342. DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2012.06.126
[8] Sabolch A, Feng F, Daignault-Newton S, et al. Gleason pattern 5 is the greatest risk factor for clinical failure and death from prostate cancer after dose-escalated radiation therapy and hormonal ablation[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2011, 81:351-360. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21493015
[9] Nanda A, Chen M, Renshaw A, et al. Gleason pattern 5 prostate cancer:further stratification of patients with high-risk disease and implications for future randomized trials[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2008, 74:1419-1423. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19131185
[10] Yamamoto S, Masuda H, Urakami S, et al. Patient-perceived satisfaction after definitive treatment for men with high-risk prostate cancer:radical prostatectomy vs. intensity-modulated radiotherapy with androgen deprivation therapy[J]. Urology, 2015, 85:407-413. DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2014.09.046
[11] Roach M 3rd. Current trends for the use of androgen deprivation therapy in conjunction with radiotherapy for patients with unfavorable intermediate-risk, high-risk, localized, and locally advanced prostate cancer[J]. Cancer, 2014, 120:1620-1629. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.28594
[12] Zelefsky MJ, Pei X, Chou JF, et al. Dose escalation for prostate cancer radiotherapy:predictors of long-term biochemical tumor control and distant metastases-free survival outcomes[J]. Eur Urol, 2011, 60:1133-1139. DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.08.029
[13] Bolla M, de Reijke TM, Van Tienhoven G, et al. Duration of androgen suppression in the treatment of prostate cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 360:2516-2527. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0810095
[14] Weir EG, Partin AW, Epstein JI. Correlation of serum prostate specific antigen and quantitative immunohistochemistry[J]. J Urol, 2000, 163:1739-1742. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-5347(05)67532-5
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 赵明曦,孙建华,罗红波,李尊柱,李欣,井杰,张青,吴欣娟,王小亭. 《重症超声临床操作技术的护理规范》解读. 中华现代护理杂志. 2024(05): 584-588 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 栾诚,郭凡,嵇艳. ICU患者外周动脉导管非计划性拔管风险预测模型的构建及验证. 护理学杂志. 2023(06): 63-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS


 下载:
下载: