Local Injections of Cholesterol-conjugated let-7a Mimics Inhibit Tumor Growth and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Subcutaneous Xenograft Nude Mouse Model by Targeting K-Ras, H-Ras, and N-Ras
-
摘要:目的 研究胆固醇包裹let-7a模拟物(mimics)是否能通过下调人3种Ras抑制肝癌发展, 寻找肝癌的潜在治疗策略目的 采用MTT增殖分析、PI单染和Annexin V/FITC双染方法检测let-7a mimics在体外对肝癌细胞的作用。使用裸鼠皮下移植瘤模型和通过肿瘤局部注射方法观察let-7a mimics对体内肝癌的作用。采用实时定量PCR和Western blot方法检测let-7a及其靶点Ras的表达结果 与阴性对照组相比, let-7a mimics转染的肝癌细胞let-7a水平升高, 细胞增殖缓慢(P均 < 0.05);let-7a mimics阻滞更多肝癌细胞停留在G0-G1期且促进肝癌细胞凋亡(P均 < 0.05)。经let-7a mimics治疗的裸鼠体内肿瘤体积较阴性对照组减小, 是阴性对照组的54.97%(P=0.039);局部浸润和肝脏转移较阴性对照组明显减轻。肝癌细胞和移植瘤组织内let-7a上调的同时, 人K-Ras、H-Rras和N-Ras mRNA和蛋白的表达降低(P均 < 0.05)结论 let-7a mimics下调人3种Ras mRNA和蛋白的表达, 影响细胞周期, 进而抑制细胞增殖和促进细胞凋亡。瘤周多点注射胆固醇包裹的let-7a mimics能抑制移植瘤的生长、浸润和转移。提示let-7阻断Ras可成为肝癌治疗的研究策略。Abstract:Objective To investigate the potential antitumor effects of cholesterol-conjugated let-7a mimics (let-7a mimics) on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by down-regulating all 3 human Ras, with the aim to explore alternative therapeutic strategy for HCC.Methods Effects of let-7a mimics on HCC cells in vitro were detected using MTT-based cell proliferation assays in combination with propidium iodide staining and annexin-V/FITC double staining. The antitumor effects in vivo of let-7a mimics on HCC growth were analyzed in subcutaneous xenograft nude mice with intra-tumoral injections. Expressions of let-7a and its target human Ras were examined with real-time PCR and Western blot.Results let-7a mimics-transfected HCC cells showed increased let-7a levels and slower proliferation compared with the negative controls (both P < 0.05). let-7a mimics induced more cell-cycle arrest at the G0-G1 phase and promoted apoptosis of HCC cells (both P < 0.05). In addition, significant reductions in tumor size, local invasion and metastasis to liver were observed in let-7a mimics-treated nude mice compared to negative controls. The tumor size after let-7a treatment was 54.97% that of negative controls (P=0.039). Furthermore, the up-regulation of let-7a coincided with the reduction of K-Ras, H-Rras, and N-Ras mRNA and protein expressions in HCC cells and xenograft tumor (all P < 0.05).Conclusions let-7a mimics could affect cell cycle, inhibit cell proliferation and promote cell apoptosis by downregulation of mRNA and protein expressions of all the 3 human Ras. Local injections of cholesterol-conjugated let-7a mimics could effectively suppress the growth, invasion and metastasis of xenograft tumor. These findings suggest that Ras-targeting let-7 mimics could be a potential therapeutic option for HCC.
-
Keywords:
- hepatocellular carcinoma /
- let-7a /
- K-Ras /
- H-Ras /
- N-Ras /
- cell cycle /
- local injection treatment
-
肝细胞性肝癌(肝癌)是世界上第五大恶性肿瘤。我国是肝癌高发区,且肝癌的发生率和死亡率有上升趋势[1-2]。肝癌侵袭力强,死亡率高,易发生肺、骨转移,缺乏有效的治疗方法。近年来报道micro-RNAs(miRNAs)是长度为19~22个核苷酸的小分子RNA,通过与靶基因的3′非翻译区特异性结合在转录后水平抑制靶基因的表达[3]。已知的人类miRNA有一半位于基因组染色体的脆弱区域[4],如存在扩增、缺失、重排等,同肿瘤的发生发展相关[5]。其中let-7是首次在线虫体内发现的miRNA家族,被证实具抑癌作用[6-8]。有研究证实,let-7通过下调K-Ras、H-Ras进而抑制肺癌和胰腺癌的生长和迁移[9-12]。
以往的研究显示,在肝癌中Ras基因突变较少见。因此阻断Ras通路治疗肿瘤的策略在肝癌中研究较少。类似地,虽然在肝癌组织中let-7表达降低[13-14],且Ras为let-7的重要靶基因[15],但目前即使涉及let-7的肝癌研究,也较少讨论肝癌中let-7对Ras的影响[16-17]。近期有研究提示,尽管在肝癌中罕见Ras基因突变,但肝癌中的Ras可通过其他途径被异常激活[18-19],Zhu等[20]检测32例肝癌患者肿瘤及其癌旁肝组织中let-7的表达,发现肝癌中let-7的表达水平显著低于癌旁肝组织,且let-7的表达水平与肝癌的分化程度呈正相关。let-7在线虫中的研究和基因扫描预测结果提示,let-7/60与人3种Ras的3′非翻译区存在不同数量的同源序列[15]。故笔者假设,let-7能够抑制人恶性肿瘤中常见的所有3种Ras表达,进而抑制肝癌生长,并在本研究中通过体外肝癌细胞和体内裸鼠皮下肝癌移植瘤模型进行验证。
材料和方法
材料
人肝癌细胞系HepG2购于中国医学科学院基础医学研究所(基础所)细胞中心,SMMC-7721由基础所分子生物学国家重点实验室刘长征老师惠赠。let-7a模拟物(mimics)和胆固醇包裹let-7a mimics及阴性对照购于广州锐博生物技术有限公司,转染和治疗浓度为推荐用50 nmol/L。雌性BALB/c裸鼠10只购买于北京维通利华实验动物技术有限公司。
细胞培养
用含有10%胎牛血清(Hyclone, Thermo Scientific,USA)的DMEM培养基(Gibco, Japan),湿度适宜,室温37 ℃,含5% CO2的培养箱(MC 0175,SANYO,Janpan)内培养。
实时定量PCR
应用Trizol(Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA)酚氯仿抽提法提取细胞或组织总RNA, 应用Taqman反转录试剂盒(Applied Biosystem,USA)逆转录为cDNA。继而ABI 7500 PCR仪(Applied Biosystems, USA)内完成目的基因let-7a、K-Ras、H-Ras和N-Ras扩增。实验条件95 ℃ 10 min, 40个循环, 95 ℃ 15 s,50 ℃ 1 min。重复实验3次。采用2-ΔΔCt法分析实验结果[21]。U6为let-7a内参;GAPDH为人K-Ras、H-Ras和N-Ras的内参。扩增时掺入荧光染料SYBR Green进行实时监测。let-7a-p、K-Ras、H-Ras和N-Ras引物根据基因组数据库设计,由Invitrogen公司合成。
Western blot
提取细胞或新鲜组织总蛋白,测定总蛋白浓度,SDS-PAGE分离蛋白样品,电转至PVDF膜,5%脱脂奶(TBST)封闭非特异性位点,孵育一抗K-Ras、H-Ras、N-Ras (Santa Cruz biatechnology, USA), 内参为GAPDH(Proteintech,Chicago, IL, USA);二抗(生物素标记山羊抗小鼠IgG,北京中杉金桥), ECL发光液于暗室中显影,Gel-Doc凝胶成像系统(BIO-RAD,USA),胶片扫描成像和分析。
MTT生长曲线
96孔板(3×103/孔)接种细胞,24 h后Lipofactamine®2000(Invitrogen)分别转染let-7a mimics及阴性对照(50 nmol/L),转染后24、48、72、96、120 h加入含MTS Reagent powder(Promega,USA) 20 μl的DMEM 100 μl。37 ℃孵育4 h后,多功能酶标仪(TECAN SPECTRA, Switzerland)测定荧光值,吸收波长为490 nm。重复3次。
PI单染测定细胞周期
6孔板(2×105/孔)接种细胞。24 h后转染let-7a mimics及阴性对照,转染24 h后胰酶消化细胞,PBS洗涤2次,加入PI染色剂(Sigma,USA),4 ℃孵育30 min, 流式细胞仪(EPICS XL,Coulter,USA)检测。每个样品收集1×104个细胞,测定G0-G1、S、G2-M各周期的细胞分布。重复3次。
Annexin V和FITC双染检测凋亡
6孔板(2×105/孔)接种细胞。24 h后转染let-7a mimics及阴性对照。转染24 h后胰酶消化细胞,PBS洗涤2次,收集细胞,乙醇-20 ℃固定过夜。24 h后除去乙醇,PBS洗涤2次,加入Annexin V,使用FITC凋亡检测试剂盒(BD,USA)10 μl,流式细胞仪(Accuri C6 Flow Cytometer,BD Accuri Cytometers, USA)检测。重复3次。
裸鼠皮下移植瘤模型
动物实验经北京大学伦理委员会和北京协和医院动物伦理委员会审核通过,符合国际动物实验伦理和动物福利原则和我国国家及北京市动物伦理和福利要求。裸鼠4周龄,体重17~22 g,饲养于北京协和医学院基础所实验动物中心动物房,饲养环境级别为SPF级,恒温(25~28 ℃)、恒湿。将HepG2细胞(5×106)直接在裸鼠(10只)颈背部皮下接种,以构建裸鼠皮下HepG2移植瘤模型。待1周后皮下成瘤,成瘤大小接近的8只随机分为2组,4只/组,按照说明书推荐剂量,在瘤周(剂量)总量相同多点注射胆固醇包裹的let-7a或阴性对照。每3天注射一次,观察裸鼠状态和移植瘤情况,每周相同时间测量裸鼠体重和肿瘤大小。4周后处死裸鼠,量取肿瘤大小,称重。取部分新鲜组织用于RNA和蛋白质提取,其余肿瘤组织福尔马林固定,常规石蜡切片,HE染色,光学显微镜下观察。
统计学处理
应用SPSS 17.0软件进行统计学分析。组间比较采用配对t检验,P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
结果
体外转染let-7a mimics对肝癌细胞的影响
肝癌细胞转染let-7a mimics或阴性对照后,实时定量PCR和Western blot方法检测肝癌细胞中let-7a及3种人Ras mRNA和蛋白水平。结果显示,转染let-7a后,肝癌细胞中let-7a含量显著增高,let-7a mimics转染的HepG2和SMMC-7721中let-7a含量分别是阴性对照的4.60和4.89倍,差异均有统计学意义(HepG2: P=0.002; SMMC-7721: P=0.004);K-Ras、H-Ras和N-Ras mRNA水平显著降低(P均<0.05);蛋白水平下调。提示let-7a mimics转染能提高肝癌细胞中let-7a水平,进而可能通过转录和翻译水平下调3种人Ras表达(数据未显示)。
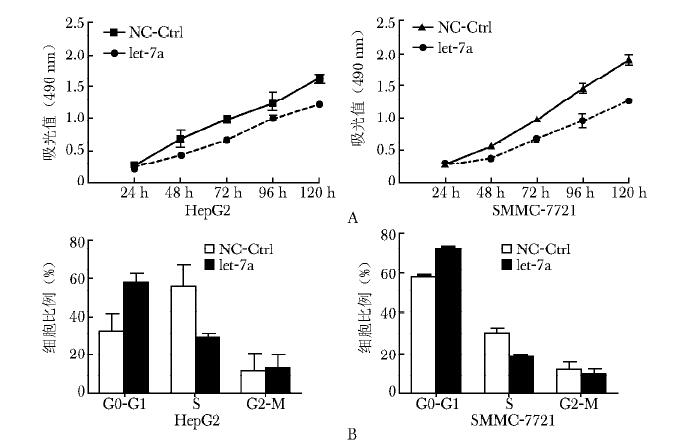
MTT生长曲线结果显示,从转染后48 h开始到120 h,let-7a mimics转染的HepG2和SMMC-7721细胞的吸光值均比阴性对照组显著降低(HepG2: P=0.016;SMMC-7721:P=0.020) (图 1A)。提示let-7a mimics明显抑制细胞的增殖。
流式Annexin V和FITC双染凋亡实验检测结果显示,let-7a mimics转染细胞的早期凋亡率高于阴性对照组。HepG2和SMMC-7721早期细胞凋亡率分别为对照组的1.27和1.85倍(HepG2: P=0.021; SMMC-7721: P=0.017),提示let-7a mimics促进肝癌细胞凋亡。
为研究let-7a抑制肝癌细胞增殖的机制,本实验应用流式细胞仪检测let-7a转染后肝癌细胞周期分布的变化。结果表明HepG2和SMMC-7721细胞转染let-7a mimics之后,G0-G1期细胞比例增加,分别是阴性对照组的1.78和1.52倍(HepG2: P=0.019; SMMC-7721: P=0.021),S期细胞比例下降,分别是对照组的29.2%和63%(HepG2: P= 0.023; SMMC-7721:P=0.017),差异均有统计学意义(图 1B)。提示let-7a mimics通过阻滞细胞周期进而抑制细胞增殖和肿瘤生长。
局部注射胆固醇包裹的let-7a mimics对裸鼠皮下移植瘤的生长、侵袭和肿瘤组织的作用
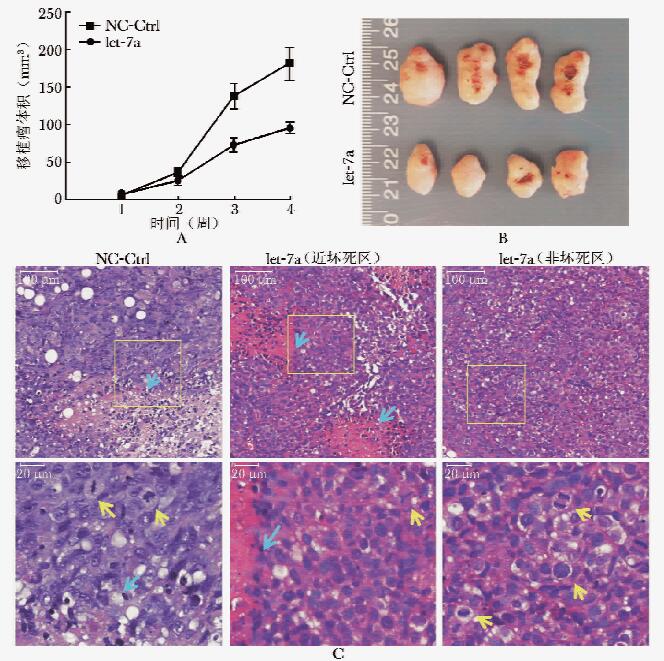
为在体内进一步证实let-7a mimics对肝癌的潜在治疗作用及初步探索给药方式,构建裸鼠皮下HepG2移植瘤模型并分别注射胆固醇包裹的let-7a mimics和阴性对照。4周后,let-7a mimics注射组移植瘤体积为(98.34±55.24)mm3,阴性对照组移植瘤体积为(178.91±69.74)mm3,治疗组移植瘤体积是对照组的54.97%,两者相比差异具有统计学意义(P=0.039)(图 2A,2B)。提示let-7a mimics局部注射治疗组的裸鼠皮下移植瘤增长速度低于阴性对照组。
![]() 图 2 let-7a mimics对裸鼠皮下肝癌移植瘤的影响A.裸鼠皮下移植瘤生长曲线;B.局部注射给药4周,移植瘤实验结束后移植瘤大小及其侵及皮肤溃疡情况;C.移植瘤组织病理学,蓝色箭头示坏死区,黄色箭头示细胞分裂象(HE染色)
图 2 let-7a mimics对裸鼠皮下肝癌移植瘤的影响A.裸鼠皮下移植瘤生长曲线;B.局部注射给药4周,移植瘤实验结束后移植瘤大小及其侵及皮肤溃疡情况;C.移植瘤组织病理学,蓝色箭头示坏死区,黄色箭头示细胞分裂象(HE染色)
let-7a、NC-Ctrl:同图 1解剖发现,在let-7a mimics注射治疗组的肝脏上多数没有结节(1/5,单个结节),而阴性对照组的裸鼠肝脏上均发现直径1 mm的白色小结节,1~2个不等(资料未显示)。经let-7a mimics局部多点注射治疗后,肿瘤浸润裸鼠皮肤引起的溃疡发生比例较阴性对照减少(let-7a mimics注射组,3/4;阴性对照组,4/4),且移植瘤侵及皮肤处引起的坏死溃疡面积明显小于阴性对照组(图 2B)。提示局部注射let-7a mimics可以抑制裸鼠皮下移植瘤的生长和直接浸润。
皮下肿瘤经HE染色后显微镜下观察,证实皮下移植瘤均为肝细胞性肝癌。在注射let-7a mimics组的肿瘤组织中,近坏死区可见明显细胞表型一致区域,细胞异型性减少,与非坏死区和对照组相比,近坏死区肿瘤组织中细胞分裂象减少(图 2C)。
let-7a mimics上调肝癌细胞和移植瘤组织中let-7a水平并降低K-Ras、H-Ras和N-Ras mRNA和蛋白表达
为验证体内多点注射let-7a mimics对肝癌组织的影响,提取let-7a mimics注射组和阴性对照组皮下移植瘤新鲜组织的总RNA, 实时定量PCR方法检测移植瘤组织内let-7a的水平。结果证实let-7a mimics注射组let-7a水平是对照组的2.87倍,差异具有统计学意义(P=0.024)(图 3A)。
![]() 图 3 let-7a mimics体内注射对裸鼠皮下肝癌移植瘤组织内let-7a和人3种Ras的作用A.实时定量PCR检测体内移植瘤组织内let-7a水平;B.实时定量PCR检测裸鼠皮下移植瘤组织内人3种Ras mRNA的水平; C.Western blot检测移植瘤组织内人3种Ras蛋白水平
图 3 let-7a mimics体内注射对裸鼠皮下肝癌移植瘤组织内let-7a和人3种Ras的作用A.实时定量PCR检测体内移植瘤组织内let-7a水平;B.实时定量PCR检测裸鼠皮下移植瘤组织内人3种Ras mRNA的水平; C.Western blot检测移植瘤组织内人3种Ras蛋白水平
let-7a、NC-Ctrl:同图 1类似地,应用实时定量PCR和Western blot方法检测移植瘤组织内的let-7a和人K-Ras、H-Ras、N-Ras mRNA和蛋白水平。结果显示,与阴性对照组相比,let-7a mimics注射组移植瘤组织K-Ras、H-Ras、N-Ras mRNA表达水平显著下调,N-Ras mRNA降低最明显(K-Ras:P=0.039;H-Ras:P=0.031;N-Ras:P=0.018)(图 3B);K-Ras、H-Ras和N-Ras蛋白表达也相应下调,N-Ras下调最明显(图 3C)。结果提示在瘤周多点注射let-7a mimics能够提高移植瘤内let-7a水平,进而下调人3种Ras mRNA和蛋白的表达
讨论
Ras及其下游信号通路的调控对于细胞增殖、分化、存活都很重要[22-23],异常的Ras蛋白活化会导致机体信号通路异常以致发生肿瘤[24-25]。阻断Ras及其信号通路是治疗肿瘤研究策略之一。近年来,miRNAs被证实不仅具有对正常细胞发育的调控作用,其异常表达会促进肿瘤的发生发展[26-28]。一些miRNAs,如miR-122、miR-199、miR-221被证实可以用于协助肝癌诊断[29]。miRNAs被认为是潜在的肿瘤治疗分子。肿瘤组织中,抑制肿瘤发生的miRNA呈低水平,促进肿瘤发生的miRNA高表达,故其对应治疗策略为补充肿瘤组织中低水平的miRNA或抑制肿瘤组织中高表达的miRNA[30]。
在线虫中发现的let-7 miRNA家族能够调控Ras表达,抑制肿瘤的生长[14]。let-7在包括肝癌在内的恶性肿瘤组织中呈低表达。本课题组验证实验室储存的2个肝癌细胞系和6对肝癌患者的肝癌及其癌旁肝组织的检测结果也证实,与正常肝细胞及癌旁肝组织相比,肝癌细胞和肝癌组织中let-7a表达量显著降低,而人3种Ras蛋白表达均上调,且let-7的表达与人3种Ras蛋白水平显示负相关趋势(数据未显示)。
本研究中体外实验结果证实let-7a mimics可以抑制细胞的周期进展和细胞增殖,促进细胞凋亡,这与let-7对其他肿瘤细胞的作用结果一致[14]。多项研究证实let-7为多靶向的肿瘤抑制基因,通过靶向调控多路径肿瘤相关的癌基因抑制肿瘤的发展[9, 17, 31],主要通过转录后靶向调控Ras发挥作用。人Ras基因家族中与人类肿瘤相关的特征性基因包括K-Ras、H-Ras和N-Ras,let-7与这3种常见Ras非翻译区均有结合域,且与N-Ras的结合域点最多。但以往研究认为N-Ras和H-Ras突变较少为导致Ras蛋白激活的原因,故研究多集中在K-Ras突变激活K-Ras蛋白的恶性肿瘤,且研究多限制在单一Ras蛋白水平的分析。文献多涉及let-7对非小细胞肺癌[9]、胰腺癌[11]等肿瘤及其K-Ras蛋白表达的影响。本研究证实,let-7a mimics确实可抑制肿瘤增殖、生长、浸润和转移。let-7a mimics可提高肝癌细胞和移植瘤组织中的let-7a水平,不仅下调人3种Ras蛋白的表达,而且下调这3种Ras的mRNA水平,以N-Ras mRNA和蛋白的下调相对更明显。提示let-7a mimics对Ras的调控过程不仅仅是发挥miRNA转录后调控功能,还可能通过转录水平下调mRNA水平。但本研究受方法和结果所限,未能直接证实let-7a的确切调控机制。
本研究应用胆固醇包裹的let-7a mimics,虽然能有效抑制皮下肝癌移植瘤的生长和转移,使肿瘤坏死区域比例增加,但组织学观察提示,在远离坏死区域,细胞核分裂依然易见(图 2C)。这反映由于局部注射方法限制,let-7a mimics可能不能到达肿瘤所有区域,因此在药物未到达区,细胞分裂象仍易见。局部注射的优点是在抑制靶向肿瘤的同时,对机体正常组织和器官的影响较少,不易产生杀伤作用。虽然肝脏血液丰富,如果在肝癌原位局部给药,抑制作用也许更明显,但是局部注射药物到达范围有限。肝癌的发生部位较为隐匿,加上其具有容易发生肝内或远处早期转移等特点,局部注射方式并不是肝癌最有效的给药方式。本研究中体内局部注射使用的胆固醇包裹的miRNA mimics在体内较稳定,半衰期为72 h。本研究组在后续研究中发现,胆固醇包裹的let-7a在裸鼠内主要分布在肝区[32],静脉给药是潜在的理想给药方式,但静脉系统给药可能引起更多的副作用,需要对有效性和毒性等作进一步的系统研究。对于一些具有Ras异常活化、发生部位表浅的恶性肿瘤,局部住射胆固醇包裹的miRNA mimics提供了一个潜在的治疗途径和方式。
总之,let-7a mimics能够提高肝癌细胞或组织中的let-7a水平,通过在转录和翻译水平下调人3种Ras的表达,抑制细胞周期进展和细胞增殖,促进细胞凋亡。局部多点注射let-7a mimics可抑制裸鼠皮下肝癌移植瘤的生长和转移。let-7阻断Ras信号传导通路可以作为肝癌治疗的潜在研究策略。
-
图 2 let-7a mimics对裸鼠皮下肝癌移植瘤的影响
A.裸鼠皮下移植瘤生长曲线;B.局部注射给药4周,移植瘤实验结束后移植瘤大小及其侵及皮肤溃疡情况;C.移植瘤组织病理学,蓝色箭头示坏死区,黄色箭头示细胞分裂象(HE染色)
let-7a、NC-Ctrl:同图 1图 3 let-7a mimics体内注射对裸鼠皮下肝癌移植瘤组织内let-7a和人3种Ras的作用
A.实时定量PCR检测体内移植瘤组织内let-7a水平;B.实时定量PCR检测裸鼠皮下移植瘤组织内人3种Ras mRNA的水平; C.Western blot检测移植瘤组织内人3种Ras蛋白水平
let-7a、NC-Ctrl:同图 1 -
[1] Aravalli RN, Steer CJ, Cressman EN. Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 48:2047-2063. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22580
[2] Wei KR, Yu X, Zheng RS, et al. Incidence and mortality of liver cancer in China, 2010[J].Chin J Cancer, 2014, 33:388-394. http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC4135368/
[3] Lai EC. MicroRNAs are complementary to 3'UTR sequence motifs that mediate negative post-transcriptional regulation[J]. Nat Genet, 2002, 30:363-364. DOI: 10.1038/ng865
[4] Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers[J]. Proc Natl Acad, 2004, 101:2999-3004. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307323101
[5] Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2006, 6:857-866. DOI: 10.1038/nrc1997
[6] Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14[J]. Cell, 1993, 75:843-854. DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-Y
[7] Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Nature, 2000, 403:901-906. DOI: 10.1038/35002607
[8] Roush S, Slack FJ. The let-7 family of microRNAs[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2008, 18:505-516. DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.07.007
[9] Kumar MS, Erkeland SJ, Pester RE, et al. Suppression of non-small cell lung tumor development by the let-7 microRNA family[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105:3903-3908. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0712321105
[10] He XY, Chen JX, Zhang Z, et al. The let-7a microRNA protects from growth of lung carcinoma by suppression of K-Ras and c-Myc in nude mice[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2010, 136:1023-1028. DOI: 10.1007/s00432-009-0747-5
[11] Torrisani J, Bournet B, du Rieu MC, et al. let-7 MicroRNA transfer in pancreatic cancer-derived cells inhibits in vitro cell proliferation but fails to alter tumor progression[J]. Hum Gene Ther, 2009, 20:831-844. DOI: 10.1089/hum.2008.134
[12] Appari M, Babu KR, Kaczorowski A, et al. Sulforaphane, quercetin and catechins complement each other in elimination of advanced pancreatic cancer by miR-let-7 induction and K-Ras inhibition[J]. Int J Oncol, 2014, 45:1391-1400. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2539
[13] Jin H, Lv S, Yang J, et al. Use of microRNA let-7 to control the replication specificity of oncolytic adenovirus in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6:e21307. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021307
[14] Johnson CD, Esquela-Kerscher A, Stefani G, et al. The let-7 microRNA represses cell proliferation pathways in human cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2007, 67:7713-7722. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1083
[15] Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, et al. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family[J]. Cell, 2005, 120:635-647. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.014
[16] Tsang WP, Kwok TT. let-7a microRNA suppresses therapeutics-induced cancer cell death by targeting caspase-3[J]. Apoptosis, 2008, 13:1215-1222. DOI: 10.1007/s10495-008-0256-z
[17] Chen KJ, Hou Y, Wang K, et al. Reexpression of let-7g microRNA inhibits the proliferation and migration via K-Ras/HMGA2/snail axis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2014, 2014:742417. DOI: 10.1155/2014/742417
[18] Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Gorden A, et al. Ubiquitous activation of Ras and Jak/Stat pathways in human HCC[J]. Gastroenterology, 2006, 130:1117-1128. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.01.006
[19] Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Conner EA, et al. Inactivation of Ras GTPase-activating proteins promotes unrestrained activity of wild-type Ras in human liver cancer[J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 54:311-319. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.06.036
[20] Zhu XM, Wu LJ, Xu J, et al. let-7c microRNA expression and clinical significance in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Int Med Res, 2011, 39:2323-2329. DOI: 10.1177/147323001103900631
[21] Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-DeltaDeltaC (T)) Method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25:402-408. DOI: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
[22] Shields JM, Pruitt K, McFall A. Understanding Ras:'it ain't over til it's over'[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2000, 10:147-154. DOI: 10.1016/S0962-8924(00)01740-2
[23] Marshall C. How do small GTPase signal transduction pathways regulate cell cycle entry?[J]. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 1999, 11:732-736. DOI: 10.1016/S0955-0674(99)00044-7
[24] Downward J. Cancer biology:signatures guide drug choice[J]. Nature, 2006, 439:274-275. DOI: 10.1038/439274a
[25] Schubbert S, Shannon K, Bollag G. Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2007, 7:295-308. DOI: 10.1038/nrc2109
[26] Bussing I, Slack FJ, Grosshans H. let-7 microRNAs indeve-lopment, stem cells and cancer[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2008, 14:400-409. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2008.07.001
[27] Boyerinas B, Park SM, Hau A, et al. The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2010, 17:F19-F36. DOI: 10.1677/ERC-09-0184
[28] Roush S, Slack FJ. The let-7 family of microRNAs[J].Trends Cell Biol, 2008, 18:505-516. DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.07.007
[29] Callegari E, Elamin BK, Sabbioni S, et al. Role of micro-RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma:a clinical perspective[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2013, 6:1167-1178. http://www.dovepress.com/role-of-micrornas-in-hepatocellular-carcinoma-a-clinical-perspective-peer-reviewed-article-OTT
[30] Hou J, Lin L, Zhou W, et al. Identification of miRNomes in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2011, 19:232-243. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.001
[31] Giordano S, Columbano A. MicroRNAs:new tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma?[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 57:840-847. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26095
[32] Liu YM, Xia Y, Dai W, et al. Cholesterol-conjugated let-7a mimics:antitumor efficacy on hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in a preclinical orthotopic xenograft model of systemic therapy[J]. BMC Cancer, 2014, 14:889. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-889
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 袁仙仙,阳洪波,朱惠娟,潘慧. 胰岛素样生长因子-1测定方法及参考值范围. 协和医学杂志. 2020(04): 472-478 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 汤红燕,肖斌,王利平,杨桂兰. 胰岛素样生长因子家族与皮肤病. 中国医学科学院学报. 2019(03): 415-418 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: