Serum IgE Levels in Patients with Bullous Pemphigoid and Its Correlation with the Activity of the Disease
-
摘要:目的 探讨大疱性类天疱疮(bullous pemphigoid, BP)患者血清中总IgE变化规律以及与BP病情的相关性。方法 收集北京协和医院皮肤科住院及门诊就诊的有完整临床资料的BP患者59例, 对其血清总IgE在治疗前后的变化规律进行总结, 并对血清总IgE与皮质类固醇激素应用最大剂量、嗜酸性粒细胞总数及间接免疫荧光滴度间的相关性进行分析。结果 59例BP患者中, 53例(89.83%)血清总IgE升高, 治疗后患者病情好转后IgE下降, 但多不能恢复到正常水平。BP患者总IgE水平与激素应用的最大剂量、嗜酸性粒细胞数量、间接免疫荧光滴度均无相关性(P > 0.05)。结论 BP患者血清中总IgE水平明显升高, 但BP病情好转后IgE不能恢复正常, IgE水平与BP病情严重程度无关。Abstract:Objective To investigate serum total IgE level in bullous pemphigoid (BP) patients and its correlation with the activity of disease.Methods A total of 59 BP patients admitted to our department were enrolled in the study. Their clinical data were analyzed. The change of serum total IgE level before and after treatment was observed. The correlations between the total IgE level and the maximum dose of steroid during hospital stay, the number of eosinophils, and indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) titer were analyzed.Results Of these 59 patients, 53 (89.83%) had elevated serum IgE level. After the disease was controlled, IgE decreased but did not return to normal level. High IgE level lasted for several months or years. The serum IgE level in these BP patients was not correlated with the maximum dose of steroid, number of eosinophils, or IIF titer (all P > 0.05).Conclusions Serum IgE remarkably increases in BP patients, and can not return to the normal thresholds even after the disease is controlled. However, it has no correlation with the severity of BP.
-
Keywords:
- bullous pemphigoid /
- IgE /
- eosinophils /
- steroid /
- indirect immunofluorescence
-
大疱性类天疱疮(bullous pemphigoid,BP)是一种严重的自身免疫性大疱性疾病,BP患者血清中出现抗BP180和BP230的IgG型自身抗体,可与皮肤基底膜结合而诱发水疱形成。近年来,一种新的抗体类型IgE逐渐进入人们的视野。IgE在过敏性疾病、系统性红斑狼疮和类风湿性关节炎等自身免疫性疾病中均发挥重要作用。早在1974年就有学者提出天疱疮和类天疱疮患者血清中IgE升高,且皮损基底膜带可见IgE沉积[1]。然而,该现象一直未引起足够重视,直到1984年,有学者提出BP患者血清中IgE水平与病情相关[2]。但随着近年来对BP180 IgE和BP230 IgE研究的逐渐深入,该结论受到质疑。国外有报道显示血清中总IgE水平与病情关系不明显[3-4],目前国内尚缺乏相关数据。为此,本研究对1990年1月至2011年8月在本院住院的具有完整临床资料的BP患者进行回顾性分析,同时对2011年8月至2012年4月门诊就诊的BP患者进行前瞻性研究,旨在探讨BP患者外周血总IgE在疾病发生发展过程中的变化特点及与病情的相关性。
对象和方法
对象
收集1990年1月至2011年8月北京协和医院皮肤科住院BP患者及2011年8月至2012年4月门诊BP患者共223例,所有患者经临床、组织病理、直接和间接免疫荧光(indirect immunofluorescence,IIF)检查证实,均满足BP的诊断标准。选取其中有总IgE检测记录的患者59例作为研究组,其中男33例、女26例,男:女为1. 27 : 1;年龄22 ~ 93岁,平均(65. 3 ± 16. 1)岁; 病程10 d至10年; 59例中,有39例同时进行了IIF检测。所有患者病程中均无哮喘、特应性皮炎、嗜酸性粒细胞(eosinophil,EOS)增多症和高IgE综合征病史。选取30名体检正常的年龄、性别匹配的健康人群作为正常对照组,其中男16例、女14例,平均年龄(62. 8 ± 6. 5)岁。两组在性别、年龄构成上差异无统计学意义(P>0. 05)。
研究方法
所有患者根据病程记录,确定病情的严重程度,记录患者不同治疗时期的EOS总数、总IgE水平、皮质类固醇激素(以下简称激素)应用的最大剂量及IIF滴度。总IgE检测方法采用ELISA法。本文所涉及到的激素剂量均换算为泼尼松的剂量,换算方法为: 5 mg泼尼松(泼尼松龙) ≈20 mg氢化可的松≈4 mg曲安西龙(甲泼尼龙,甲强龙) ≈0. 75 mg地塞米松≈0. 8 mg倍他米松。
统计学处理
数据以M (QL,QU)表示,数据为非正态分布且存在非精确测量值,因此组间比较采用秩和检验,IgE与激素应用最大剂量、EOS数量、IIF滴度间的相关性检验采用Spearman等级相关分析,P<0. 05为差异具有统计学意义。
结果
总IgE检测结果
59例BP患者中,53例(89. 83%)总IgE升高,其中位数为712. 00 (178. 00,2500. 00) kU/L; 30名正常对照者中,3名(10%)总IgE升高,其中位数为58. 20 (31. 78,68. 50) kU/L。两组间比较差异有统计学意义(Z = - 6. 232,P<0. 001)。
治疗前后总IgE变化规律
59例BP患者中,19例有治疗前后IgE的记录,其中14例(73. 68%)患者治疗后IgE下降,但仅有2例(10. 53%)患者降至正常; 4例(21. 05%)患者治疗后轻度升高; 1例(5. 26%)患者病情复发,IgE升高(表 1)。对所有患者治疗前后总IgE进行比较,发现治疗前后体内IgE含量明显变化(Z = - 2. 374,P = 0. 018)。
表 1 19例大疱性类天疱疮患者治疗前后总IgE的变化病例 治疗前(kU/L) 治疗后(kU/L) 1 117 37. 4 2 4633 4789 3 1330 1540 4 2312 4138* 5 655 138 6 >5000 3699 7 >5000 4423 8 >5000 3028 9 4804 1664 10 6. 9 9 11 84. 3 28. 2 12 197 128 13 3902 375 14 970 344 15 150 135 16 26 41. 3 17 >5000 3495 18 2911 898 19 712 657 *该患者病情复发时的数据 治疗前后IgE与新发水疱数量间的关系
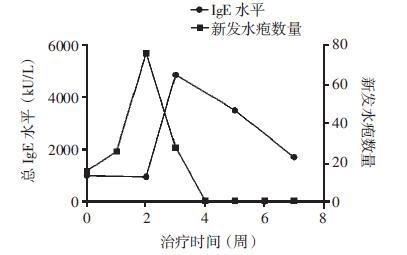
选择1例有详细记录的BP患者,对其IgE水平与新发水疱数量间的关系进行分析,结果显示患者IgE水平与新发水疱数量的变化趋势大致相同,但IgE水平变化晚于水疱数量变化,且在患者病情控制(无新发水疱)后,IgE水平呈缓慢下降趋势但未降至正常(图 1)。
不同性别间IgE的比较
59例BP患者中,33例男性患者和26例女性患者的IgE中位数分别为1006. 00 (310. 00,2705. 50) kU/L和496 (144. 75,1575. 50) kU/L,两组间差异无统计学意义(Z = - 1. 191,P = 0. 234)。
IgE与激素应用最大剂量的相关性
对59例患者的激素应用最大剂量与总IgE水平进行Spearman等级相关分析,结果显示两者间无相关性(r = 0. 040,P = 0. 765)。
IgE与EOS数量的相关性
对IgE水平与EOS数量进行Spearman相关分析,结果显示两者间无相关性(r = 0. 203,P = 0. 123)。
IgE与IIF滴度的相关性
对39例患者总IgE与IIF滴度进行Spearman等级相关分析,结果显示两者间无相关性(r = 0. 161,P = 0. 328)。
讨论
虽然已有大量证据表明抗BP180 IgG抗体与BP发病相关,且与病情相平行[5-6],但越来越多的证据显示IgE水平在BP发病过程中起重要作用:在大多数BP患者血清中可检测到IgE抗体,且沿基底膜带呈线状沉积[7],这些抗体同样结合于BP180 NC16A[8]; 体外实验证明IgE抗体与BP发病相关[9]; 用抗IgE人源化抗体成功治疗1例皮质类固醇治疗无效的BP患者,该抗体能抑制IgE与其相应受体结合[10]。种种迹象表明IgE抗体在BP发病中起重要作用,但IgE水平是否与病情严重程度相关,至今仍无定论。
BP患者中出现高IgE已是不争的事实。由于所采用方法不同及病例选择不同,测得的IgE升高率也不尽相同。据报道70% ~ 90%的BP患者出现高IgE[3, 11],77%的患者可检测到抗BP180 NC16A IgE抗体[12]。本组资料中高IgE占BP患者的89. 83%,与国外报道的数据相似。高IgE多出现于变态反应性疾病、寄生虫感染等。BP患者出现高IgE,也从一个侧面解释了临床所观测到的BP发病早期出现湿疹皮炎样皮损的原因,提示变态反应可能是BP发病的始动环节。
为了评价总IgE水平与BP病情的相关性,本研究对所有患者的总IgE水平和激素应用的最大剂量、EOS数量、IIF滴度进行了相关性分析,结果显示总IgE与激素应用最大剂量、EOS数量、IIF滴度均无相关性。激素应用的最大剂量可一定程度反映疾病的严重程度,疾病越重,所需激素的最大剂量越大。既往有研究显示EOS与BP间有明确的相关性,EOS的数量与病情的严重程度相关[13]。本研究组的初步研究结果显示BP患者EOS水平与激素应用剂量呈明显的正相关,EOS越高,激素应用剂量越高[14]。众所周知,IIF滴度不能作为评价疾病严重程度的指标,其原因是仅从IIF检测结果不能判定是BP180还是BP230占优势,抗BP180抗体滴度与BP的严重程度相关,而抗BP230抗体与BP的关系不明确[5]。本研究证实总IgE水平与反映病情严重程度的指标(激素应用的最大剂量、EOS水平)均无明显相关性,提示BP患者出现高IgE不能作为病情严重的指标,也不能根据IgE水平指导临床治疗。
本研究中19例患者记录了治疗前后IgE的变化,其中18例患者是在一次病程中治疗前后的比较,1例患者是在病情复发时得到的数据。18例患者中14例患者治疗后IgE下降(但仅有2例患者降至正常水平),4例患者治疗后轻度升高,另有1例患者在病情复发时IgE升高。提示IgE水平随着病情的好转可有所下降,但即使临床得到完全缓解,其IgE水平仍超过正常。在2例有详细IgE记录的患者中,IgE水平与病情变化趋势相一致,当病情未控制时,IgE呈直线上升趋势,水疱控制后IgE达最高水平,此后IgE缓慢下降,高IgE持续时间与总IgE明显相关,IgE越高持续时间越长(目前的观察可长达2年)。若在疾病早期病情未控制时(IgE呈上升状态)采血测得IgE,即使病情控制后仍会出现治疗后IgE高于治疗前的假象。提示动态观察IgE水平对研究IgE与BP间的相关性至关重要。
此外,本研究还就性别对IgE产生的影响作了分析。有报道表明妊娠妇女血清中抗BP180 IgE抗体水平明显高于非妊娠妇女[15],提示妊娠亦是抗体产生的原因之一。为排除妊娠导致IgE升高的因素,本研究对患者按性别进行分组,所有女性患者均有妊娠史,均无妊娠疱疹史,结果显示在不考虑病情严重程度、激素治疗剂量等因素的情况下,单独就性别比较,两组差异无统计学意义,证实妊娠并非IgE升高的因素。
本研究的局限性: (1)本研究只评价了激素应用的最大剂量,而未对免疫抑制剂的应用情况进行分析。因为免疫抑制剂种类繁多,且无等量换算方法。(2)在既往的研究报道中,多数是以水疱的数量和皮损累及面积来衡量疾病的严重程度[5, 16],本研究中的部分病例不能完全再现患者入院时的状况,故未能通过上述临床指标评价患者病情的严重程度。(3)病例例数限制。
总之,本研究结果显示BP患者血清中总IgE水平明显升高,但与病情严重程度无关。BP患者出现高IgE的确切机制有待进一步探讨。
-
表 1 19例大疱性类天疱疮患者治疗前后总IgE的变化
病例 治疗前(kU/L) 治疗后(kU/L) 1 117 37. 4 2 4633 4789 3 1330 1540 4 2312 4138* 5 655 138 6 >5000 3699 7 >5000 4423 8 >5000 3028 9 4804 1664 10 6. 9 9 11 84. 3 28. 2 12 197 128 13 3902 375 14 970 344 15 150 135 16 26 41. 3 17 >5000 3495 18 2911 898 19 712 657 *该患者病情复发时的数据 -
[1] Arbesman CE, Wypych JI, Reisman RE, et al. IgE levels in sera of patients with pemphigus or bullous pemphigoid[J]. Arch Dermatol, 1974, 110:378-381. DOI: 10.1001/archderm.1974.01630090016003
[2] Asbrink E, Hovmark A. Serum IgE levels in patients with bullous pemphigoid and its correlation to the activity of the disease and anti-basement membrane zone antibodies[J]. Acta Derm Venereol, 1984, 64:243-246. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6204487
[3] Ishiura N, Fujimoto M, Watanabe R, et al. Serum levels of IgE anti-BP180 and anti-BP230 autoantibodies in patients with bullous pemphigoid[J]. J Dermatol Sci, 2008, 49:153-161. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.08.008
[4] Iwata Y, Komura K, Kodera M, et al. Correlation of IgE autoantibody to BP180 with a severe form of bullous pemphigoid[J]. Arch Dermatol, 2008, 144:41-48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c9910ad9659c07beff2cbb637e1d675f
[5] Tsuji-Abe Y, Akiyama M, Yamanaka Y, et al. Correlation of clinical severity and ELISA indices for the NC16A domain of BP180 measured using BP180 ELISA kit in bullous pemphigoid[J]. J Dermatol Sci, 2005, 37:145-149. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2004.10.007
[6] Ujiie H, Nishie W, Shimizu H. Pathogenesis of bullous pemphigoid[J]. Dermatol Clin, 2011, 29:439-446. DOI: 10.1016/j.det.2011.03.008
[7] Yayli S, Pelivani N, Beltraminelli H, et al. Detection of linear IgE deposits in bullous pemphigoid and mucous membrane pemphigoid:a useful clue for diagnosis[J]. Br J Dermatol, 2011, 165:1133-1137. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10481.x
[8] Fairley JA, Fu CL, Giudice GJ. Mapping the binding sites of anti-BP180 immunoglobulin E autoantibodies in bullous pemphigoid[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2005, 125:467-472. DOI: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23853.x
[9] Fairley JA, Burnett CT, Fu CL, et al. A pathogenic role for IgE in autoimmunity:bullous pemphigoid IgE reproduces the early phase of lesion development in human skin grafted to nu/nu mice[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2007, 127:2605-2611. DOI: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700958
[10] Fairley JA, Baum CL, Brandt DS, et al. Pathogenicity of IgE in autoimmunity:successful treatment of bullous pemphigoid with Omalizumab[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2009, 123:704-705. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.11.035
[11] Dimson OG, Giudice GJ, Fu CL, et al. Identification of a potential effector function for IgE autoantibodies in the organspecific autoimmune disease bullous pemphigoid[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2003, 120:784-788. DOI: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12146.x
[12] Messingham KA, Noe MH, Chapman MA. A novel ELISA reveals high frequencies of BP180-specific IgE production in bullous pemphigoid[J]. J Immunol Methods, 2009, 346:18-25. DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2009.04.013
[13] Toosi S, Bystryn JC. Potential role of interleukin-17 in the pathogenesis of bullous pemphigoid[J]. Med Hypotheses, 2010, 74:727-728. DOI: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.10.038
[14] 左亚刚, 刘冰, 李丽, 等.嗜酸性粒细胞水平与大疱性类天疱疮激素应用剂量间的关系[J].中国医学科学院学报, 2012, 34:130-133. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgyxkxyxb201202006 [15] Noe MH, Messingham KA, Brandt DS, et al. Pregnant women have increased incidence of IgE autoantibodies reactive with the skin and placental antigen BP180(type ⅩⅦ collagen)[J]. J Reprod Immunol, 2010, 85:198-204. DOI: 10.1016/j.jri.2010.03.005
[16] D'Auria L, Pietravalle M, Mastroianni A, et al. IL-5 levels in the serum and blister fluid of patients with bullous pemphigoid:correlations with eosinophil cationic protein, RANTES, IgE and disease severity[J]. Arch Dermatol Res, 1998, 290:25-27. DOI: 10.1007/s004030050272
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 董毅飞,罗乾坤,付强,刘攀,张凯伦,潘长杰,郑胜浩,秦涛. 胰腺导管腺癌术后外分泌功能不全的危险因素分析及预测模型构建与验证. 中华实验外科杂志. 2025(02): 343-347 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)

 作者投稿
作者投稿 专家审稿
专家审稿 编辑办公
编辑办公 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: